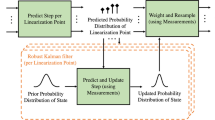
Abstract
The extended Kalman filter (EKF) simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) requires the uncertainty to be Gaussian noise. This assumption can be relaxed to bounded noise by the set membership SLAM. However, the published set membership SLAMs are not suitable for large-scale and online problems. In this paper, we use ellipsoid algorithm for solving SLAM problem. The proposed ellipsoid SLAM has advantages over EKF SLAM and the other set membership SLAMs, in noise condition, online realization, and large-scale problem. By bounded ellipsoid technique, we analyze the convergence and stability of the ellipsoid SLAM. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed ellipsoid SLAM is effective for online and large-scale problems such as Victoria Park dataset.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borenstein, J., Everett, H. R., & Feng, L. (1997). Mobile robot positioning: sensors and techniques. Journal of Robotic Systems, 14(4), 231–249.
Correa, M. V., Aguirre, L. A., & Saldanha, R. R. (2002). Using steady-state prior knowledge to constrain parameter estimates in nonlinear system identification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, Part I, 49(9), 1376–1381.
Di Marco, M., Garulli, A., Giannitrapani, A., & Vicino, A. (2004). A set theoretic approach to dynamic robot localization and mapping. Autonomous Robots, 16(1), 23–47.
Dissanayake, G., Newman, P., Clark, S., Durrant-Whyte, H., & Csorba, M. (2001). A solution to the simultaneous localization and map building (SLAM) problem. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(3), 229–241.
Dissanayake, G., Williams, S. B., Durrant-Whyte, H., & Bailey, T. (2002). Map management for efficient simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). Autonomous Robots, 12(3), 267–286.
Fogel, E., & Huang, Y. F. (1982). On the value of information in system identification: Bounded noise case. Automatica, 18(2), 229–238.
Folkesson, J., & Christensen, H. (2007). Closing the loop with graphical SLAM. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 23(4), 731–741.
Garulli, A., & Vicino, A. (2001). Set membership localization of mobile robots via angle measurements. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(4), 450–463.
Goodwin, G. C., & Sang Sin, K. (1984). Adaptive filtering prediction and control. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Guivant, J. E., & Nebot, E. M. (2001). Optimization of the simultaneous localization and map-building algorithm for real-time implementation. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(3), 242–257.
Ho, K. L., & Newman, P. (2006). Loop closure detection in SLAM by combining visual and spatial appearance. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 54(9), 740–749.
Jaulin, L. (2009). A nonlinear set membership approach for the localization and map building of underwater robots. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 25(1), 88–98.
Jaulin, L. (2011). Range-only SLAM with occupancy maps: a set-membership approach. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 27(5), 1004–1010.
Kaess, M., Johannsson, H., Roberts, R., Ila, V., Leonard, J., & Dellaert, F. (2012). iSAM2: Incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree. International Journal of Robotics Research, 31, 216–235.
K-Team Corporation. (2013). http://www.k-team.com/contact-k-team.
Lorenz, R. G., & Boyd, S. P. (2005). Robust minimum variance beam-forming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 53(5), 1684–1696.
Maksarov, D. G., & Norton, J. P. (1996). State bounding with ellipsoidal set description of the uncertainty. International Journal of Control, 65(5), 847–866.
Montemerlo, M., & Thrun, S. (2007). FastSLAM, a scalable method for the simultaneous localization and mapping problem in robotics. Springer tracts in advanced robotics. New York: Springer.
Mullane, J., Ba-Ngu Vo, Adams, M., & Ba-Tuong Vo, (2011). A random-finite-set approach to Bayesian SLAM. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 27(2), 268–282.
Natural Point Inc. (2013). http://www.naturalpoint.com/optitrack/.
Nazin, S.A. & Polyak, B.T. (2001). Limiting behavior of bounding ellipsoid for state estimation. Proceedings of the 5th IFAC symposium on nonlinear control systems. St.Petersburg, 585–589.
Neira, J., & Tardos, J. D. (2001). Data association in stochastic mapping using the joint compatibility test. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(6), 890–897.
Nieto, J., Guivant, J., & Nebot, E. (2006). DenseSLAM: simultaneous localization and dense mapping. International Journal of Robotics Research, 25, 711–744.
Ros, L., Sabater, A., & Thomas, F. (2002). An ellipsoid calculus based on propagation and fusion. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 32(4), 430–442.
Scholte, E., & Campbell, M. E. (2003). A nonlinear set-membership filter for online applications. International Journal of Robust Nonlinear Control, 13, 1337–1358.
Schweppe, F. C. (1968). Recursive state estimation: Unknown but bounded errors and system inputs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 13(1), 22–28.
Schweppe, F. C. (1973). Uncertain dynamic systems. Englewood cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Schweppe, F. C. (1973). Uncertain dynamic systems. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Sibley, G., Matthies, L., & Sukhatme, G. (2010). Sliding window filter with application to planetary landing. Journal of Field Robotics, 27(5), 587–608.
Thrun, S., Liu, Y., Koller, D., Ng, A. Y., Ghahramani, Z., & Durrant-Whyte, H. (2004). Simultaneous localization and mapping with sparse extended information filters. International Journal of Robotics Research, 23, 693–716.
Wang, Z., Huang, S., & Dissanayake, G. (2007). D-SLAM: A decoupled solution to simultaneous localization and mapping. International Journal of Robotics Research, 26(2), 187–204.
Weyer, E., & Campi, M.C. (2000). Non-asymptotic confidence ellipsoids for the least squares estimate, 39rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Sydney, 2688–2693.
Williams, S.B. (2001). “Efficient solutions to autonomous mapping and navigation problems”, PhD Thesis, The University of Sidney.
Yu, W., & de Jesus Rubio, J. (2009). Recurrent neural networks training with stable bounding ellipsoid algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 20(6), 983–991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W., Zamora, E. & Soria, A. Ellipsoid SLAM: a novel set membership method for simultaneous localization and mapping. Auton Robot 40, 125–137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-015-9447-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-015-9447-y