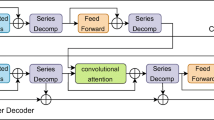
Abstract
The improvement of performance and efficiency in long-term time series forecasting is significant for practical applications. However, while enhancing overall performance, existing time series forecasting methods often exhibit unsatisfactory capabilities in the restoration of details and prediction efficiency. To address these issues, an autocorrelation Transformer with multiscale decomposition (MSDformer) is proposed for long-term multivariate time series forecasting. Specifically, a multiscale decomposition (MSDecomp) module is designed, which identifies the temporal repeating patterns in time series with different scales to retain more historical details while extracting trend components. An Encoder layer is proposed based on the MSDecomp module and Auto-Correlation mechanism, which discovers the similarity of subsequences in a periodic manner and effectively captures the seasonal components to improve the degree of restoration of prediction details while extracting the residual trend components. Finally, unlike the traditional Transformer structure, the decoder structure is replaced by the proposed Autoregressive module to simplify the output mode of the decoder and enhance linear information. Compared to other advanced and representative models on six real-world datasets, the experimental results demonstrate that the MSDformer has a relative performance improvement of an average of 8.1%. MSDformer also has lower memory usage and temporal consumption, making it more advantageous for long-term time series forecasting.
Graphical abstract





















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and materials
All the datasets used in this paper are publicly available and can be acquired from the above links. All data are available by contacting the corresponding author by reasonable request.
References
Sbrana G, Antonetti P (2023) Persistence modeling for sales prediction: A simple, self-contained approach. J Bus Res 166:114103
Ruan L, Bai Y, Li S, He S, Xiao L (2021) Workload time series prediction in storage systems: a deep learning based approach. Cluster Computing, 1–11
Camastra F, Capone V, Ciaramella A, Riccio A, Staiano A (2022) Prediction of environmental missing data time series by support vector machine regression and correlation dimension estimation. Environ Model Softw 150:1043–1053
Jassim MS, Coskuner G, Sultana N, Hossain SZ (2023) Forecasting domestic waste generation during successive covid-19 lockdowns by bidirectional lstm super learner neural network. Appl Soft Comput 133:1099–1108
Callot L, Caner M, Önder AÖ, Ulaşan E (2021) A nodewise regression approach to estimating large portfolios. J Bus Econ Stat 39(2):520–531
Mohanty MK, Thakurta PKG, Kar S (2023) Agricultural commodity price prediction model: a machine learning framework. Neural Comput Appl 35(20):15109–15128
Babu CN, Reddy BE (2014) Arima-based and multiapplication workload prediction with wavelet decomposition and savitzky–golay filter in clouds. Appl Soft Comput 23:27–38
Smyl S (2020) A hybrid method of exponential smoothing and recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting. Int J Forecast 36(1):75–85
Sun Y, Leng B, Guan W (2015) Exploiting pso-svm and sample entropy in bemd for the prediction of interval-valued time series and its application to daily pm2. 5 concentration forecasting. Neurocomput 166:109–121
Yu H, Dai Q (2023) Ae-dil: A double incremental learning algorithm for non-stationary time series prediction via adaptive ensemble. Inf Sci 636:118916
Vosoughi S, Mohsenvand MN, Roy D (2017) Ensemble conformalized quantile regression for probabilistic time series forecasting. ACM Trans knowl Discov Data (TKDD) 11(4):1–36
Liu Y, Zhang Q, Song L, Chen Y (2019) Recurrent neural network-fitnets: improving early prediction of student performanceby time-series knowledge distillation. Comput Electron Agric 165:1049–1064
Hu J, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Zhang M, Xue J (2020) Time series prediction method based on variant lstm recurrent neural network. Neural Process Lett 52:1485–1500
Li Q, Xu Y (2019) Single-layer folded rnn for time series prediction and classification under a non-von neumann architecture. Appl Sci 9(15):30–41
Hewage P, Behera A, Trovati M, Pereira E, Ghahremani M, Palmieri F, Liu Y (2020) Temporal convolutional neural (tcn) network for an effective weather forecasting using time-series data from the local weather station. Soft Comput 24:16453–16482
Zheng Y, Gao Z, Wang Y, Fu Q (2020) Mooc dropout prediction using fwts-cnn model based on fused feature weighting and time series. IEEE Access 8:225324–225335
Gao C, Zhang N, Li Y, Bian F, Wan H (2020) Self-attention-based time-variant neural networks for multi-step time series forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 34(11):8737–8754
Chen L, Chen D, Shang Z, Wu B, Zheng C, Wen B, Zhang W (2023) Multi-scale adaptive graph neural network for multivariate time series forecasting. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 35(10):10748–10761
Bai L, Yao L, Li C, Wang X, Wang C (2020) Adaptive graph convolutional recurrent network for traffic forecasting. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:17804–17815
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30:1–11
Zhou H, Zhang S, Peng J, Zhang S, Li J, Xiong H, Zhang W (2021) Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 35:11106–11115
Kitaev N, Kaiser L, Levskaya A (2020) Reformer: The efficient transformer. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations, pp 1–12
Liu S, Yu H, Liao C, Li J, Lin W, Liu AX, Dustdar S (2021) Pyraformer: Low-complexity pyramidal attention for long-range time series modeling and forecasting. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations, pp 1–20
Geng Z, Chen Z, Meng Q, Han Y (2021) Novel transformer based on gated convolutional neural network for dynamic soft sensor modeling of industrial processes. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 18(3):1521–1529
Wang Y, Peng J, Wang X, Zhang Z, Duan J (2024) Replacing self-attentions with convolutional layers in multivariate long sequence time-series forecasting. Appl Intell 54(1):522–543
Song W, Fujimura S (2021) Capturing combination patterns of long-and short-term dependencies in multivariate time series forecasting. Neurocomput 464:72–82
Bandara K, Bergmeir C, Hewamalage H (2020) Lstm-msnet: Leveraging forecasts on sets of related time series with multiple seasonal patterns. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(4):1586–1599
Wang X, Liu H, Yang Z, Du J, Dong X (2023) Cnformer: a convolutional transformer with decomposition for long-term multivariate time series forecasting. Appl Intell 1–15
Wu H, Xu J, Wang J, Long M (2021) Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:22419–22430
Zhou T, Ma Z, Wen Q, Wang X, Sun L, Jin R (2022) Fedformer: Frequency enhanced decomposed transformer for long-term series forecasting. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning, pp 27268–27286. PMLR
Han Z, Zhao J, Leung H, Ma KF, Wang W (2019) A review of deep learning models for time series prediction. IEEE Sensors J 21(6):7833–7848
Natarajan YJ, Subramaniam Nachimuthu D (2020) New svm kernel soft computing models for wind speed prediction in renewable energy applications. Soft Comput 24:11441–11458
Yu H, Dai Q (2022) Dwe-il: a new incremental learning algorithm for non-stationary time series prediction via dynamically weighting ensemble learning. Appl Intell 52(1):174–194
Liu B (2023) Robust sequential online prediction with dynamic ensemble of multiple models: A review. Neurocomputing, 126553
Mbuli N, Mathonsi M, Seitshiro M, Pretorius JHC (2020) Decomposition forecasting methods: A review of applications in power systems. Energy Rep 6:298–306
Dudek G (2023) Std: a seasonal-trend-dispersion decomposition of time series. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 35(10):10339–10350
Zhou Y, Zhao J, Song Y, Sun J, Fu H, Chu M (2022) A seasonal-trend-decomposition-based voltage-source-inverter open-circuit fault diagnosis method. IEEE Trans Power Electr 37(12):15517–15527
He X, Li Y, Tan J, Wu B, Li F (2023) Oneshotstl: One-shot seasonal-trend decomposition for online time series anomaly detection and forecasting. Proc VLDB Endowment 16(6):1399–1412
Wang X, Chen G, Qian G, Gao P, Wei XY, Wang Y, Tian Y, Gao W (2023) Large-scale multi-modal pre-trained models: A comprehensive survey. Mach Intell Res 20(4):447–482
Zerveas G, Jayaraman S, Patel D, Bhamidipaty A, Eickhoff C (2021) A transformer-based framework for multivariate time series representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, pp 2114–2124
Wang X, Liu H, Du J, Yang Z, Dong X (2023) Clformer: Locally grouped auto-correlation and convolutional transformer for long-term multivariate time series forecasting. Eng Appl Artif Intell 121:106042
Lai G, Chang W, Yang Y, Liu H (2018) Modeling long-and short-term temporal patterns with deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of The 41st International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, pp 95–104
Abdulkadirov R, Lyakhov P, Nagornov N (2023) Survey of optimization algorithms in modern neural networks. Math 11(11):2466
Funding
This work is supported in part by National Key R&D program of China (Grant no. 2020YFC1523004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.S. presented the innovation of paper, designed and carried out the experiments, analyzed the result of the experiments. Y.G. drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical and informed consent for data used
This paper does not contain any studies involving humans or animals.
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
The authors have no competing financial interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, G., Guan, Y. MSDformer: an autocorrelation transformer with multiscale decomposition for long-term multivariate time series forecasting. Appl Intell 55, 179 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06105-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06105-6