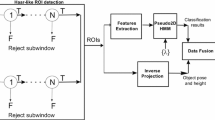
Abstract
This paper describes a method for spatial representation, place recognition and qualitative self-localization in dynamic indoor environments, based on omnidirectional images. This is a difficult problem because of the perceptual ambiguity of the acquired images, and their weak robustness to noise, geometrical and photometric variations of real world scenes. The spatial representation is built up invariant signatures using Invariance Theory where we suggest to adapt Haar invariant integrals to the particular geometry and image transformations of catadioptric omnidirectional sensors. It follows that combining simple image features in a process of integration over visual transformations and robot motion, can build discriminant percepts about robot spatial locations. We further analyze the invariance properties of the signatures and the apparent relation between their similarity measures and metric distances. The invariance properties of the signatures can be adapted to infer a hierarchical process, from global room recognition to local and coarse robot localization.
The approach is validated in real world experiments and compared to some local and global state-of-the-art methods. The results demonstrate a very interesting performance of the proposed approach and show distinctive behaviors of global and local methods. The invariant signature method, while being very time and memory efficient, provides good separability results similarly to approaches based on local features.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Andreasson, H., Treptow, A., & Duckett, T. (2005). Localization for mobile robots using panoramic vision, local features and particle filter. In IEEE int. conf. on robotics and automation (pp. 3348–3353).
Bogdanova, I., Vandergheynst, P., Antoine, J., Jacques, L., & Morvidone, M. (2005). Stereographic wavelet frames on the sphere. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 19(2), 223–252.
Burkhardt, H., & Siggelkow, S. (2001). Invariant features in pattern recognition—fundamentals and applications. In C. Kotropoulos & I. Pitas (Eds.), Nonlinear model-based image/video processing and analysis (pp. 269–307). Wiley: New York.
Charron, C. (2007). Constitution active de percepts spatiaux, application à la reconnaissance de lieux. Ph.D. thesis, Université de Picardie Jules Verne.
Charron, C., Labbani-Igibida, O., & Mouaddib, E. (2005). Qualitative localization using omnidirectional images and invariant features. In IEEE/RSJ int. conf. on intelligent robots and systems, Edmonton, Canada (pp. 3009–3014).
Charron, C., Labbani-Igbida, O., & Mouaddib, E. (2006). On building omnidirectional image signatures using Haar invariant features: application to the localization of robots. In Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 3179. Advanced concepts for intelligent vision systems, Antwerp, Belgium (pp. 1099–1110). Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer.
Gaspar, J., Winters, N., & Santos-Victor, J. (2000). Vision-based navigation and environmental representations with an omnidirectional camera. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation 16, 890–898.
Geyer, C., & Daniilidis, K. (2001). Catadioptric projective geometry. International Journal of Computer Vision, 45(3), 223–243.
Gonzalez, J., & Lacroix, S. (2002). Rover localization in natural environments by indexing panoramic images. In IEEE int. conf. on robotics and automation (pp. 1365–1370).
Halawani, A., & Burkhardt, H. (2004). Image retrieval by local evaluation of nonlinear kernel functions around salient points. In Int. conf. on pattern recognition (Vol. 2, pp. 955–960).
Halawani, A., & Burkhardt, H. (2005). On using histograms of local invariant features for image retrieval. In IAPR workshop on machine vision applications (pp. 538–541).
Ishiguro, H., & Tsuji, S. (1996). Image-based memory of environment. In IEEE/RSJ int. conf. on intelligent robots and systems (Vol. 2, pp. 634–639).
Ishikawa, M., Kawashima, S., & Homma, N. (1998). Memory-based location estimation and navigation using Bayesian estimation. In Int. conf. on neural information processing (Vol. 1, pp. 112–117). 1998.
Jogan, M., & Leonardis, A. (2003). Robust localization using an omnidirectional appearance-based subspace model of environment. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 45(1), 51–72.
Labbani-Igbida, O., Charron, C., & Mouaddib, E. (2006). Extraction of Haar integral features on omnidirectional images: supplication to local and global localization. In Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 4174. Pattern Recognition, Berlin, Germany (pp. 334–343). Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer.
Leonardis, A., & Bischof, H. (2000). Robust recognition using eigenimages. Computer Vision and Image Understanding Special Issue on Robust Statistical Techniques in Image Understanding, 78(1), 99–118.
Leprêtre, S., Gaussier, P., & Cocquerez, J. P. (2000). From navigation to object recognition. In Int. conf. on simulation of adaptive behavior, Paris, France.
Lindeberg, T. (1994). Scale-space theory: A basic tool for analysing structures at different scales. Journal of Applied Statistics, 21(2), 224–270.
Lowe, D. (1999). Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Int. conf. on computer vision (pp. 1150–1157).
Lowe, D. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 91–110.
Maeda, S., Kuno, Y., & Shirai, Y. (1997). Active navigation vision based on eigenspace analysis. In Int. conf. on intelligent robots and systems, IEEE/RSJ, Grenoble, France (pp. 1018–1023). 1997.
Menegatti, E., Maeda, T., & Ishiguro, H. (2004a). Image-based memory for robot navigation using properties of the omnidirectional images. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 47(4), 251–267.
Menegatti, E., Zoccarato, M., Pagello, E., & Ishiguro, H. (2004b). Image-based Monte-Carlo localisation with omnidirectional images. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 48(1), 17–30.
Murillo, A., Sagues, C., Guerrero, J., Goedeme, T., Tuytelaars, T., & Gool, L.V. (2007). From omnidirectional images to hierarchical localization. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 55(5), 372–382.
Murillo, A., Campos, P., Kosecka, J., & Guerrero, J. (2010). Gist vocabularies in omnidirectional images for appearance based mapping and localization. In 10th IEEE workshop on omnidirectional vision, camera networks and non-classical cameras, (OMNIVIS), held with robotics, science and systems.
Pajdla, T., & Hlavac, V. (1999). Zero phase representation of panoramic images for image based localization. In F. Solina, & A. Leonardis (Eds.), Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 1689. 8-th int. conf. on computer analysis of images and patterns, Ljubljana, Slovenia (pp. 550–557). Berlin: Springer.
Puzicha, J., Buhmann, J., Rubner, Y., & Tomasi, C. (1999). Empirical evaluation of dissimilarity measures for color and texture. In IEEE int. conf. on computer vision (pp. 1165–1172).
Ramisa, A., de Mantaras, R. L., Aldavert, D., & Toledo, R. (2007). Comparing combinations of feature regions for panoramic vslam. In 4th int. conf. on informatics in control, automation and robotics, Angers, France (pp. 292–297).
Ramisa, A., Tapus, A., de Mantaras, R. L., & Toledo, R. (2008). Mobile robot localization using panoramic vision and combination of local feature region detectors. In IEEE int. conf. on robotics and automation, Pasadena, California (pp. 538–543).
Rubinstein-Salzedo, S. (2004). On the existence and uniqueness of invariant measures on locally compact groups (Expository paper). Berkeley: University of California.
Scaramuzza, D., Criblez, N., Martinelli, A., & Siegwart, R. (2008). Field and service robotics, robust feature extraction and matching for omnidirectional images. Springer tracts in advanced robotics (Vol. 42, pp. 71–81). Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer.
Schulz-Mirbach, H., Burkhardt, H., & Sigglekow, S. (1996). Using invariant features for content based data retrieval. In First NOBLESSE workshop on nonlinear methods in model-based image interpretation, Lausanne, Switzerland
Sigglekow, S. (2002). Feature histograms for content-based image retrieval. Ph.D. thesis, Universität Freiburg im Breusgau.
Tamimi, H., Andreasson, H., Treptow, A., Duckett, T., & Zell, A. (2005). Localization of mobile robots with omnidirectional vision using particle filter and iterative sift. In European conf. on mobile robots, Ancona, Italy
Tapus, A., & Siegwart, R. (2006). A cognitive modeling of space using fingerprints of places for mobile robot navigation. In IEEE int. conf. on robotics and automation, Orlando, USA (pp. 1188–1193).
Ulrich, I., & Nourbakhsh, I. (2000). Appearance-based place recognition for topological localization. In Int. conf. on robotics and automation, San Francisco, CA (pp. 1023–1029). New York: IEEE Press.
Vasudevan, S., Gachter, S., & Nguyen, V. Siegwart, R. (2007). Cognitive maps for mobile robots—an object based approach. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 55(5), 359–371.
Weil, A. (1979). L’intégration dans les groupes topologiques et ses applications. Paris: Hermann.
Wolf, J., Burgard, W., & Burkhardt, H. (2002). Using an image retrieval system for vision-based mobile robot localization. In M. Lew, N. Sebe, & J. Eakins (Eds.), Int. conf. on image and video retrieval (CIVR) (pp. 108–119). Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer.
Wolf, J., Burgard, W., & Burkhardt, H. (2005). Robust vision-based localization by combining an image retrieval system with Monte Carlo localization. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 21(2), 208–216.
Zivkovic, Z., Booij, O., & Kröse, B. (2007). From images to rooms. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 55(5), 411–418.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Region of Picardie under the DIVA program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labbani-Igbida, O., Charron, C. & Mouaddib, E.M. Haar invariant signatures and spatial recognition using omnidirectional visual information only. Auton Robot 30, 333–349 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-011-9222-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-011-9222-7