Abstract
This paper presents a novel approach to address the challenge of planning paths for multi-agent systems subject to complex constraints. The technique, called the Decentralized Multi-Agent Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (DMA-RRT) algorithm, extends the Closed-loop RRT (CL-RRT) algorithm to handle multiple agents while retaining its ability to plan quickly. A core component of the DMA-RRT algorithm is a merit-based token passing coordination strategy that makes use of the tree of feasible trajectories grown in the CL-RRT algorithm to dynamically update the order in which agents replan. The reordering is based on a measure of each agent’s incentive to change the plan and allows agents with a greater potential improvement to replan sooner, which is demonstrated to improve the team’s overall performance compared to a traditional, scripted replan order. The main contribution of the work is a version of the algorithm, called Cooperative DMA-RRT, which introduces a cooperation strategy that allows an agent to modify its teammates’ plans in order to select paths that reduce their combined cost. This modification further improves team performance and avoids certain common deadlock scenarios. The paths generated by both algorithms are proven to satisfy inter-agent constraints, such as collision avoidance, and numerous simulation and experimental results are presented to demonstrate their performance.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
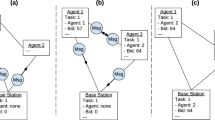
The arrow is cyan in this case since one of the other agents has the token. If agent 1 were the current token holder, its arrow would be green instead.
References
Amir, Y., Moser, L., Melliar-Smith, P., Agarwal, D., & Ciarfella, P. (1993). Fast message ordering and membership using a logical token-passing ring. In Proceedings the 13th international conference on distributed computing systems (pp. 551–560). New York: IEEE Press.
Aoude, G. S., Luders, B. D., Levine, D. S., & How, J. P. (2010). Threat-aware path planning in uncertain urban environments. In IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), Taipei, Taiwan (pp. 6058–6063).
Ayanian, N., & Kumar, V. (2010). Decentralized feedback controllers for multiagent teams in environments with obstacles. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 26(5), 878–887.
Azarm, K., & Schmidt, G. (1997). Conflict-free motion of multiple mobile robots based on decentralized motion planning and negotiation. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (Vol. 4, pp. 3526–3533).
Banerjee, S., & Chrysanthis, P. (1996). A new token passing distributed mutual exclusion algorithm. In Proceedings of the 16th international conference on distributed computing systems (pp. 717–724). New York: IEEE Press.
Barraquand, J., Langlois, B., & Latombe, J. C. (1992). Numerical potential field techniques for robot path planning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 22(2), 224–241.
Basar, T. (1988). Asynchronous algorithms in non-cooperative games. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 12(1), 167–172.
Bertsekas, D., & Gallager, R. (1992). Data networks. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Chun, L., Zheng, Z., & Chang, W. (1999). A decentralized approach to the conflict-free motion planning for multiple mobile robots. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (Vol. 2, pp. 1544–1549).
Desaraju, V., Ro, H. C., Yang, M., Tay, E., Roth, S., & Del Vecchio, D. (2009). Partial order techniques for vehicle collision avoidance: application to an autonomous roundabout test-bed. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) (pp. 82–87).
Dunbar, W., & Murray, R. (2006). Distributed receding horizon control for multi-vehicle formation stabilization. Automatica, 42(4), 549–558.
Erdmann, M., & Lozano-Pérez, T. (1987). On multiple moving objects. Algorithmica, 2, 477–521.
Frazzoli, E., Dahleh, M. A., & Feron, E. (2002). Real-time motion planning for agile autonomous vehicles. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 25(1), 116–129.
Hoffmann, G., & Tomlin, C. (2008). Decentralized cooperative collision avoidance for acceleration constrained vehicles. In IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC) (pp. 4357–4363).
How, J. P., Bethke, B., Frank, A., Dale, D., & Vian, J. (2008). Real-time indoor autonomous vehicle test environment. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 28(2), 51–64.
Inalhan, G., Stipanovic, D., & Tomlin, C. (2002). Decentralized optimization, with application to multiple aircraft coordination. In IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC), Las Vegas, NV.
Jager, M., & Nebel, B. (2001). Decentralized collision avoidance, deadlock detection, and deadlock resolution for multiple mobile robots. In IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) (Vol. 3, pp. 1213–1219).
Johnson, E., Tang, Z., Balakrishnan, M., Rubio, J., Zhang, H., & Sreepuram, S. (2003). Robust token management for unreliable networks. In Military communications conference. MILCOM 2003 (Vol. 1, pp. 399–404). New York: IEEE Press.
Karaman, S., & Frazzoli, E. (2010). Incremental sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning. In Robotics: science and systems (RSS).
Karaman, S., Walter, M., Perez, A., Frazzoli, E., & Teller, S. (2011). Anytime motion planning using the rrt*. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, institute of electrical and electronics engineers.
Kavraki, L. E., Svestka, P., Latombe, J. C., & Overmars, M. H. (1996). Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 12(4), 566–580.
Keviczky, T., Borrelli, F., & Balas, G. J. (2004). A study on decentralized receding horizon control for decoupled systems. In American control conference (ACC), Boston, MA (pp. 4921–4926).
Khatib, O. (1985). Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (Vol. 2, pp. 500–505).
Kim, J., & Kim, C. (1997). A total ordering protocol using a dynamic token-passing scheme. Distributed Systems Engineering, 4, 87.
Koenig, S., & Likhachev, M. (2002). D ∗ lite. In Proceedings AAAI national conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 476–483).
Koenig, S., Likhachev, M., & Furcy, D. (2004). Lifelong planning A*. Artificial Intelligence, 155(1–2), 93–146.
Koren, Y., & Borenstein, J. (1991). Potential field methods and their inherent limitations for mobile robot navigation. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (pp. 1398–1404).
Kuwata, Y., & How, J. P. (2011). Cooperative distributed robust trajectory optimization using receding horizon MILP. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 19(2), 423–431.
Kuwata, Y., Richards, A., Schouwenaars, T., & How, J. P. (2007). Distributed robust receding horizon control for multivehicle guidance. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 15(4), 627–641.
Kuwata, Y., Teo, J., Karaman, S., Fiore, G., Frazzoli, E., & How, J. P. (2008). Motion planning in complex environments using closed-loop prediction. In AIAA guidance, navigation, and control conference (GNC) (AIAA-2008-7166), Honolulu, HI.
Kuwata, Y., Teo, J., Fiore, G., Karaman, S., Frazzoli, E., & How, J. P. (2009). Real-time motion planning with applications to autonomous urban driving. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 17(5), 1105–1118.
LaValle, S. M. (1998). Rapidly-exploring random trees: a new tool for path planning (Tech. Rep. 98–11). Iowa State University.
LaValle, S. M. (2006). Planning algorithms. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lee, J., Nam, H., & Lyou, J. (1995). A practical collision-free trajectory planning for two robot systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (Vol. 3, pp. 2439–2444). New York: IEEE Press.
Leonard, N., Paley, D., Lekien, F., Sepulchre, R., Fratantoni, D., & Davis, R. (2007). Collective motion, sensor networks, and ocean sampling. Proceedings of the IEEE, 95(1), 48–74.
Leonard, J., How, J. P., Teller, S., Berger, M., Campbell, S., Fiore, G., Fletcher, L., Frazzoli, E., Huang, A., Karaman, S., Koch, O., Kuwata, Y., Moore, D., Olson, E., Peters, S., Teo, J., Truax, R., Walter, M., Barrett, D., Epstein, A., Maheloni, K., Moyer, K., Jones, T., Buckley, R., Antone, M., Galejs, R., Krishnamurthy, S., & Williams, J. (2008). A perception-driven autonomous urban vehicle. Journal of Field Robotics, 25(10), 727–774.
Likhachev, M., & Stentz, A. (2008). R* search. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 344–350).
Luders, B., Karaman, S., Frazzoli, E., & How, J. P. (2010). Bounds on track error using closed-loop rapidly-exploring random trees. In American control conference (ACC), Baltimore (pp. 5406–5412).
Mueller, F. (2001). Fault tolerance for token-based synchronization protocols. In Proceedings 15th international parallel and distributed processing symposium (pp. 1257–1264). New York: IEEE Press.
Murray, R. (2007). Recent research in cooperative control of multi-vehicle systems. ASME Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 129(5), 571–583.
Narváez, P., Siu, K., & Tzeng, H. (2000). New dynamic algorithms for shortest path tree computation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 8(6), 734–746.
Olfati-Saber, R., Fax, J., & Murray, R. (2007). Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 95(1), 215–233.
Pallottino, L., Scordio, V., & Bicchi, A. (2004). Decentralized cooperative conflict resolution among multiple autonomous mobile agents. In IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC) (Vol. 5, pp. 4758–4763).
Parker, L. (2002). Distributed algorithms for multi-robot observation of multiple moving targets. Autonomous Robots, 12(3), 231–255.
Purwin, O., D’Andrea, R., & Lee, J. (2008). Theory and implementation of path planning by negotiation for decentralized agents. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 56(5), 422–436.
Richards, A. G. (2005). Robust constrained model predictive control. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Cambridge, MA.
Richards, A., Schouwenaars, T., How, J. P., & Feron, E. (2002). Spacecraft trajectory planning with avoidance constraints using mixed-integer linear programming. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 25(4), 755–764.
Sae-Hau, C. (2003). Multi-vehicle rover testbed using a new indoor positioning sensor. S.M. thesis draft, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Scerri, P., Owens, S., Yu, B., & Sycara, K. (2007). A decentralized approach to space deconfliction. In Proc. 10th int. information fusion conf. (pp. 1–8).
Schouwenaars, T., How, J., & Feron, E. (2004). Decentralized cooperative trajectory planning of multiple aircraft with hard safety guarantees. In AIAA guidance, navigation, and control conference (GNC), Providence, RI.
Si, J. (2004). Handbook of learning and approximate dynamic programming (Vol. 2). New York: Wiley–IEEE Press.
Swigart, J., & Lall, S. (2010). An explicit dynamic programming solution for a decentralized two-player optimal linear-quadratic regulator. In Proceedings of mathematical theory of networks and systems.
Tanner, H., Loizou, S., & Kyriakopoulos, K. (2001). Nonholonomic stabilization with collision avoidance for mobile robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (Vol. 3, pp. 1220–1225). New York: IEEE Press.
Teller, S., Walter, M. R., Antone, M., Correa, A., Davis, R., Fletcher, L., Frazzoli, E., Glass, J., How, J. P., Huang, A. S., Jeon, J., Karaman, S., Luders, B., Roy, N., & Sainath, T. (2010). A voice-commanded robotic forklift working alongside humans in minimally-prepared outdoor environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Anchorage, AK.
Trodden, P. (2009). Robust distributed control of constrained linear systems. Ph.D. thesis, University of Bristol.
Trodden, P., & Richards, A. (2006). Robust distributed model predictive control using tubes. In Proceedings of the American control conference, Minneapolis, MN (pp. 2034–2039).
van den Berg, J., Snoeyink, J., Lin, M., & Manocha, D. (2009). Centralized path planning for multiple robots: optimal decoupling into sequential plans. In Proceedings of robotics: science and systems, Seattle, USA.
Velagapudi, P., Sycara, K., & Scerri, P. (2010). Decentralized prioritized planning in large multirobot teams. In IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) (pp. 4603–4609).
Venkat, A. N., Rawlings, J. B., & Wright, S. J. (2005). Stability and optimality of distributed model predictive control. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on decision and control, Seville, Spain (pp. 6680–6685).
Wang, P., & Zhuang, W. (2008). A token-based scheduling scheme for wlans supporting voice/data traffic and its performance analysis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(5), 1708–1718.
Yershova, A., Jaillet, L., Siméon, T., & LaValle, S. M. (2005). Dynamic-domain RRTs: Efficient exploration by controlling the sampling domain. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Barcelona, Spain (pp. 3856–3861).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Brandon Luders and Georges Aoude for their contributions to this research effort. Research funded in part by the Office of Secretary of Defense under Air Force Contract FA8721-05-C-0002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desaraju, V.R., How, J.P. Decentralized path planning for multi-agent teams with complex constraints. Auton Robot 32, 385–403 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-012-9275-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-012-9275-2