Abstract
Since existing GNN methods use a fixed input graph structure for messages passing, they cannot solve the problems of heterogeneity, over-squashing, long-range dependencies, and graph incompleteness. The all-pair message passing scheme is an effective means to address the above issues. However, owing to the quadratic complexity problem of self-attention used in the all-pair message passing scheme, it is not possible to simultaneously guarantee the scalability and accuracy of the algorithm on large-scale graph datasets. In this paper, we propose Proformer, which uses multilayer dilation convolution to project the key and value in self-attention and uses a focused function to further enhance the model representation and reduce the computational complexity of the all-pair message passing scheme from quadratic to linear. The experimental results show that Proformer performs very well in tasks such as nodes, images, and text. Additionally, when scaled to large-scale graph datasets, it is able to effectively reduce the inference time and GPU memory utilization while guaranteeing the algorithm's accuracy. On OGB-Proteins, it not only improves the ROC-AUC by 3.2% but also conserves 27.8% of the GPU memory.
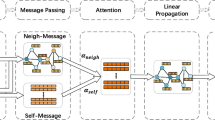
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets used or analysed for the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes used for the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Yang L, Liu Z, Dou Y et al (2021) ConsisRec: Enhancing gnn for social recommendation via consistent neighbor aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 44th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, pp 2141–2145
Veličković P (2023) Everything is connected: Graph neural networks. Curr Opin Struct Biol 79:102538
Romanova A (2023) GNN graph classification method to discover climate change patterns. In: International conference on artificial neural networks, vol 14257. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, pp 388–397
Yang X, Yan M, Pan S et al (2023) Simple and efficient heterogeneous graph neural network. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 37(9):10816–10824
Qureshi S (2023) Limits of depth: Over-smoothing and over-squashing in gnns. Big Data Min Anal 7(1):205–216
Li J, Zhang X, Zhang K et al (2024) Transformer helps GNNs express better via distillation of longrange dependencies. Available at SSRN 4768939
Franceschi L, Niepert M, Pontil M et al (2019) Learning discrete structures for graph neural networks. In: International conference on machine learning, vol 97. PMLR, pp 1972–1982
Duan W, Xuan J, Qiao M et al (2022) Learning from the dark: boosting graph convolutional neural networks with diverse negative samples. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 36(6):6550–6558
Duan W, Lu J, Wang Y G et al (2024) Layer-diverse negative sampling for graph neural networks. Trans Mach Learn Res
Han K, Wang Y, Guo J et al (2022) Vision gnn: An image is worth graph of nodes. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 35:8291–8303
Xing Y, He T, Xiao T et al (2021) Learning hierarchical graph neural networks for image clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 3467–3477
Wang J (2020) Text classification based on GNN[C]. In: 2020 international workshop on electronic communication and artificial intelligence (IWECAI). IEEE, pp 94–97
Li X, Wang B, Wang Y et al (2024) Graph-based text classification by contrastive learning with text-level graph augmentation. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data 18(4):1–21
Tzes M, Bousias N, Chatzipantazis E et al (2023) Graph neural networks for multi-robot active information acquisition. In: 2023 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 3497–3503
Goarin M, Loianno G (2024) Graph neural network for decentralized multi-robot goal assignment. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 9:4051–4058
Liu X, Wu Y, Fiumara G, et al (2024) Heterogeneous graph community detection method based on K-nearest neighbor graph neural network. Intell Data Anal (Preprint) 1–22
Ai G, Gao Y, Wang H et al (2024) Neighbors selective graph convolutional network for homophily and heterophily. Pattern Recogn Lett 184:44–51
Wu L, Lin H, Hu B et al (2024) Beyond homophily and homogeneity assumption: Relation-based frequency adaptive graph neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 35:8497–8509
Li L, Yang W, Bai S et al (2024) KNN-GNN: A powerful graph neural network enhanced by aggregating K-nearest neighbors in common subspace. Expert Syst Appl 253:124217
Ben J, Sun Q, Liu K et al (2024) Multi-head multi-order graph attention networks. Appl Intell 54:8092–8107
Gabrielsson RB, Yurochkin M, Solomon J (2023) Rewiring with positional encodings for graph neural networks. Transact Mach Learn Res
Jiawei E, Zhang Y, Yang S et al (2024) GraphSAGE++: Weighted Multi-scale GNN for Graph Representation Learning. Neural Process Lett 56(1):24
Wu Q, Zhao W, Li Z et al (2022) Nodeformer: A scalable graph structure learning transformer for node classification. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 35:27387–27401
Vaswani A (2017) Attention is all you need. In: Advances in neural information processing systems
Yang J, Liu Z, Xiao S et al (2021) Graphformers: Gnn-nested transformers for representation learning on textual graph. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:28798–28810
Yun S, Jeong M, Kim R et al (2019) Graph transformer networks. In: Proceedings of the 33rd international conference on neural information processing systems, vol 32, pp 11983–11993
Chen D, O’Bray L, Borgwardt K (2022) Structure-aware transformer for graph representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 39th international conference on machine learning, vol 162. PMLR, pp 3469–3489
Rampášek L, Galkin M, Dwivedi VP et al (2022) Recipe for a general, powerful, scalable graph transformer. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 35:14501–14515
He X, Hooi B, Laurent T et al (2023) A generalization of ViT/MLP-mixer to graphs. In: Proceedings of machine learning research, pp 12724–12745
Shirzad H, Velingker A, Venkatachalam B et al (2023) Exphormer: sparse transformers for graphs. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 31613–31632
Chen J, Gao K, Li G, et al (2022) NAGphormer: A tokenized graph transformer for node classification in large graphs. In: The eleventh international conference on learning representations
Micikevicius P, Narang S, Alben J, et al (2018) Mixed precision training. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.03740
Child R, Gray S, Radford A, et al (2019) Generating long sequences with sparse transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.10509
Kitaev N, Kaiser Ł, Levskaya A (2020) Reformer: The efficient transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.04451
Shen Z, Zhang M, Zhao H, et al (2021) Efficient attention: Attention with linear complexities. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 3531–3539
Wang S, Li B Z, Khabsa M, et al (2020) Linformer: Self-attention with linear complexity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.04768
Rahimi A, Recht B (2007) Random features for large-scale kernel machines. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, vol 20, pp 1177–1184
Jang E, Gu S, Poole B (2017) Categorical reparameterization with gumbel-softmax. In: International conference on learning representations
Liu F, Huang X, Chen Y et al (2022) Random Features for Kernel Approximation: A Survey on Algorithms, Theory, and Beyond. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(10):7128–7148
Lorberbom G, Johnson DD, Maddison CJ et al (2021) Learning generalized gumbel-max causal mechanisms. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:26792–26803
Han D, Pan X, Han Y, et al (2023) FLatten transformer: vision transformer using focused linear attention. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 5938–5948
Shazeer N, Lan Z, Cheng Y, et al (2020) Talking-heads attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.02436
Touvron H, Cord M, Douze M, et al (2021) Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 10347–10357
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A et al (2020) An image is worth 16×16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: International conference on learning representations
You H, Xiong Y, Dai X, et al (2023) Castling-vit: Compressing self-attention via switching towards linear-angular attention at vision transformer inference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 14431–14442
Zhu J, Yan Y, Zhao L et al (2020) Beyond homophily in graph neural networks: Current limitations and effective designs. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:7793–7804
Lim D, Li X, Hohne F, et al (2021) New benchmarks for learning on non-homophilous graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.01404
Hu W, Fey M, Zitnik M et al (2020) Open graph benchmark: Datasets for machine learning on graphs. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:22118–22133
Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T et al (2016) Matching networks for one shot learning. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 29:3637–3645
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A et al (2011) Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Kipf T N, Welling M (2016) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907
Velickovic P, Cucurull G, Casanova A et al (2017) Graph attention networks. stat 1050(20):10–48550
Xu K, Li C, Tian Y et al (2018) Representation learning on graphs with jumping knowledge networks. In: International conference on machine learning, vol 80. PMLR, pp 5453–5462
Abu-El-Haija S, Perozzi B, Kapoor A et al (2019) Mixhop: higher-order graph convolutional architectures via sparsified neighborhood mixing. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 21–29
Rong Y, Huang W, Xu T, et al (2019) Dropedge: Towards deep graph convolutional networks on node classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.10903
Franceschi L, Niepert M, Pontil M et al (2019) Learning discrete structures for graph neural networks. In: International conference on machine learning, vol 97. PMLR, pp 1972–1982
Chen Y, Wu L, Zaki M (2020) Iterative deep graph learning for graph neural networks: Better and robust node embeddings. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:19314–19326
Zeng H, Zhou H, Srivastava A, et al (2020) GraphSAINT: Graph sampling based inductive learning method. In: International conference on learning representations
Wu F, Souza A, Zhang T et al (2019) Simplifying graph convolutional networks. In: International conference on machine learning, vol 97. PMLR, pp 6861–6871
Van der Maaten L, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9(11):2579–2605
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my heartfelt gratitude to everyone who has supported me in completing this research paper. I give special thanks to my advisor for their guidance and expertise. I am also thankful to my colleagues for their valuable insights and encouragement. Additionally, I appreciate the support of my family and friends, whose unwavering belief in me kept me motivated. Finally, I acknowledge the financial assistance provided by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, which made this research possible. Thank you all for your contributions. I am truly grateful for your help and support.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, (Grant No. 2021M702030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhu Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software.
Peng Wang: Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation.
Cui Ni: Visualization, Investigation.
Qingling Zhang: Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest or competing interests regarding the publication of this article.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The work described has not been published before, and its publication has been approved by the responsible authorities at the institution where the work was carried out.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Wang, P., Ni, C. et al. Proformer: a scalable graph transformer with linear complexity. Appl Intell 55, 157 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06065-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06065-x