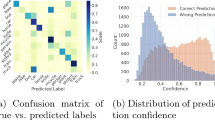
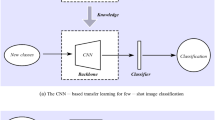
Abstract
Few-shot learning focuses on training efficient models with limited amounts of training data. Its mainstream approaches have evolved from single-modal to multi-modal methods. The Contrastive Vision-Language Pre-training model, known as CLIP, achieves image classification by aligning the embedding spaces of images and text. To better achieve knowledge transfer between image domain and text domain, we propose a fine-tuning framework for vision-language models with CLIP. It introduces a novel adversarial domain adaptation approach, which trains a text and image symmetrical classifier to identify the differences between two domains. To more effectively align text and image into the same space, we adapt two types of confusion loss to construct the aligned semantic space by fine-tuning multi-modal features extractor. Experiments on 11 public datasets show that our proposed method has superior performance compared with state of art CLIP-driven learning methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
In our research and data use, we strictly adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring that informed consent is obtained from all participants. The datasets generated or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Shen Z, Liu Z, Qin J, Savvides M, Cheng K-T (2021) Partial is better than all: Revisiting fine-tuning strategy for few-shot learning. In: AAAI. pp 9594–9602
Liu H, Tam D, Muqeeth M, Mohta J, Huang T, Bansal M, Raffel CA (2022) Few-shot parameter-efficient fine-tuning is better and cheaper than in-context learning. In: NeurIPS
Radford A, Kim JW, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S, Sastry G, Askell A, Mishkin P, Clark J, et al (2021) Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. pp 8748–8763
Gao P, Geng S, Zhang R, Ma T, Fang R, Zhang Y, Li H, Qiao Y (2023) Clip-adapter: Better vision-language models with feature adapters. Int J Comput Vis 1–15
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 770–778
Zhang R, Zhang W, Fang R, Gao P, Li K, Dai J, Qiao Y, Li H (2022) Tip-adapter: Training-free adaption of clip for few-shot classification. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp 493–510
Adnan M, Arunkumar A, Jain G, Nair P, Soloveychik I, Kamath P (2024) Keyformer: Kv cache reduction through key tokens selection for efficient generative inference. MLsys
Khandelwal U, Levy O, Jurafsky D, Zettlemoyer L, Lewis M (2020) Generalization through memorization: Nearest neighbor language models. ICLR
Liao B, Tan S, Monz C (2023) Make pre-trained model reversible: From parameter to memory efficient fine-tuning. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst
Huisman M, Rijn JN, Plaat A (2021) A survey of deep meta-learning. Artif Intell Rev 54:4483–4541
Menon S, Vondrick C (2023) Visual classification via description from large language models. In: The eleventh international conference on learning representations
Zhuang F, Qi Z, Duan K, Xi D, Zhu Y, Zhu H, Xiong H, He Q (2021) A comprehensive survey on transfer learning. Proc IEEE 109(1):43–76
Wang Y, Yao Q, Kwok JT, Ni LM (2021) Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning. ACM Comput Surv 53:1–34
Bateni P, Goyal R, Masrani V, Wood F, Sigal L (2020) Improved few-shot visual classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 14493–14502
Parnami A, Lee M (2022) Learning from few examples: A summary of approaches to few-shot learning. Comput Vis Pattern Recogn
Touvron H, Lavril T, Izacard G, Martinet X, Lachaux M, Lacroix T, Rozière B, Goyal N, Hambro E, Azhar F et al (2023) Open and efficient foundation language models. 2302. Preprint at https://doi. org/10.48550/arXiv
Achiam J, Adler S, Agarwal S, Ahmad L, Akkaya I, Aleman FL, Almeida D, Altenschmidt J, Altman S, Anadkat S et al (2023) Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv:2303.08774
Li J, Li D, Savarese S, Hoi S (2023) Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, pp 19730–19742
Xu H, Liu B, Shu L, Yu PS (2019) Bert post-training for review reading comprehension and aspect-based sentiment analysis. NAACL, pp 2324–2335
Qu C, Yang L, Qiu M, Croft WB, Zhang Y, Iyyer M (2019) Bert with history answer embedding for conversational question answering. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. pp 1133–1136
Zhang Y, Sun S, Galley M, Chen Y-C, Brockett C, Gao X, Gao J, Liu J, Dolan B (2020) Dialogpt: Large-scale generative pre-training for conversational response generation. ACL, pp 270–278
Dathathri S, Madotto A, Lan J, Hung J, Frank E, Molino P, Yosinski J, Liu R (2020) Plug and play language models: A simple approach to controlled text generation. ACLR
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 25
Minderer M, Gritsenko AA, Stone A, Neumann M, Weissenborn D (2022) Simple open-vocabulary object detection. In: European conference on computer vision. pp 728–755
Du Y, Wei F, Zhang Z, Shi M, Gao Y, Li G (2022) Learning to prompt for open-vocabulary object detection with vision-language model. Comput Vis Pattern Recogn 14064–14073
Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko S (2020) End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp 213–229
Xu M, Zhang Z, Wei F, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Bai X (2022) A simple baseline for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation with pre-trained vision-language model. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp 736–753
Ghifary M, Kleijn WB, Zhang M, Balduzzi D, Li W (2016) Deep reconstruction-classification networks for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part IV 14. pp 597–613
Gu X, Lin T-Y, Kuo W, Cui Y (2022) Open-vocabulary object detection via vision and language knowledge distillation. ACLR
Liu Q, Wen Y, Han J, Xu C, Xu H, Liang X (2022) Open-world semantic segmentation via contrasting and clustering vision-language embedding. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp 275–292
Gan Z, Li L, Li C, Wang L, Liu Z, Gao J et al (2022) Vision-language pre-training: Basics, recent advances, and future trends. Found Trend Comput Graph Vis 14(3–4):163–352
Vinker Y, Pajouheshgar E, Bo JY, Bachmann RC, Bermano AH, Cohen-Or D, Zamir A, Shamir A (2022) Clipasso: Semantically-aware object sketching. ACM Trans Graph 41(4):1–11
Wilson G, Cook DJ (2020) Claims: A survey of unsupervised deep domain adaptation. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 11:1–46
Zonoozi MH, Seydi V (2022) A survey on adversarial domain adaptation. Neural Process Lett 55:2429–2469
Li L, Wan Z, He H (2020) Dual alignment for partial domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Cybern 51:3404–3416
Li J, Jing M, Lu K, Zhu L, Shen HT (2019) Locality preserving joint transfer for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(12):6103–6115
Zhang C, Zhao Q, Wu H (2022) Deep domain adaptation via joint transfer networks. In: Neurocomputing, vol. 489. pp 441–448
Zhang Y, Tang H, Jia K, Tan M (2019) Domain-symmetric networks for adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 5031–5040
Zhang L, Gao X (2022) Transfer adaptation learning: A decade survey. In: IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 35. pp 23–44
Ge P, Ren C-X, Xu X-L, Yan H (2023) Unsupervised domain adaptation via deep conditional adaptation network. Pattern Recogn 134
Fei-Fei L, Fergus R, Perona P (2004) Learning generative visual models from few training examples: An incremental Bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. In: 2004 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop. pp 178–178
Cimpoi M, Maji S, Kokkinos I, Mohamed S, Vedaldi A (2014) Describing textures in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 3606–3613
Helber P, Bischke B, Dengel A, Borth D (2019) Eurosat: A novel dataset and deep learning benchmark for land use and land cover classification. IEEE J Selec Topics Appl Earth Obser Remote Sens 12(7):2217–2226
Bossard L, Guillaumin M, Van Gool L (2014) Food-101–mining discriminative components with random forests. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part VI 13. pp 446–461
Nilsback M-E, Zisserman A (2008) Automated flower classification over a large number of classes. In: 2008 Sixth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics & Image Processing. pp 722–729
Maji S, Rahtu E, Kannala J, Blaschko M, Vedaldi A (2013) Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft. Comput Vis Pattern Recogn
Parkhi OM, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A, Jawahar C (2012) Cats and dogs. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp 3498–3505
Krause J, Stark M, Deng J, Fei-Fei L (2013) 3d object representations for fine-grained categorization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. pp 554–561
Soomro K, Zamir AR, Shah M (2012) Ucf101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. Comput Vis Pattern Recogn
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. ICLR
Zhou K, Yang J, Loy CC, Liu Z (2022) Learning to prompt for vision-language models. Int J Comput Vision 130(9):2337–2348
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62306320), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20231063)), the Fundamental Research Funds of Central Universities (No. 2019XKOYMS87), Science and Technology Planning Project of Xuzhou (No. KC21193).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tongfeng Sun, Hongjian Yang, and Zhongnian Li conceived and designed the study. Tongfeng Sun, Hongjian Yang, Zhongnian Li, Xinzheng Xu, and Xiurui Wang performed material preparation, data collection, and analysis. The initial draft of the manuscript was written by Tongfeng Sun, and all authors provided comments on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, T., Yang, H., Li, Z. et al. Adversarial domain adaptation with CLIP for few-shot image classification. Appl Intell 55, 59 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06088-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06088-4