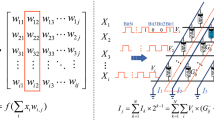
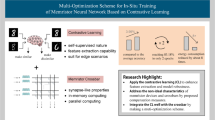
Abstract
Memristor Neural Networks (MNNs) stand out for their low power consumption and accelerated matrix operations, making them a promising hardware solution for neural network implementations. The efficacy of MNNs is significantly influenced by the careful selection of memristor update thresholds and the in-situ update scheme during hardware deployment. This paper addresses these critical aspects through the introduction of a novel scheme that integrates Dynamic Threshold (DT) and Gradient Accumulation (GA) with Threshold Properties. In this paper, realistic memristor characteristics, including pulse-to-pulse (P2P) and device-to-device (D2D) behaviors, were simulated by introducing random noise to the Vteam memristor model. A dynamic threshold scheme is proposed to enhance in-situ training accuracy, leveraging the inherent characteristics of memristors. Furthermore, the accumulation of gradients during back propagation is employed to finely regulate memristor updates, contributing to an improved in-situ training accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate a significant enhancement in test accuracy using the DTGA scheme on the MNIST dataset (82.98% to 96.15%) and the Fashion-MNIST dataset (75.58% to 82.53%). Robustness analysis reveals the DTGA scheme’s ability to tolerate a random noise factor of 0.03 for the MNIST dataset and 0.02 for the Fashion-MNIST dataset, showcasing its reliability under varied conditions. Notably, in the Fashion-MNIST dataset, the DTGA scheme yields a 7% performance improvement accompanied by a corresponding 7% reduction in training time. This study affirms the efficiency and accuracy of the DTGA scheme, which proves adaptable beyond multilayer perceptron neural networks (MLP), offering a compelling solution for the hardware implementation of diverse neuromorphic systems.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability and Access
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H et al (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115:211–252
Young T, Hazarika D, Poria S et al (2018) Recent trends in deep learning based natural language processing. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 13(3):55–75
Zheng WL, Liu W, Lu Y et al (2018) Emotionmeter: A multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(3):1110–1122
Ji X, Dong Z, Zhu L, et al (2024) An efficient human activity recognition in-memory computing architecture development for healthcare monitoring. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf
Eryilmaz SB, Kuzum D, Yu S, et al (2015) Device and system level design considerations for analog-non-volatile-memory based neuromorphic architectures. In: 2015 IEEE international electron devices meeting (IEDM), IEEE, pp 4–1
Le QV (2013) Building high-level features using large scale unsupervised learning. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, IEEE, pp 8595–8598
Merolla PA, Arthur JV, Alvarez-Icaza R et al (2014) A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Sci 345(6197):668–673
Pei J, Deng L, Song S et al (2019) Towards artificial general intelligence with hybrid tianjic chip architecture. Nat 572(7767):106–111
Chi P, Li S, Xu C et al (2016) Prime: A novel processing-in-memory architecture for neural network computation in reram-based main memory. ACM SIGARCH Comput Archit News 44(3):27–39
Gao B, Bi Y, Chen HY et al (2014) Ultra-low-energy three-dimensional oxide-based electronic synapses for implementation of robust high-accuracy neuromorphic computation systems. ACS nano 8(7):6998–7004
Dong Z, Ji X, Wang J, et al (2023) Icncs: internal cascaded neuromorphic computing system for fast electric vehicle state of charge estimation. IEEE Trans Consum Electron
Zidan MA, Strachan JP, Lu WD (2018) The future of electronics based on memristive systems. Nat Electr 1(1):22–29
Ji X, Lai CS, Zhou G et al (2022) A flexible memristor model with electronic resistive switching memory behavior and its application in spiking neural network. IEEE Trans NanoBiosci 22(1):52–62
Dong Z, Qian Z, Zhou G et al (2022) Memory circuit design, implementation and analysis based on memristor full-function pavlov associative. J Electr & Inf Technol 44(6):2080–2092
Xia L, Tang T, Huangfu W, et al (2016) Switched by input: Power efficient structure for rram-based convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Design Automation Conference, pp 1–6
Li C, Hu M, Li Y et al (2018) Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat Electr 1(1):52–59
Gao T, Zhou Y, Duan S et al (2022) Memristive kdg-bnn: Memristive binary neural networks trained via knowledge distillation and generative adversarial networks. Knowl-Based Syst 249(108):962
Sun F, Li J, Xiao H, et al (2022) Lightweight memristive neural network for gas classification based on heterogeneous strategy. Int J Bifurcation Chaos 32(07):2250,108
Guo MJ, Duan SK, Wang LD (2022) Pulse coding off-chip learning algorithm for memristive artificial neural network. Chin Phys B 31(7):078,702
Zhou Y, Hu X, Wang L et al (2021) Quantbayes: Weight optimization for memristive neural networks via quantization-aware bayesian inference. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I Regular Paper 68(12):4851–4861
Wen S, Chen J, Wu Y et al (2020) Ckfo: Convolution kernel first operated algorithm with applications in memristor-based convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Comput-Aided Des Integr Circ Syst 40(8):1640–1647
Yang C, Wang X, Zeng Z (2022) Full-circuit implementation of transformer network based on memristor. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I Regular Paper 69(4):1395–1407
Dong Z, Duan S, Hu X, et al (2014) A novel memristive multilayer feedforward small-world neural network with its applications in pid control. Sci World J 2014(1):394,828
Rao M, Tang H, Wu J et al (2023) Thousands of conductance levels in memristors integrated on cmos. Nat 615(7954):823–829
Yao P, Wu H, Gao B et al (2020) Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nat 577(7792):641–646
Wan W, Kubendran R, Schaefer C et al (2022) A compute-in-memory chip based on resistive random-access memory. Nat 608(7923):504–512
Zhang Y, Cui M, Shen L et al (2019) Memristive quantized neural networks: A novel approach to accelerate deep learning on-chip. IEEE Trans Cybern 51(4):1875–1887
Li C, Belkin D, Li Y et al (2018) Efficient and self-adaptive in-situ learning in multilayer memristor neural networks. Nat Commun 9(1):2385
He Z, Lin J, Ewetz R, et al (2019) Noise injection adaption: End-to-end reram crossbar non-ideal effect adaption for neural network mapping. In: Proceedings of the 56th Annual Design Automation Conference 2019, pp 1–6
Zhu Z, Sun H, Qiu K, et al (2020) Mnsim 2.0: A behavior-level modeling tool for memristor-based neuromorphic computing systems. In: Proceedings of the 2020 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, pp 83–88
Yao P, Wu H, Gao B, et al (2017) Face classification using electronic synapses. Nat Commun 8(1):15,199
Chen PY, Peng X, Yu S (2017) Neurosim+: An integrated device-to-algorithm framework for benchmarking synaptic devices and array architectures. In: 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), IEEE, pp 6–1
Zhang Q, Wu H, Yao P et al (2018) Sign backpropagation: an on-chip learning algorithm for analog rram neuromorphic computing systems. Neural Netw 108:217–223
Wang Y, Wu S, Tian L et al (2020) Ssm: a high-performance scheme for in situ training of imprecise memristor neural networks. Neurocomputing 407:270–280
Zhang W, Wang Y, Ji X, et al (2021) Roa: a rapid learning scheme for in-situ memristor networks. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, p 144
Li J, Zhou G, Li Y, et al (2022) Reduction 93.7% time and power consumption using a memristor-based imprecise gradient update algorithm. Artif Intell Rev 55(1):657–677
Gao B, Zhou Y, Zhang Q, et al (2022) Memristor-based analogue computing for brain-inspired sound localization with in situ training. Nat Commun 13(1):2026
Hu M, Graves CE, Li C, et al (2018) Memristor-based analog computation and neural network classification with a dot product engine. Adv Mater 30(9):1705,914
Chua L (1971) Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circ Theory 18(5):507–519
Strukov DB, Snider GS, Stewart DR et al (2008) The missing memristor found. Nat 453(7191):80–83
Guan X, Yu S, Wong HSP (2012) A spice compact model of metal oxide resistive switching memory with variations. IEEE Electr Device Lett 33(10):1405–1407
Jiang Z, Wu Y, Yu S et al (2016) A compact model for metal-oxide resistive random access memory with experiment verification. IEEE Trans Electr Devices 63(5):1884–1892
Choi S, Sheridan P, Lu WD (2015) Data clustering using memristor networks. Sci Rep 5(1):1–10
Kvatinsky S, Ramadan M, Friedman EG et al (2015) Vteam: A general model for voltage-controlled memristors. IEEE Trans Circ Systems II Express Briefs 62(8):786–790
Chen PY, Peng X, Yu S (2018) Neurosim: A circuit-level macro model for benchmarking neuro-inspired architectures in online learning. IEEE Trans Comput-Aided Des Integr Circ Syst 37(12):3067–3080
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Southwest University High-Value Patent Cultivation Project (Grant No. SWU-ZLPY07), Open Fund Project of State Key Laboratory of Intelligent Vehicle Safety Technology (Grant No. IVSTSKL-202309), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U20A20227,62076208, 62076207), Chongqing Talent Plan Project (Grant No. CQYC20210302257), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. SWU-XDZD22009, SWU-XDJH202319), Chongqing Higher Education Teaching Reform Research Project (Grant No. 211005), the Youth Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62306246) and Key Project of Chongqing Natural Science Foundation Joint Fund (Grant No. CSTB2024NSCQ-LZX0087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Siyuan Shen: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing - original draft, Revised paper. Mingjian Guo: Investigation,Visualization, Validation, Revised paper. Lidan Wang: Supervision, Writing - review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Shukai Duan: Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical and Informed Consent for Data Used
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, S., Guo, M., Wang, L. et al. DTGA: an in-situ training scheme for memristor neural networks with high performance. Appl Intell 55, 167 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06091-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06091-9