Abstract
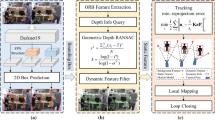
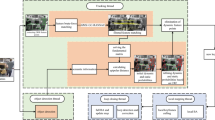
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is currently a prominent research topic in robotics, playing a crucial role in the domains of localization and navigation within unfamiliar environments. Traditional SLAM algorithms typically assume static surroundings, yet dynamic elements in real-world environments significantly impact both localization accuracy and robustness, thereby limiting algorithm applicability. To address the challenge of degraded localization accuracy caused by dynamic objects in indoor settings, we propose a dynamic point-line SLAM algorithm based on ORB-SLAM2. To address the issue of insufficient feature points caused by the removal of dynamic points in ORB-SLAM2, we augment the point features with additional line features to introduce more constraints. Additionally, we propose a novel lightweight object detection algorithm called YOLOv5s-Lightweight(YOLOv5sL) based on YOLOv5s. Experimental results on the VOC dataset demonstrate that our model achieves better real-time performance while maintaining high accuracy compared to the original YOLOv5s. Furthermore, leveraging the RGB-D model of ORB-SLAM2, we present an adaptive epipolar constraint-based dynamic feature filtering algorithm. This algorithm effectively removes dynamic points and lines by utilizing prior information from object detection networks and incorporating depth information through a new tracking thread. As a result, it efficiently filters out dynamic feature points and significantly reduces the influence of dynamic objects. Finally, we validate the effectiveness of our improved algorithm using dynamic sequences from the TUM RGB-D dataset, showing notable reductions in Absolute Trajectory Error (ATE) and Relative Pose Error (RPE), thus confirming its efficacy.














Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
The datasets generated during and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wang H, Zhang A (2022) Rgb-d slam method based on object detection and k-means, 94–98. https://doi.org/10.1109/IHMSC55436.2022.00031
Mur-Artal R, Tardós JD (2017) Orb-slam2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans Rob 33(5):1255–1262. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103
Campos C, Elvira R, Rodríguez JJG, Montiel, JMM., Tardós, JD (2021) Orb-slam3: An accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap slam. IEEE Trans Robot 37(6):1874–1890. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644
Qin T, Li P, Shen S (2018) VINS-Mono: A Robust and Versatile Monocular Visual-Inertial State Estimator vol 34, pp 1004–1020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729
Qin T, Li P, Shen S (2018) Vins-mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Trans Rob 34(4):1004–1020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729
Mokssit S, Licea DB, Guermah B, Ghogho M (2023) Deep learning techniques for visual slam: A survey. IEEE Access 11:20026–20050. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3249661
Mokssit S, Licea DB, Guermah B, Ghogho M (2023) Deep learning techniques for visual slam: A survey. IEEE Access 11:20026–20050. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3249661
Liu J, Cai Q, Zou F, Zhu Y, Liao L, Guo F (2023) Biga-yolo: A lightweight object detection network based on yolov5 for autonomous driving. Electronics 12(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122745
Tan M, Pang R, Le QV (2020) Efficientdet: Scalable and efficient object detection, pp 10781–10790
Wang R, Wan W, Wang Y, Di K (2019) A new rgb-d slam method with moving object detection for dynamic indoor scenes. Remote Sens 11(10)
Yang S, Fan G, Bai L et al (2021) Geometric constraint-based visual slam under dynamic indoor environment. Comput Eng Appl 57(16):203–212
Kundu A, Krishna KM, Sivaswamy J (2009) Moving object detection by multi-view geometric techniques from a single camera mounted robot, pp 4306–4312. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2009.5354227
Zhang C, Zhang R, Jin S, Yi X (2022) Pfd-slam: A new rgb-d slam for dynamic indoor environments based on non-prior semantic segmentation. Remote Sens 14(10):2445
Song B, Yuan X, Ying Z, Yang B, Song Y, Zhou F (2023) Dgm-vins: Visual–inertial slam for complex dynamic environments with joint geometry feature extraction and multiple object tracking. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 72:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2023.3280533
Zhong F, Wang S, Zhang Z, Chen C, Wang Y (2018) Detect-slam: Making object detection and slam mutually beneficial, pp 1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2018.00115
Yu C, Liu Z, Liu X-J, Xie F, Yang Y, Wei Q, Fei Q (2018) Ds-slam: A semantic visual slam towards dynamic environments, 1168–1174. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8593691
Bescos B, Fácil JM, Civera J, Neira J (2018) Dynaslam: Tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Robot Autom Lett 3(4):4076–4083. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2018.2860039
Pan Z, Hou J, Yu L (2023) Optimization rgb-d 3-d reconstruction algorithm based on dynamic slam. IEEE Trans on Instrum Meas72:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2023.3248116
Liu Y, Miura J (2021) Rds-slam: Real-time dynamic slam using semantic segmentation methods. IEEE Access 9:23772–23785. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3050617
Li A, Wang J, Xu M, Chen Z (2021) Dp-slam: A visual slam with moving probability towards dynamic environments. Inform Sci 556:128–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.12.019
Wei Y, Zhou B, Duan Y, Liu J, An D (2023) Do-slam: research and application of semantic slam system towards dynamic environments based on object detection. Appl Intell 53(24):30009–30026
Zhou Y, Tao F, Fu Z, Zhu L, Ma H (2023) Rvd-slam: A real-time visual slam toward dynamic environments based on sparsely semantic segmentation and outlier prior. IEEE Sens J 23(24):0773–30785. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2023.3329123
Wu W, Guo L, Gao H, You Z, Liu Y, Chen Z (2022) Yolo-slam: A semantic slam system towards dynamic environment with geometric constraint. Neural Comput Appl pp 1–16
Dai Y, Liu W, Wang H, Xie W, Long K (2022) Yolo-former: Marrying yolo and transformer for foreign object detection. IEEE Trans Inst Meas 71:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3219468
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
Lin T-Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollar P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection
Iandola FN (2016) Squeezenet: Alexnet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and¡ 0.5 mb model size. arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.07360
Howard AG (2017) Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861
Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices, pp 6848–6856
Vaswani A (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst
Dosovitskiy A (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows, pp 10012–10022
Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko S (2020) End-to-end object detection with transformers, Springer, pp 213–229
Soares JCV, Gattass M, Meggiolaro MA (2021) Crowd-slam: visual slam towards crowded environments using object detection. J Intell Robot Syst 102(2):50
Newcombe RA, Lovegrove SJ, Davison AJ (2011) Dtam: Dense tracking and mapping in real-time, pp 2320–2327. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126513
Engel J, Schöps T, Cremers D (2014) Lsd-slam: Large-scale direct monocular slam, Springer, pp 834–849
Pumarola A, Vakhitov A, Agudo A, Sanfeliu A, Moreno-Noguer F (2017) Pl-slam: Real-time monocular visual slam with points and lines, pp 4503–4508. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2017.7989522
Han K, Wang Y, Tian Q, Guo J, Xu C, Xu C (2020) Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations, pp 1580–1589
Chen J, Kao S-h, He H, Zhuo W, Wen S, Lee C-H, Chan S-HG (2023) Run, don’t walk: chasing higher flops for faster neural networks, pp 12021–12031
Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J (2021) Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design, pp 13713–13722
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks, pp 7794–7803
Ganesh P, Chen Y, Yang Y, Chen D, Winslett M (2022) Yolo-ret: Towards high accuracy real-time object detection on edge gpus, pp 3267–3277
Wang RJ, Li X, Ling CX (2018) Pelee: A real-time object detection system on mobile devices. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst 31
Huang X, Wang X, Lv W, Bai X, Long X, Deng K, Dang Q, Han S, Liu Q, Hu X et al (2021) Pp-yolov2: A practical object detector. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.10419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, J., Qian, H. Dynamic point-line SLAM based on lightweight object detection. Appl Intell 55, 260 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06164-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06164-9