Abstract
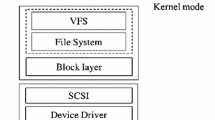
Modern storage systems are facing an important challenge of making the best use of fast storage devices. Even though the underlying storage devices are being enhanced, the traditional storage stack falls short of utilizing the enhanced characteristics, as it has been optimized specifically for hard disk drives. In this article, we optimize the storage stack to maximize the benefit of low latency that fast storage devices provide. Our approach is to simplify the I/O path from application to the fast storage device by removing inefficient layers and the conventional block I/O. The proposed stack consists of three layers: an optimized device driver, a low-latency file system called L2FS, and a simplified VFS. The device driver provides a simple file I/O API to the file system instead of the existing block I/O API. L2FS, a variant of EXT4, performs low-latency I/O operations by using the file I/O API that our optimized device driver provides. We implement our storage stack on Linux 3.14.3 and evaluate it with multiple benchmarks. The results show that our system improves the throughput by up to 6.6 times and reduces the latency by an average of 54% compared to the existing storage stack on fast storage.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In this article, we assume that fast NVM has near-DRAM performance in terms of latency and bandwidth. Thus, flash memory does not fall into the fast NVM.
NVM that is directly attached to a memory bus is called Storage Class Memory (SCM).
The term ‘NVM-based SSD’ is used as SSD based on the fast NVM in this article.
References
Ahmed, M., Uddin, M.M., Azad, M.S., Haseeb, S.: MySQL performance analysis on a limited resource server: Fedora vs. Ubuntu Linux. In: Proceedings of the 2010 Spring Simulation Multiconference, p. 99. Society for Computer Simulation International (2010)
Belay, A., Prekas, G., Klimovic, A., Grossman, S., Kozyrakis, C., Bugnion, E. IX: A protected dataplane operating system for high throughput and low latency. In: 11th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 14), pp. 49–65 (2014)
Bonwick, J., Moore, B. ZFS: The last word in file systems
Caulfield, A.M., Mollov, T.I., Eisner, L.A., De, A., Coburn, J., Swanson, S.: Providing safe, user space access to fast, solid state disks. SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 40(1), 387–400 (2012)
Chen, J., Wei, Q., Chen, C., Wu, L.: FSMAC: A file system metadata accelerator with non-volatile memory. In: 2013 IEEE 29th Symposium on Mass Storage Systems and Technologies (MSST), pp. 1–11 (2013)
Chen, P.M., Ng, W.T., Chandra, S., Aycock, C., Rajamani, G., Lowell, D.: The Rio file cache: surviving operating system crashes. In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (New York, NY, USA, 1996), ASPLOS VII, ACM, pp. 74–83
Chen, S., Ailamaki, A., Athanassoulis, M., Gibbons, P.B., Johnson, R., Pandis, I., Stoica, R.: TPC-E vs. TPC-C: characterizing the new TPC-E benchmark via an I/O comparison study. SIGMOD Rec. 39, 5–10 (2011)
Chidambaram, V., Pillai, T.S., Arpaci-Dusseau, A.C., Arpaci-Dusseau, R.H.: Optimistic crash consistency. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, SOSP ’13, pp. 228–243. ACM, New York (2013)
Coburn, J., Bunker, T., Gupta, R.K., Swanson, S.: From ARIES to MARS: reengineering transaction management for next-generation, solid-state drives
Coburn, J., Bunker, T., Schwarz, M., Gupta, R., Swanson, S.: From ARIES to MARS: transaction support for next-generation, solid-state drives. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, SOSP ’13, pp. 197–212. ACM, New York (2013)
Coburn, J., Caulfield, A.M., Akel, A., Grupp, L.M., Gupta, R.K., Jhala, R., Swanson, S.: NV-Heaps: making persistent objects fast and safe with next-generation. Non-volatile memories. SIGPLAN Not. 46(3), 105–118 (2011)
Condit, J., Nightingale, E.B., Frost, C., Ipek, E., Lee, B., Burger, D., Coetzee, D.: Better I/O through byte-addressable, persistent memory. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGOPS 22nd Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, SOSP ’09, pp. 133–146. ACM, New York (2009)
Dieny, B., Sousa, R., Prenat, G., Ebels, U.: Spin-dependent phenomena and their implementation in spintronic devices. In: International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Applications, 2008 (VLSI-TSA 2008), pp. 70–71. IEEE (2008)
Dong, B., Zheng, Q., Tian, F., Chao, K.M., Ma, R., Anane, R.: An optimized approach for storing and accessing small files on cloud storage. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 35(6), 1847–1862 (2012)
Dulloor, S.R., Kumar, S., Keshavamurthy, A., Lantz, P., Reddy, D., Sankaran, R., Jackson, J.: System software for persistent memory. In: Proceedings of the Ninth European Conference on Computer Systems, EuroSys ’14, pp. 15:1–15:15. ACM, New York (2014)
Hitz, D., Lau, J., Malcolm, M.A.: File system design for an NFS file server appliance. In: USENIX winter, vol. 94 (1994)
Husain, M.I., Ko, S.Y., Uurtamo, S., Rudra, A., Sridhar, R.: Bidirectional data verification for cloud storage. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 45, 96–107 (2014)
J. Axboe. Fiobenchmark. http://freecode.com/projects/fio
Jiang, W., Ma, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Shao, Z.: Adaptive security management of real-time storage applications over NAND based storage systems. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 52, 139–153 (2015)
Kang, J., Zhang, B., Wo, T., Yu, W., Du, L., Ma, S., Huai, J.: SpanFS: a scalable file system on fast storage devices. In: 2015 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 15), pp. 249–261 (2015)
Kannan, S., Gavrilovska, A., Schwan, K.: pVM: persistent virtual memory for efficient capacity scaling and object storage. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh European Conference on Computer Systems, EuroSys ’16, pp. 13:1–13:16. ACM, New York (2016)
Katti, R.R., Stadler, H.L., Wu, J.-C. Non-volatile magnetic random access memory. US Patent 5,289,410, 22 Feb 1994
Kim, H., Seshadri, S., Dickey, C.L., Chiu, L.: Evaluating phase change memory for enterprise storage systems: a study of caching and tiering approaches. In: Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies (FAST 14), pp. 33–45. USENIX, Santa Clara 2014
Kim, H., Seshadri, S., Dickey, C.L., Chiu, L. Evaluating phase change memory for enterprise storage systems: a study of caching and tiering approaches. In: Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies (FAST 14), pp. 33–45 (2014)
Kim, Y., Tauras, B., Gupta, A., Urgaonkar, B. Flashsim: A simulator for nand flash-based solid-state drives. In: First International Conference on Advances in System Simulation, 2009. SIMUL’09, pp. 125–131. IEEE (2009)
Lee, C., Sim, D., Hwang, J., Cho, S.: F2FS: A new file system for flash storage. In: 13th USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies (FAST 15), pp. 273–286 (2015)
Mathur, A., Cao, M., Bhattacharya, S., Dilger, A., Tomas, A., Vivier, L.: The New ext4 filesystem: current status and future plans. In: In Ottawa Linux Symposium. http://ols.108.redhat.com/2007/ Reprints/mathur-Reprint.pdf (2007)
McKusick, M.K., Joy, W.N., Leffler, S.J., Fabry, R.S.: A Fast File System for UNIX. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 2(3), 181–197 (1984)
NVM Express. http://www.nvmexpress.org/wp-content/uploads/NVM-Express-1_1.pdf
Oi, H.: A case study: performance evaluation of a DRAM-based solid state disk. In: Japan-China Joint Workshop on Frontier of Computer Science and Technology, 2007 (FCST 2007), pp. 57–60
Ou, J., Shu, J., Lu, Y.: A high performance file system for non-volatile main memory. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh European Conference on Computer Systems, EuroSys ’16, pp. 12:1–12:16. ACM, New York (2016)
Peter, S., Li, J., Zhang, I., Ports, D.R., Woos, D., Krishnamurthy, A., Anderson, T., and Roscoe, T. Arrakis: The operating system is the control plane. In: Proceedings of the 11th Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation (OSDI14) (2014)
Prabhakaran, V., Bairavasundaram, L.N., Agrawal, N., Gunawi, H.S., Arpaci-Dusseau, A.C., Arpaci-Dusseau, R.H.: IRON file systems. In: Proceedings of the Twentieth ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, SOSP ’05, pp. 206–220. ACM, New York (2005)
Raoux, S., Burr, G., Breitwisch, M., Rettner, C., Chen, Y., Shelby, R., Salinga, M., Krebs, D., Chen, S.-H., Lung, H.L., Lam, C.: Phase-change random access memory: a scalable technology. IBM J. Res. Dev. 52(4.5), 465–479 (2008)
Rodeh, O., Bacik, J., Mason, C.: BTRFS: The Linux B-tree filesystem. ACM Trans. Storage (TOS) 9(3), 9 (2013)
Santos, J. FFSB (flexible file system benchmark). http://sourceforge.net/projects/ffsb/
Sato, K., Mohror, K., Moody, A., Gamblin, T., d. Supinski, B. R., Maruyama, N., Matsuoka, S.: A user-level infiniband-based file system and checkpoint strategy for burst buffers. In: 2014 14th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing (CCGrid), pp. 21–30 (2014)
Seppanen, E., O’Keefe, M., Lilja, D.: High performance solid state storage under Linux. In: 2010 IEEE 26th Symposium on Mass Storage Systems and Technologies (MSST), pp. 1–12 (2010)
Sweeney, A., Doucette, D., Hu, W., Anderson, C., Nishimoto, M., Peck, G.: Scalability in the XFS file system. In: USENIX Annual Technical Conference, vol. 15 (1996)
TAILWINDSTORAGE. Extreme S3804. http://www.taejin.co.kr
Volos, H., Tack, A.J., Swift, M.M.: Mnemosyne: lightweight persistent memory. SIGPLAN Not. 47(4), 91–104 (2011)
Vučinić, D., Wang, Q., Guyot, C., Mateescu, R., Blagojević, F., Franca-Neto, L., Le Moal, D., Bunker, T., Xu, J., Swanson, S., et al.: DC express: shortest latency protocol for reading phase change memory over PCI express. In: Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies (FAST 14), pp. 309–315 (2014)
Woodhouse, D.: JFFS: the journalling flash file system. In: Ottawa linux symposium, vol. 2001 (2001)
Wu, M., Zwaenepoel, W.: eNVy: a non-volatile, main memory storage system. In: ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, , vol. 28, pp. 86–97. ACM (1994)
Wu, X., Reddy, A.L.N.: SCMFS: a file system for storage class memory. In: Proceedings of 2011 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis (SC ’11) pp. 39:1–39:11. ACM, New York (2011)
Xu, J., Swanson, S.: NOVA: a log-structured file system for hybrid volatile/non-volatile main memories. In: 14th USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies (FAST 16), pp. 323–338. USENIX Association, Santa Clara (2016)
Yang, J., Minturn, D.B., Hady, F.: When poll is better than interrupt. In: Proceedings of the 10th USENIX Conference on File and Storage Technologies, FAST’12, p. 3. USENIX Association, Berkeley (2012)
Yu, Y.J., Shin, D.I., Shin, W., Song, N.Y., Choi, J.W., Kim, H.S., Eom, H., Yeom, H.Y.: Optimizing the block I/O subsystem for fast storage devices. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 32(2), 6 (2014)
Zhang, J., Shu, J., Lu, Y. ParaFS: a log-structured file system to exploit the internal parallelism of flash devices. In: 2016 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 16) (2016)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2015M3C4A7065581, 2015M3C4A7065645) and NRF funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2015R1A2A2A01005995). This work was also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2016R1D1A1B03934393). Prof. Han is the corresponding author of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, Y., Song, N.Y., Yeom, H.Y. et al. A low-latency storage stack for fast storage devices. Cluster Comput 20, 2627–2640 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0776-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0776-9