Abstract
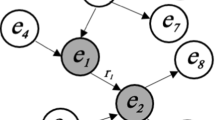
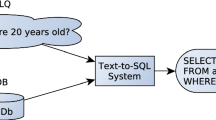
In order to precisely represent natural language questions (NLQs) in question answering system (QAS) and provide a more naturally interactive mode, we require SPARQL, a formalized query patterns, instead of search expression to express the user’s semantic query intention. However, how to generate and evaluate SPARQL query from NLQ is a mostly open research question. In this paper, we propose a framework that can help users translating NLQ into well-formed queries for knowledge based systems. We define a new graph structure, semantic query graph, and vocabulary to match all kinds of complex and compound questions without using domain ontology. Through query expansion and semantic query graph generation, the framework resembles subgraphs of the knowledge base and can be directly mapped to a logical form. Extensive experiments over NLQ in real RDF QASs verify the feasibility and efficiency of semantic query graph and our proposed framework with average F-measure of 0.825.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berant, J., Chou, A., Frostig, R., et al.: Semantic parsing on freebase from question-answer pairs. EMNLP 2(5), 6 (2013)
Cabrio, E., Cojan, J., Gandon, F, et al.: Querying multilingual DBpedia with QAKiS. In: Extended Semantic Web Conference. Springer, Berlin, pp. 194–198 (2013)
Cai, Q., Yates, A.: Large-scale semantic parsing via schema matching and lexicon extension. ACL 1, 423–433 (2003)
Dubey, M., Dasgupta, S., Sharma, A., et al.: Asknow: a framework for natural language query formalization in SPARQL. In: International Semantic Web Conference, pp. 300–316. Springer, Cham (2016)
Faleiro, J.M., Abadi, D.J.: FIT: A Distributed Database Performance Tradeoff. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 38(1), 10–17 (2015)
Ferré, S.: Sparklis: an expressive query builder for SPARQL endpoints with guidance in natural language. Semant. Web 8(3), 405–418 (2017)
Hasan, A., Hammoud, M., Nouri, R., et al.: DREAM in action: a distributed and adaptive RDF system on the cloud. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference Companion on World Wide Web. International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, pp. 191–194 (2016)
Horridge, M., Musen, M.: Snap-SPARQL: a java framework for working with SPARQL and OWL. In: International Experiences and Directions Workshop on OWL, pp. 154–165. Springer, Cham (2015)
Lehmann, J., Bühmann, L.: Autosparql: let users query your knowledge base. Semanti. Web Res. Appl. 63–79 (2011)
Lopez, V., Tommasi, P., Kotoulas, S., et al.: Queriodali: question answering over dynamic and linked knowledge graphs. In: International Semantic Web Conference, pp. 363–382. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Marginean, A.: Question answering over biomedical linked data with grammatical framework. Semant. Web 8(4), 565–580 (2017)
Matteis, L., Hogan, A., Navigli, R.: Keyword-based navigation and search over the linked data web.In: LDOW@ WWW (2015)
Mazzeo, G.M., Zaniolo, C.: Answering controlled natural language questions on RDF knowledge bases. In: EDBT, pp. 608–611 (2016)
Nakashole, N., Weikum, G., Suchanek, F.: PATTY: a taxonomy of relational patterns with semantic types. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning, pp. 1135–1145 . Association for Computational Linguistics (2012)
Paredes-Valverde, M.A., Rodríguez-García, M.Á., Ruiz-Martínez, A., et al.: ONLI: an ontology-based system for querying DBpedia using natural language paradigm. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(12), 5163–5176 (2015)
Pradel, C., , Haemmerlé, O., Hernandez, N.: Natural language query interpretation into sparql using patterns. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Consuming Linked Data, vol. 1034, pp. 13–24. CEUR-WS.org (2013)
Qiang, L.: Painting semantic retrieval algorithm research based on ontology. In: Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), pp. 621–624. IEEE (2015)
Sander, M., Waltinger, U., Roshchin, M., Runkler, T.: Ontology-based translation of natural language queries to SPARQL. In: Proceedings of the Natural Language Access to Big Data. AAAI 2014 Fall Symposium. Citeseer (2014)
Shekarpour, S., Marx, E., Ngonga Ngomo, A.-C., Soren, A.: Semantic Interpretation Of User Queries For Question Answering On Interlinked Data. Elsevier-Web Semantics (2015)
Song, D., Schilder, F., Smiley, C., et al.: Natural language question answering and analytics for diverse and interlinked datasets. In: HLT-NAACL, pp. 101–105 (2015)
Song, D., Schilder, F., Smiley, C., et al.: TR discover: a natural language interface for querying and analyzing interlinked datasets. In: International Semantic Web Conference, pp. 21–37. Springer, Cham (2015)
Tatu, M., Balakrishna, M., Werner, S., et al.: Automatic extraction of actionable knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), pp. 396–399. IEEE (2016)
Tatu, M., Balakrishna, M., Werner, S., et al.: A semantic question answering framework for large data sets. Open J. Semant. Web (OJSW) 3(1), 16–31 (2016)
Unger, C., Forascu, C., Lopez, V., et al.: Question answering over linked data (QALD-4). Working Notes for CLEF 2014 Conference (2014)
Xu, K., Zhang, S., Feng, Y., et al.: Answering natural language questions via phrasal semantic parsing. In: Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, pp. 333–344. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Zheng, W., Zou, L., Lian, X., et al.: How to build templates for RDF question/answering: an uncertain graph similarity join approach. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 1809–1824. ACM (2015)
Zhou, Q., Luo, J.: The study on evaluation method of urban network security in the big data era. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/10798587.2016.1267444
Zhou, Q.: Multi-layer affective computing model based on emotional psychology. Electron. Commer. Res. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-017-9265-8
Zhou, Q.: Research on heterogeneous data integration model of group enterprise based on cluster computing. Clust. Comput. 19, 1275–1282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0580-y
Zhou, Q., Luo, J.: The service quality evaluation of ecologic economy systems using simulation computing. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 31(6), 453–460 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S., Huang, W. & Sun, Y. Semantic query graph based SPARQL generation from natural language questions. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 1), 847–858 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1332-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1332-3