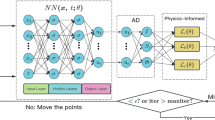
Abstract
Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) in various scientific and engineering applications. PINNs integrate the PDEs into the loss functions of neural networks through automatic differentiation, which comprises a weighted combination of the PDE residuals, boundary and initial constraints, and observed data. However, the accuracy and efficiency of PINNs need substantial improvement to meet the requirements across a wider range of challenging problems. In this paper, we propose a hybrid adaptive (HA) sampling method and a feature embedding layer for PINN. The spatiotemporal points for PINN training (called residual points) are resampled during iteration procedure via the proposed HA method. The HA method ensures randomness in the selection of points while also prioritizing those with large PDE residuals, thereby ensuring efficient training by focusing the network’s learning on areas where the model’s predictions are less accurate. Moreover, the vanilla PINN architecture is further enhanced by a feature embedding layer, which transforms the raw input into a higher-dimensional space, enabling the network to better capture complex relationships underlying in PDEs and improve its fitting ability. The numerical experiments on a variety of forward and inverse PDE problems have shown that the proposed methods significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of PINN with reduced reliance on the number of sampling points. The L2 relative error of vanilla PINN can be reduced by approximately 1\(\sim \)2 orders of magnitude and the proposed methods outperform state-of-the-art baselines.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
The data in this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Chernyshenko AY, Olshanskii MA (2015) An adaptive octree finite element method for PDEs posed on surfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 291:146–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2015.03.025
Strikwerda JC (1984) Finite difference methods for the stokes and navier-stokes equations. SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 5(1):56–68. https://doi.org/10.1137/0905004
Javidi M (2006) A numerical solution of the generalized burger’s-huxley equation by spectral collocation method. Appl Math Comput 178(2):338–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.11.051
Darbon J, Osher S (2016) Algorithms for overcoming the curse of dimensionality for certain hamilton-jacobi equations arising in control theory and elsewhere. Res Math Sci 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40687-016-0068-7
Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis GE (2019) Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 378:686–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045
Zhang D, Guo L, Karniadakis GE (2020) Learning in modal space: Solving time-dependent stochastic pdes using physics-informed neural networks. SIAM J Sci Comput 42(2):639–665. https://doi.org/10.1137/19m1260141
Pang G, Lu L, Karniadakis GE (2019) fPinns: Fractional physics-informed neural networks. SIAM J Sci Comput 41(4):2603–2626. https://doi.org/10.1137/18m1229845
Jin X, Cai S, Li H, Karniadakis GE (2021) Nsfnets (navier-stokes flow nets): Physics-informed neural networks for the incompressible navier-stokes equations. J Comput Phys 426:109951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109951
Raissi M, Yazdani A, Karniadakis GE (2020) Hidden fluid mechanics: Learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations. Science 367(6481):1026–1030. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw4741
Yin M, Zheng X, Humphrey JD, Karniadakis GE (2021) Non-invasive inference of thrombus material properties with physics-informed neural networks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 375:113603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113603
Chen Y, Lu L, Karniadakis GE, Dal Negro L (2020) Physics-informed neural networks for inverse problems in nano-optics and metamaterials. Opt Express 28(8):11618. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.384875
Sahli Costabal F, Yang Y, Perdikaris P, Hurtado DE, Kuhl E (2020) Physics-informed neural networks for cardiac activation mapping. Front Phys 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2020.00042
Olivares E, Ye H, Herrero A, Nia BA, Ren Y, Donovan RP, Flaviis F (2021) Applications of information channels to physics-informed neural networks for wifi signal propagation simulation at the edge of the industrial internet of things. Neurocomputing 454:405–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.021
Wu C, Zhu M, Tan Q, Kartha Y, Lu L (2023) A comprehensive study of non-adaptive and residual-based adaptive sampling for physics-informed neural networks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 403:115671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2022.115671
Zeng S, Zhang Z, Zou Q (2022) Adaptive deep neural networks methods for high-dimensional partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 463:111232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111232
Yu J, Lu L, Meng X, Karniadakis GE (2022) Gradient-enhanced physics-informed neural networks for forward and inverse pde problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 393:114823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2022.114823
Buzaev F, Gao J, Chuprov I, Kazakov E (2023) Hybrid acceleration techniques for the physics-informed neural networks: a comparative analysis. Mach Learn 113(6):3675–3692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-023-06442-6
Lu L, Meng X, Mao Z, Karniadakis GE (2021) DeepXDE: A deep learning library for solving differential equations. SIAM Rev 63(1):208–228. https://doi.org/10.1137/19m1274067
Nabian MA, Gladstone RJ, Meidani H (2021) Efficient training of physics-informed neural networks via importance sampling. Comput-Aid Civil Infr Eng 36(8):962–977. https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12685
Hao Z, Yao J, Su C, Su H, Wang Z, Lu F, Xia Z, Zhang Y, Liu S, Lu L, Zhu J (2023) PINNacle: A comprehensive benchmark of physics-informed neural networks for solving PDEs
Hanna JM, Aguado JV, Comas-Cardona S, Askri R, Borzacchiello D (2022) Residual-based adaptivity for two-phase flow simulation in porous media using physics-informed neural networks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 396:115100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2022.115100
Tang K, Wan X, Yang C (2023) DAS-PINNs: a deep adaptive sampling method for solving high-dimensional partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 476:111868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111868
Daw A, Bu J, Wang S, Perdikaris P, Karpatne A (2023) Mitigating propagation failures in physics-informed neural networks using retain-resample-release (R3) sampling. In: Proceedings of the 40th international conference on machine learning, vol. 202. pp 7264–7302. https://proceedings.mlr.press/v202/daw23a.html
Jiao Y, Li D, Lu X, Yang JZ, Yuan C (2024) A Gaussian mixture distribution-based adaptive sampling method for physics-informed neural networks. Eng Appl Artif Intell 135:108770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2024.108770
Lau GKR, Hemachandra A, Ng S-K, Low BKH (2024) PINNACLE: PINN adaptive collocation and experimental points selection. In: The twelfth international conference on learning representations
Tang K, Zhai J, Wan X, Yang C (2024) Adversarial adaptive sampling: Unify PINN and optimal transport for the approximation of PDEs. In: The twelfth international conference on learning representations. https://openreview.net/forum?id=7QI7tVrh2c
Zhang Z, Li J, Liu B (2024) Annealed adaptive importance sampling method in PINNs for solving high dimensional partial differential equations. arXiv:2405.03433. [math.NA]
Yang Z, Qiu Z, Fu D (2023) DMIS: dynamic mesh-based importance sampling for training physics-informed neural networks. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 37(4):5375–5383. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v37i4.25669
Wang S, Teng Y, Perdikaris P (2021) Understanding and mitigating gradient flow pathologies in physics-informed neural networks. SIAM J Sci Comput 43(5):3055–3081. https://doi.org/10.1137/20m1318043
Wang S, Yu X, Perdikaris P (2022) When and why pinns fail to train: a neural tangent kernel perspective. J Comput Phys 449:110768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110768
Xiang Z, Peng W, Liu X, Yao W (2022) Self-adaptive loss balanced physics-informed neural networks. Neurocomputing 496:11–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.05.015
Lu L, Pestourie R, Yao W, Wang Z, Verdugo F, Johnson SG (2021) Physics-informed neural networks with hard constraints for inverse design. SIAM J Sci Comput 43(6):1105–1132. https://doi.org/10.1137/21m1397908
Gu Y, Yang H, Zhou C (2021) SelectNet: self-paced learning for high-dimensional partial differential equations. J Comput Phys 441:110444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110444
Li W, Zhang C, Wang C, Guan H, Tao D (2022) Revisiting PINNs: generative adversarial physics-informed neural networks and point-weighting method. arXiv:2205.08754. [cs.LG]
McClenny LD, Braga-Neto UM (2023) Self-adaptive physics-informed neural networks. J Comput Phys 474:111722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111722
Song Y, Wang H, Yang H, Taccari ML, Chen X (2024) Loss-attentional physics-informed neural networks. J Comput Phys 501:112781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2024.112781
Psaros AF, Kawaguchi K, Karniadakis GE (2022) Meta-learning pinn loss functions. J Comput Phys 458:111121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111121
Gao H, Sun L, Wang J-X (2021) Phygeonet: physics-informed geometry-adaptive convolutional neural networks for solving parameterized steady-state pdes on irregular domain. J Comput Phys 428:110079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.110079
Ren P, Rao C, Liu Y, Wang J-X, Sun H (2022) Phycrnet: Physics-informed convolutional-recurrent network for solving spatiotemporal pdes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 389:114399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.114399
Kumar R (2022) A Lyapunov-stability-based context-layered recurrent pi-sigma neural network for the identification of nonlinear systems. Appl Soft Comput 122:108836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108836
Kumar R (2023) Memory recurrent Elman neural network-based identification of time-delayed nonlinear dynamical system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 53(2):753–762. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2022.3186610
Kumar R (2023) Double internal loop higher-order recurrent neural network-based adaptive control of the nonlinear dynamical system. Soft Comput 27(22):17313–17331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08061-8
Kumar R (2024) Recurrent context layered radial basis function neural network for the identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Neurocomputing 580:127524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127524
Guan W, Yang K, Chen Y, Liao S, Guan Z (2023) A dimension-augmented physics-informed neural network (dapinn) with high level accuracy and efficiency. J Comput Phys 491:112360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112360
Wang S, Wang H, Perdikaris P (2021) On the eigenvector bias of Fourier feature networks: From regression to solving multi-scale pdes with physics-informed neural networks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 384:113938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.113938
Li X, Wu J, Tai X, Xu J, Wang Y-G (2024) Solving a class of multi-scale elliptic PDEs by Fourier-based mixed physics informed neural networks. J Comput Phys 508:113012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2024.113012
Jagtap AD, Kharazmi E, Karniadakis GE (2020) Conservative physics-informed neural networks on discrete domains for conservation laws: Applications to forward and inverse problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 365:113028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113028
Shukla K, Jagtap AD, Karniadakis GE (2021) Parallel physics-informed neural networks via domain decomposition. J Comput Phys 447:110683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110683
Wu W, Feng X, Xu H (2022) Improved deep neural networks with domain decomposition in solving partial differential equations. J Sci Comput 93(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-022-01980-y
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980
Zhu C, Byrd RH, Lu P, Nocedal J (1997) Algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B: Fortran subroutines for large-scale bound-constrained optimization. ACM Trans Math Softw 23(4):550–560. https://doi.org/10.1145/279232.279236
Mckay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ (2000) A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 42(1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.2000.10485979
Stein M (1987) Large sample properties of simulations using latin hypercube sampling. Technometrics 29(2):143–151. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1987.10488205
Möller M, Kuzmin D (2006) Adaptive mesh refinement for high-resolution finite element schemes. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 52(5):545–569. https://doi.org/10.1002/fld.1183
Mildenhall B, Srinivasan P, Tancik M, Barron J, Ramamoorthi R, Ng R (2020) Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. In: European conference on computer vision. pp 405–421
Tancik M, Srinivasan P, Mildenhall B, Fridovich-Keil S, Raghavan N, Singhal U, Ramamoorthi R, Barron J, Ng R (2020) Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33:7537–7547
Acknowledgements
The work in this paper is partially supported by Guangdong Innovation and Entrepreneurship Team Project under Grant 2021ZT09X070, Guangdong Zhujiang Leadership Project under Grant 2021CX02X011, and Chinese Huoju Talents Project under Grant 2023HJJH01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Liao, S., Guan, Z. et al. An enhanced hybrid adaptive physics-informed neural network for forward and inverse PDE problems. Appl Intell 55, 255 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06195-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-06195-2