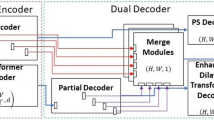
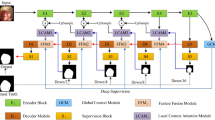
Abstract
Colorectal cancer is considered one of the deadliest diseases, contributing to an alarming increase in annual deaths worldwide, with colorectal polyps recognized as precursors to this malignancy. Early and accurate detection of these polyps is crucial for reducing the mortality rate of colorectal cancer. However, the manual detection of polyps is a time-consuming process and requires the expertise of trained medical professionals. Moreover, it often misses polyps due to their varied size, color, and texture. Computer-aided diagnosis systems offer potential improvements, but they often struggle with precision in complex visual environments. This study presents an enhanced deep learning approach using encoder-decoder architecture for colorectal polyp segmentation to capture and utilize complex feature representations. Our approach introduces an enhanced dual attention mechanism, combining spatial and channel-wise attention to focus precisely on critical features. Channel-wise attention, implemented via an optimized Squeeze-and-Excitation (S&E) block, allows the network to capture comprehensive contextual information and interrelationships among different channels, ensuring a more refined feature selection process. The experimental results showed that the proposed model achieved a mean Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.9054 and 0.9277, a dice coefficient of 0.9006 and 0.9128, a precision of 0.8985 and 0.9517, a recall of 0.9190 and 0.9094, and an accuracy of 0.9806 and 0.9907 on the Kvasir-SEG and CVC-ClinicDB datasets, respectively. Moreover, the proposed model outperforms the existing state-of-the-art resulting in improved patient outcomes with the potential to enhance the early detection of colorectal polyps.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
The dataset used in this study is publicly available at https://datasets.simula.no/kvasir-seg/ and https://universe.roboflow.com/teste-mhypc/cvc-clinicdb
References
Siegel RL et al (2017) Colorectal cancer statistics. CA: a Cancer J Clin 2017(67):177–193
Li Q, Yang G, Chen Z, Huang B, Chen L, Xu D, ... Wang T (2017) Colorectal polyp segmentation using a fully convolutional neural network. In: 2017 10th international congress on image and signal processing, biomedical engineering and informatics (CISP-BMEI). IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/CISP-BMEI.2017.8301980
Ahn SB et al (2012) The Miss Rate for Colorectal Adenoma Determined by Quality-Adjusted Back-to-Back Colonoscopies. Gut Liver 6:64
Ameling S, Wirth S, Paulus D, Lacey G, Vilarino F (2009) Texture-based polyp detection in colonoscopy. In: Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2009: Algorithmen—Systeme—Anwendungen Proceedings des Workshops vom 22. bis 25. März 2009 in Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 346–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-93860-6_70
Zimmermann-Fraedrich K et al (2019) Right-Sided Location Not Associated With Missed Colorectal Adenomas in an Individual-Level Reanalysis of Tandem Colonoscopy Studies. Gastroenterology 157:660-671.e2
Heresbach D et al (2008) Miss rate for colorectal neoplastic polyps: A prospective multicenter study of back-to-back video colonoscopies. Endoscopy 40:284–290
Bonnington SN et al (2016) Surveillance of colonic polyps: Are we getting it right? World J Gastroenterol 22:1925
Safarov S et al (2021) A-denseunet: Adaptive densely connected unet for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images with atrous convolution. Sensors 21:1–15
Shaukat A et al (2015) Longer Withdrawal Time Is Associated With a Reduced Incidence of Interval Cancer After Screening Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology 149:952–957
Alam MR et al (2023) Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers. Brief Bioinform 24:bbad151
Alam MR et al (2022) Recent Applications of Artificial Intelligence from Histopathologic Image-Based Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Solid Cancers: A Systematic Review. Cancers 14:2590
Cihan P et al (2022) A new approach for determining SARS-CoV-2 epitopes using machine learning-based in silico methods. Comput Biol Chem 98:107688
Ahmad N, Asghar S, Gillani SA (2022) Transfer learning-assisted multi-resolution breast cancer histopathological images classification. Vis Comput 38(8):2751–2770
Ahmad N et al (2024) Voxel-wise body composition analysis using image registration of a three-slice CT imaging protocol: methodology and proof-of-concept studies. Biomed Eng Online 23(1):42
Ahmad N et al (2023) Automatic segmentation of large-scale CT image datasets for detailed body composition analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 24(1):346
Hayat M, Aramvith S (2024) E-SEVSR-Edge guided stereo endoscopic video super-resolution. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3367980
Hayat M, Aramvith S (2024) Saliency-aware deep learning approach for enhanced endoscopic image super-resolution. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3402953
Liu D et al (2022) 3-D Prostate MR and TRUS Images Detection and Segmentation for Puncture Biopsy. IEEE Trans Instrument Meas 19(71):1–3
Tashk A, Herp J, Nadimi E (2019) Fully automatic polyp detection based on a novel U-Net architecture and morphological post-process. In: 2019 International Conference on Control, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics & Optimization (ICCAIRO). IEEE, pp 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAIRO47923.2019.00015
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, proceedings, part III 18. Springer International Publishing, pp 234–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1411.4038
Qiu Z et al (2022) BDG-Net: boundary distribution guided network for accurate polyp segmentation. Med Imag 2022 : Image Proc 12032:792–799
Jia X et al (2020) Automatic Polyp Recognition in Colonoscopy Images Using Deep Learning and Two-Stage Pyramidal Feature Prediction. IEEE Trans Automat Sci Eng 17:1570–1584
Sang DV, Chung TQ, Lan PN, Hang DV, Van Long D, Thuy NT (2021) Ag-curesnest: A novel method for colon polyp segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.00402. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.00402
Xiao WT, Chang LJ, Liu WM (2018) Semantic segmentation of colorectal polyps with DeepLab and LSTM networks. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW). IEEE, pp 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE-China.2018.8448568
Chen LC (2017) Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.05587
Shi W, Xu J, Gao P (2022) Ssformer: a lightweight transformer for semantic segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE 24th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP). IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/MMSP55362.2022.9949177
Fang Y et al (2020) ABC-Net: Area-Boundary Constraint Network with Dynamical Feature Selection for Colorectal Polyp Segmentation. IEEE Sensors J 21(10):11799–809
Zhang Y, et al (2021) TransFuse: Fusing Transformers and CNNs for Medical Image Segmentation 12901 LNCS: p. 14–24 https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2102.08005
Fan DP et al (2020) PraNet: Parallel Reverse Attention Network for Polyp Segmentation. International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 263–273
Srivastava A et al (2021) MSRF-Net: A Multi-Scale Residual Fusion Network for Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(5):2252–63
Srivastava A et al (2021) GMSRF-Net: An improved generalizability with global multi-scale residual fusion network for polyp segmentation. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR56361.2022.9956726
Thapa SK et al (2023) Task-Aware Active Learning for Endoscopic Polyp Segmentation. Authorea Preprints. https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.22810595.v1
Yu T, Wu Q (2023) HarDNet-CPS: Colorectal polyp segmentation based on Harmonic Densely United Network. Biomed Sign Proc Contr 85:104953
Fitzgerald K, Matuszewski B (2023) FCB-SwinV2 transformer for polyp segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.01027. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.01027
Zhu J et al (2023) GCCSwin-UNet: Global Context and Cross-Shaped Windows Vision Transformer Network for Polyp Segmentation. Processes 11(4):1035
Shen T et al (2023) Automatic polyp image segmentation and cancer prediction based on deep learning. Front Oncol 12:1087438
Ige AO et al (2023) ConvSegNet: Automated Polyp Segmentation From Colonoscopy Using Context Feature Refinement With Multiple Convolutional Kernel Sizes. IEEE Access. 11:16142–16155
Tomar NK, Jha D, Bagci U (2023) Dilatedsegnet: A deep dilated segmentation network for polyp segmentation. International conference on multimedia modeling. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 334–344
Sanderson E, Matuszewski BJ (2022) FCN-transformer feature fusion for polyp segmentation. Annual conference on medical image understanding and analysis. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 892–907
Wen Y et al (2023) Rethinking the Transfer Learning for FCN Based Polyp Segmentation in Colonoscopy. IEEE Access. 11:16183–93
Bhattacharya D et al (2023) Squeeze and multi-context attention for polyp segmentation. Int J Imag Syst Technol 33(1):123–42
Jha D, Tomar NK, Sharma V, Bagci U (2024) TransNetR: transformer-based residual network for polyp segmentation with multi-center out-of-distribution testing. In: Medical Imaging with Deep Learning. PMLR, pp 1372–1384. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.07428
Tomar NK, Shergill A, Rieders B, Bagci U, Jha D (2022) TransResU-Net: transformer based ResU-Net for real-time colonoscopy polyp segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.08985. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2206.08985
Rahman MM, Marculescu R (2023) Medical image segmentation via cascaded attention decoding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp 6222–6231. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00616
Zhang M, et al (2024) HMT-UNet: A hybird Mamba-Transformer Vision UNet for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.11289
Fan C., et al (2024) SliceMamba with Neural Architecture Search for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.08481.
Kang Y, et al (2024) SurANet: Surrounding-Aware Network for Concealed Object Detection via Highly-Efficient Interactive Contrastive Learning Strategy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.06842
Patel K, Li F, Wang G (2024) Multi-layer dense attention decoder for polyp segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2024 14th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology, pp 115–120. https://doi.org/10.1145/3678935.3678955
Zhang M, et al (2024) Vm-unet-v2 rethinking vision mamba unet for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2024. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.09157.
Wu R, et al (2024) H-vmunet: High-order vision mamba unet for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.13642.
Huang S, Sirejiding S, Lu Y, Ding Y, Liu L, Zhou H, Lu H (2024) YOLO-Med: multi-task interaction network for biomedical images. In: ICASSP 2024-2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, pp 2175–2179. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10446165
Biswas K, Pal R, Patel S, Jha D, Karri M, Reza A, ... Bagci U (2024) A novel momentum-based deep learning techniques for medical image classification and segmentation. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, pp 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-73284-3_1
Nam JH, Park SH, Syazwany NS, Jung Y, Im YH, Lee SC (2023) M3FPolypSegNet: segmentation network with multi-frequency feature fusion for polyp localization in colonoscopy images. In: 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 1530–1534. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP49359.2023.10222864
Lan L, et al (2024) BRAU-Net++: U-Shaped Hybrid CNN-Transformer Network for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.00722.
Jiang J, et al (2024) LV-UNet: A Lightweight and Vanilla Model for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.16886.
Tomar NK, Jha D, Biswas K, Berzin TM, Keswani R, Wallace M, Bagci U (2024) Transformer-enhanced iterative feedback mechanism for polyp segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.05875. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.05875
Shibata T et al (2020) Automated detection and segmentation of early gastric cancer from endoscopic images using mask R-CNN. Appl Sci 10(11):3842
Duc NT et al (2022) ColonFormer: An Efficient Transformer Based Method for Colon Polyp Segmentation. IEEE Access. 10:80575–86
Lin A et al (2022) DS-TransUNet: Dual Swin Transformer U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Instrument Meas 71:1–5
Tomar NK et al (2022) FANet: A Feedback Attention Network for Improved Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 34(11):9375–88
Han J et al (2022) PRAPNet: A Parallel Residual Atrous Pyramid Network for Polyp Segmentation. Sensors. 22(13):4658
Tomar NK, Jha D, Bagci U, Ali S (2022) TGANet: Text-guided attention for improved polyp segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, pp 151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16437-8_15
Jha D, Smedsrud PH, Riegler MA, Halvorsen P, De Lange T, Johansen D, Johansen HD (2020) Kvasir-seg: a segmented polyp dataset. In: MultiMedia modeling: 26th international conference, MMM 2020, Daejeon, South Korea, January 5–8, 2020, proceedings, part II 26. Springer International Publishing, pp 451–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37734-2_37
Bernal J et al (2015) WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: Validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comp Med Imag Graph 43:99–111
Prencipe B et al (2022) Focal Dice Loss-Based V-Net for Liver Segments Classification. Appl Sci 12:3247
Dong B, Wang W, Fan DP, Li J, Fu H, Shao L (2021) Polyp-pvt: polyp segmentation with pyramid vision transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.06932. https://doi.org/10.26599/AIR.2023.9150015
Erol T, Sarikaya D (2024) PlutoNet: an efficient polyp segmentation network with modified partial decoder and decoder consistency training. Healthcare Technology Letters. https://doi.org/10.1049/htl2.12105
Zhang W et al (2022) HSNet: A hybrid semantic network for polyp segmentation. Comp Biol Med 150:106173
Nguyen M, Bui TT, Van Nguyen Q, Nguyen TT, Van Pham T (2022) LAPFormer: a light and accurate polyp segmentation transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04393. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2210.04393
Gautam A, Das S, Sharma P, Maji P, Balabantaray BK (2022) SAU-NET: Scale aware polyp segmentation using encoder-decoder network. In: 2022 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP). IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/TENSYMP54529.2022.9864338
Sharma P et al (2022) Li-SegPNet: Encoder-decoder Mode Lightweight Segmentation Network for Colorectal Polyps Analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 70(4):1330–9
Tomar NK, Jha D, Bagci U (2023) Dilatedsegnet: A deep dilated segmentation network for polyp segmentation. International conference on multimedia modeling. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 334–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Ameer Hamza and Muhammad Bilal; methodology, Ameer Hamza and M.R; software, Ameer Hamza and Nadia Malik; validation, Muhammad Bilal, Muhammad Ramzan, and Nadia Malik; formal analysis, Muhammad Ramzan; investigation, Nadia Malik; resources, Muhammad Bilal; data curation, Ameer Hamza; writing—original draft preparation, Ameer Hamza and Muhammad Bilal; writing—review and editing, Muhammad Ramzan and Nadia Malik; visualization, Nadia Malik; supervision, Muhammad Bilal and Muhammad Ramzan; project administration, Muhammad Ramzan.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent
The publishers’ “terms of use” are followed for the use of both published datasets.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamza, A., Bilal, M., Ramzan, M. et al. Effectiveness of encoder-decoder deep learning approach for colorectal polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images. Appl Intell 55, 290 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06167-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06167-6