Abstract
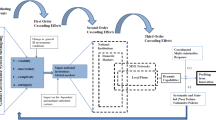
Based on network embedding, enterprise technology innovation and knowledge management theories, the study has built theoretical conceptual model of multiple network embedding influencing enterprises’ technological innovation performance from the perspective of knowledge management. The work discussed the internal mechanism of knowledge management activities affected by embedded relationship, embedded structure and embedded resource influencing technological innovation performance. Through obtaining 190 SME’s survey data in the Yangtze River Delta region, we systematically validated the conceptual model with the structural equation model. It showed that embedded relationship, embedded structure and embedded resource in enterprise organization network can effectively improve the enterprise’s knowledge management capability, bringing significant promotion in technological innovation performance. Wherein, the embedded relationship and embedded resource can promote not only the technological innovation performance of the enterprise, but also the performance by improving the knowledge management ability of the enterprise. While, the promotion effect of embedded structure to enterprises’ technological innovation majorly relies on the fully-mediated knowledge management to achieve.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Laham, A., Souitaris, V.: Network embeddedness and new-venture internationalization: analyzing international linkages in the German biotech industry. J. Bus. Ventur. 23(5), 567–586 (2008)
Andersson, U., Forsgren, M., Holm, U.: The strategic impact of external networks: subsidiary performance and competence development in the multinational corporation. Strateg. Manag. J. 23(11), 979–996 (2002)
Balland, E., Dam, J., Langlet, F., Caron, E., Steculorum, S., Messina, A., Trinquet, E.: Hypothalamic tanycytes are an ERK-gated conduit for leptin into the brain. Cell Metab. 19(2), 293–301 (2014)
Balland, P.-A., Belso-Martínez, J.A., Morrison, A.: The dynamics of technical and business knowledge networks in industrial clusters: embeddedness, status, or proximity? Econ. Geogr. 92(1), 35–60 (2016)
Barney, B.: Introduction to parallel computing. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 10:6(13) (2010)
Barney, J.B.: Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Adv. Strateg. Manag. 17, 203–227 (2000)
Capaldo, A.: Network structure and innovation: the leveraging of a dual network as a distinctive relational capability. Strateg. Manag. J. 28(4), 585–608 (2007a)
Capaldo, A.: Network structure and innovation: the leveraging of a dual network as a distinctive relational capability. Strateg. Manag. J. 28(6), 585–608 (2007b)
Clifton, N., Keast, R., Pickernell, D., Senior, M.: Network structure, knowledge governance, and firm performance: evidence from innovation networks and SMEs in the UK. Growth Change 41(3), 337–373 (2010)
Coleman, J.S.: Social capital in the creation of human capital. Am. J. Sociol. 94(1), 95–120 (2008)
Echols, A., Tsai, W.: Niche and performance: the moderating role of network embeddedness. Strateg. Manag. J. 26(3), 219–238 (2005)
Fukugawa, N.: Determining factors in innovation of small firm networks: a case of cross industry groups in Japan. Small Bus. Econ. 27(2–3), 181–193 (2006)
Gargiulo, M., Ertug, G., Galunic, C.: The two faces of control: network closure and individual performance among knowledge workers. Adm. Sci. Q. 54(2), 299–333 (2009)
Gay, B., Dousset, B.: Innovation and network structural dynamics: study of the alliance network of a major sector of the biotechnology industry. Res. Policy 34(10), 1457–1475 (2005)
Grewal, R., Lilien, G.L., Mallapragada, G.: Location, location, location: how network embeddedness affects project success in open source systems. Manag. Sci. 52(7), 1043–1056 (2006)
Gulati, R.: Network location and learning: the influence of network resources and firm capabilities on alliance formation. Strateg. Manag. J. 20(5), 397–420 (1999)
Gulati, R., Lavie, D., Singh, H.: The nature of partnering experience and the gains from alliances. Strategic Manage. J. 30(11), 1213–1233 (2009)
Hsueh, J.T., Lin, N.P., Li, H.C.: The effects of network embeddedness on service innovation performance. Serv. Ind. J. 30(10), 1723–1736 (2010a)
Hsueh, J.-T., Lin, N.-P., Li, H.-C.: The effects of network embeddedness on service innovation performance. Serv. Ind. J. 10(30), 1723–1736 (2010b)
Guo, J.: Network embeddedness: embedded differences and performance. Econ. Rev. 6, 24–30 (2006)
Hongming, X., Ying, Z., Cong, C., Ying, C.: The impact of network embedding on technical innovative performance based on the perspective of learning capability. Sci. Res. Manag. 35(12), 1–8 (2014)
Hu, M.: Empirical study on the impact of organizational knowledge sharing to knowledge capital and organizational performance case study of hotel chains based on social capital theory. J. Southeast Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 11(2), 39–42 (2009)
Jia, X., Zhang, X.: Impact of network embeddedness and organizational learning to enterprise’s technology innovation performance based on the investigation of marine equipment manufacturing enterprises. J. Intell. 33(9), 199–207 (2014)
Juan, L.: A study on multiple network embeddedness and knowledge creation performance of cluster firms. Stud. Sci. 33(1), 90–97 (2015)
Koka, B.R., Prescott, J.E.: Designing alliance networks: the influence of network position, environmental change, and strategy on firm performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 29(6), 639–661 (2008)
Liu, R.: Impact of network embeddedness to enterprise performance from a theoretical perspective. Huxiang Forum 6, 88–90 (2008)
Liu, X.: Research on the relationship in network embeddedness, knowledge acquisition and enterprise innovation. Econ. Manag. J. 37(3), 150–159 (2015)
Ma, X., He, H.: Impact of network embeddedness on the technology innovation performance of SME with the consideration of mediation of knowledge acquisition. Technol. Econ. 34(7), 13–17 (2015)
Marco, T., et al.: Activating cross-boundary knowledge: the role of simmelian ties in the generation of innovations. Acad. Manag. J. 1(53), 1167–1181 (2010)
Moran, P.: Structural vs relational embeddedness: social capital and managerial performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 26(12), 1129–1151 (2005)
Morone, P., Taylor, R.: Knowledge diffusion dynamics and network properties of face-to-face interactions. J. Evol. Econ. 14(3), 327–351 (2004)
Piergiuseppe, M., et al.: Knowledge diffusion dynamics and network properties of face-to-face interactions. J. Evol. Econ. 3(14), 327–351 (2004)
Presutti, M., et al.: The importance of proximity for the start-ups’ knowledge acquisition and exploitation. J. Small Bus. Manag. 49(3), 361–389 (2011)
Renyong, Ci: Research on the node connection and efficiency evaluation of innovation networks of regional SME. Manag. World 1, 105–112 (2007)
Ting Helena Chiu, Y.: How network competence and network location influence innovation performance. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 24(1), 46–55 (2008)
Thune, T.: University industry collaboration: the network embeddedness approach. Sci. Public Policy 3(34), 22–29 (2007)
Uzzi, B.: Social structure and competition in interfirm networks: the paradox of embeddedness. Adm. Sci. Q. 1(42), 35–67 (1997)
Uzzi, B., Lancaster, R.: The role of relationships in interfirm knowledge transfer and learning: the case of corporate debt markets. Manag. Sci. 4(49), 383–399 (2003)
Vasudeva, G., Zaheer, A., Hernandez, E.: The embeddedness of networks: institutions, structural holes, and innovativeness in the fuel cell industry. Organ. Sci. 24(3), 645–663 (2013)
Wang, J.: Impact of Relational Embeddedness to Service Innovation Performance. Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai (2011)
Wang, A., et al.: Impact of formal/informal knowledge search width on innovation performance. Stud. Sci. Sci. 33(10), 1573–1583 (2015)
Wei, J., et al.: Dual embeddedness of knowledge and network knowledge integration and cluster enterprise innovation. J. Manag. Sci. China 17(2), 34–47 (2014)
Wincent, J., Anokhin, S., et al.: Does network board capital matter? A study of innovative performance in strategic SME networks. J. Bus. Res. 63(3), 265–275 (2010)
Wincent, J., Thorgren, S., Anokhin, S.: Entrepreneurial orientation and network board diversity in network organizations. J. Bus. Venturing 29(2), 327–344 (2014)
Wu, J., Xu, M.: Network density and cluster competition advantages: mediation of agglomeration economy and collective learning empirical analysis of cluster of Zhejiang textile industry from 2001–2004. Manage. World 8, 69–76 (2008)
Xu, G., et al.: Case study on the relational embeddedness to technology innovation performance. Stud. Sci. Sci. 11, 1728–1734 (2011)
Yang, Y.: Research on the relationship between network embeddedness, knowledge search and innovation performance. South China Univ. Technol. (6), 10–50 (2014)
Yli-Renko, H., Autio, E., Sapienza, H.J.: Social capital, knowledge acquisition, and knowledge exploitation in young technology-based firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 6(22), 587–613 (2001)
Yu, S.: Impact of Knowledge Circulation on Innovation Performance from the Perspective of Social Capital: A Case Study of Manufactures in Science Park. National Cheng Kung University, Tainan (2005)
Zaheer, A., Bell, G.G.: Benefiting from network position: firm capabilities, structural holes, and performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 26(9), 809–825 (2005)
Zahra, S.A., Ireland, R.D., Hitt, M.A.: International expansion by new venture firms: international diversity, mode of market entry, technological learning and performance. Acad. Manag. J. 43, 925–950 (2000)
Zhao, Y., Zheng, X.: Impacts of network and geographical embeddedness to the innovation performance of affiliated enterprises empirical study of Chinese high-tech listed companies. Sci. Res. Manag. 34(11), 9–17 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang under Grant Nos. LY17G030014, LY17G030010, LQ17G030001, the Academic Leader Cultivation Project of Ningbo Philosophy Social Sciences under Grant No. G15-XK01. This research is sponsored by K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University and Key Research Institute of Philosophy and Social Sciences of Zhejiang Province: Modern Port Service Industry and Creative Culture Research Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cong, H., Zou, D. & Wu, F. Influence mechanism of multi-network embeddedness to enterprises innovation performance based on knowledge management perspective. Cluster Comput 20, 93–108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0735-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0735-5