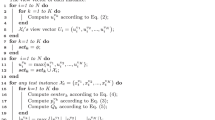Abstract
Multi-view classification methods have better generalization performance compared to the single-view classification methods due to the consistency information from multiple views. In recent years, the combination of support vector machine (SVM) and multi-view learning has been widely studied. To improve the robustness of multi-view classification methods, emphasis has shifted to the integration of multi-view classification approaches with fully-connected and convolutional neural networks. A classical deep two-view classification method named deep SVM-2K is a combination of support vector machine with two stage kernel canonical correlation analysis (SVM-2K) and deep learning. However, limitations of deep SVM-2K are that it can not cope with multi-view classification and multiclass classification problems. To address these issues, we propose two novel deep multi-view models named deep multi-view support vector machine (DMVSVM) for multiclass classification. DMVSVM uses the learned features by auto-encoder (AE) or deep neural network (DNN) to train the SVM classifier for each view. The two models then impose some constraints to make the output of the multi-view SVM classifiers as consistent as possible, which used to exploring intrinsic relations. Experiments performed on different real-word datasets show the effectiveness of our proposed approaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [Xj Xie], upon reasonable request.
References
Sun S (2013) A survey of multi-view machine learning. Neural Comput Appl 23(7–8):2031–2038
Yan X, Hu S, Mao Y, Ye Y, Yu H (2021) Deep multi-view learning methods: A review. Neurocomputing 448(1):106–129
Yin J, Sun S (2019) Multiview uncorrelated locality preserving projection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(9):3442–3455
Sun S, Dong W, Liu Q (2020) Multi-view representation learning with deep gaussian processes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(12):4453–4468
Deepak K, Srivathsan G, Roshan S, Chandrakala S (2021) Deep multi-view representation learning for video anomaly detection using spatiotemporal autoencoders. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40(3):1333–1349
Hotelling H (1935) Relations between two sets of variates. Biometrika 28(3/4):321–377
Muirhead RJ, Anderson TW (1986) An introduction to multivariate statistical analysis. J Business Econ Stat 4(1):135–135
Lai PL, Fyfe C (2000) Kernel and nonlinear canonical correlation analysis. Int J Neural Syst 10(05):365–377
Park HJ, Kang BH, Shin W, Kim JS, Han SW (2022) Manner: Multi-view attention network for noise erasure. In: ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 7842–7846
Xia W, Wang S, Yang M, Gao Q, Han J, Gao X (2022) Multi-view graph embedding clustering network: Joint self-supervision and block diagonal representation. Neural Netw 145:1–9
Yan X, Hu S, Mao Y, Ye Y, Yu H (2021) Deep multi-view learning methods: A review. Neurocomputing 448:106–129
Liu J, Cao F, Liang J (2022) Centroids-guided deep multi-view k-means clustering. Inf Sci 609:876–896
Kaya B, Kumar S, Oliveira C, Ferrari V, Van Gool L (2022) Uncertainty-aware deep multi-view photometric stereo. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 12601–12611
Du G, Zhou L, Li Z, Wang L, Lü K (2023) Neighbor-aware deep multi-view clustering via graph convolutional network. Inf Fusion 93:330–343
Su J, Yu X, Wang X, Wang Z, Chao G (2024) Enhanced transfer learning with data augmentation. Eng Appl Artif Intell 129:107602
Wang J, Wu B, Ren Z, Zhang H, Zhou Y (2023) Multi-scale deep multi-view subspace clustering with self-weighting fusion and structure preserving. Expert Syst Appl 213:119031
Zhang C, Liu Y, Fu H (2019) Ae2-nets: Autoencoder in autoencoder networks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2572–2580
Wang Q, Tao Z, Xia W, Gao Q, Cao X, Jiao L (20222) Adversarial multiview clustering networks with adaptive fusion. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst pp 1–13
Hosseinzadeh H (2022) Deep multi-view feature learning for detecting covid-19 based on chest x-ray images. Biomed Signal Process Control 75:103595
Song D, Zhang Z, Li W, Yuan L, Zhang W (2022) Judgment of benign and early malignant colorectal tumors from ultrasound images with deep multi-view fusion. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 215:106634
Chen R, Tang Y, Zhang W, Feng W (2022) Deep multi-view semi-supervised clustering with sample pairwise constraints. Neurocomputing 500:832–845
Li Y, Ge Z, Yu G, Yang J, Wang Z, Shi Y, Sun J, Li Z (2023) Bevdepth: Acquisition of reliable depth for multi-view 3d object detection. Proceed AAAI Conference Artif Intell 37:1477–1485
Li R, Gong D, Yin W, Chen H, Zhu Y, Wang K, Chen X, Sun J, Zhang Y (2023) Learning to fuse monocular and multi-view cues for multi-frame depth estimation in dynamic scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition pp 21539–21548
Liu Y, Han C, Zhang L, Gao X (2022) Pedestrian detection with multi-view convolution fusion algorithm. Entropy 24(2):165
Geremias J, Viegas EK, Santin AO, Britto A, Horchulhack P (2022) Towards multi-view android malware detection through image-based deep learning. In: 2022 International wireless communications and mobile computing (IWCMC), IEEE, pp 572–577
Ravi V, Alazab M, Selvaganapathy S, Chaganti R (2022) A multi-view attention-based deep learning framework for malware detection in smart healthcare systems. Comput Commun 195:73–81
Rahmawati FD, Hadiprakoso RB, Yasa RN (2022) Comparison of single-view and multi-view deep learning for android malware detection. In: 2022 International conference on information technology research and innovation (ICITRI), IEEE, pp 53–58
Shawe-Taylor J, Sun S (2011) A review of optimization methodologies in support vector machines. Neurocomputing 74(17):3609–3618
Xie X, Sun S (2020) Multi-view support vector machines with the consensus and complementarity information. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(12):2401–2413
Wu C, Wang S, Pan B, Chen H (2016) Facial expression recognition with deep two-view support vector machine. (Amsterdam, United kingdom), pp 616–620
Xue Z, Du J, Du D, Lyu S (2019) Deep low-rank subspace ensemble for multi-view clustering. Inf Sci: An Int J vol. 482, pp 210–227, 1
Farquhar JD, Hardoon DR, Meng H, Shawe-Taylor J, Szedmak S (2005) Two view learning: Svm-2k, theory and practice. In: Advances in neural information processing systems ( Weiss Y, Schölkopf B, and Platt J, eds.), vol. 18, pp. 355 – 362, MIT Press,
Hao Q, Zheng W, Xiao Y, Zhu W (2023) Multi-view support vector machines with sub-view learning. Soft Comput 27(10):6241–6259
Fu S, Tian Y, Tang J (2023) Iterative privileged learning for multi-view classification. Procedia Comput Sci 221:1358–1365
Yu S, Li X, Sun S, Wang H, Zhang X, Chen S (2022) Ibmvsvm: An instance-based multi-view svm algorithm for classification. Appl Intell 52(13):14739–14755
Lou C, Xie X (2023) Multi-view intuitionistic fuzzy support vector machines with insensitive pinball loss for classification of noisy data. Neurocomputing 126458
Jana GC, Praneeth MS, Agrawal A (2023) A multi-view svm approach for seizure detection from single channel eeg signals. IETE J Res 69(6):3120–3131
Barajas Montiel SE, Morales EF, Escalante HJ (2022) Multi-view learning for eeg signal classification of imagined speech. In: Mexican conference on pattern recognition, Springer, pp 191–200
Barajas-Montiel SE, Morales EF, Escalante HJ, Reyes-García CA (2023) Automatic selection of multi-view learning techniques and views for pattern recognition in electroencephalogram signals. Computación y Sistemas 27(1):211–221
Long KK, Kwok SWH, Kotz J, Wang G (2023) A deep multi-view imbalanced learning approach for identifying informative covid-19 tweets from social media. Comput Biol Med 164:107232
Kumar V, Chaurasia PK, Aydav PSS, et al (2023) Deep multi-view learning for healthcare domain. In: Computational intelligence aided systems for healthcare domain, CRC Press, pp 55–90
Tian Y, Fu S, Tang J (2021) Incomplete-view oriented kernel learning method with generalization error bound. Inf Sci 581:951–977
Cheng Y, Fu L, Luo P, Ye Q, Liu F, Zhu W (2020) Multi-view generalized support vector machine via mining the inherent relationship between views with applications to face and fire smoke recognition. Knowl-Based Syst 210:106488
Bousahba N, Adjoudj R, Belhia S, Chachou L (2022) Dimensionality reduction method apply for multi-view multimodal person identification. Int J Comput Digital Syst 12(1):675–685
Liu S, Guo S, Wang W, Qiao H, Wang Y, Luo W (2020) Multi-view laplacian eigenmaps based on bag-of-neighbors for rgb-d human emotion recognition. Inf Sci 509:243–256
Zhang R, Li X, Zhang H, Nie F (2020) Deep fuzzy k-means with adaptive loss and entropy regularization. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(11):2814–2824
Hinton GE, Salakhutdinov RR (2006) Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313:504–507
Vapnik VN (1995) The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer science, New York
Tang Y (2013) Deep learning using linear support vector machines. Computer ence
Zhang S-X, Liu C, Yao K, Gong Y (2015) Deep neural support vector machines for speech recognition. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 4275–4279
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceed IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Li Y, Nie F, Huang H, Huang J (2015) Large-scale multi-view spectral clustering via bipartite graph. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI conference on artificial intelligence
Fei-Fei L, Fergus R, Perona P (2004) Learning generative visual models from few training examples: An incremental bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. In: 2004 Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshop, IEEE, pp 178–178
Chua T-S, Tang J, Hong R, Li H, Luo Z, Zheng Y (2009) Nus-wide: a real-world web image database from national university of singapore. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on image and video retrieval, pp 1–9
Basu S, Karki M, Ganguly S, DiBiano R, Mukhopadhyay S, Gayaka S, Kannan R, Nemani R (2017) Learning sparse feature representations using probabilistic quadtrees and deep belief nets. Neural Process Lett 45(3):855–867
Xu J, Han J, Nie F, Li X (2020) Multi-view scaling support vector machines for classification and feature selection. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(7):1419–1430
Liang Z, Zhang L (2022) Intuitionistic fuzzy twin support vector machines with the insensitive pinball loss. Appl Soft Comput 115:108231
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61906101). It is also supported by the Ningbo Municipal Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2023J115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
\(\bullet \)Yanfeng Li: Conceptualization, Data Curation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing-Original Draft, Writing-Review and Editing.\(\bullet \)Xijiong Xie: Conceptualization, Funding Acquisition, Writing-Re-view and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interensts
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical and Informed Consent for Data Used
This study strictly followed the research ethics and moral requirements, and all data involved in the research process were properly protected and processed. The data used in this study were drawn from publicly available datasets, or from fully licensed sources. During the processing and analysis of data, we have taken measures to protect personal privacy and ensure that personally identifiable information will not be disclosed. In addition, we have strictly complied with relevant laws, regulations and ethical requirements to ensure that the research will not harm or improperly influence anyone.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xie, X. Two novel deep multi-view support vector machines for multiclass classification. Appl Intell 55, 182 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06126-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06126-1