Abstract
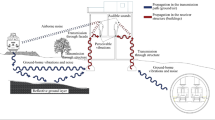
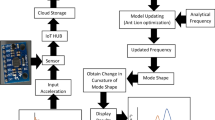
The Real Time BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) has evolved into a reliable technique to detect both the three-dimensional magnitudes and frequencies of displacement of structures. BDS technology is exactly what monitoring needs for the bridge deformation. Also, the oscillations and damage severity can be evaluated and classified according to the dynamic bridge characteristics obtained from BDS. The intention of the present work is to demonstrate the use of BDS to provide data for the assessment of existing structures safety. The raw data were collected continuously over a period of 24 h at a minimum rate of 1 Hz. The collected data include traffic flow (for load estimation) and environment factors (such as wind speed, wind direction, relative humidity and temperature). The vibration frequencies are also measured from BDS data and compared with those given in the literature. The results of all the experiments proved to be very encouraging, and showed that the performance of BDS as it has developed in recent years, and that the BDS is reliably in quantifying both environmental induced bridge vibrations and high-frequency transient motion caused by vehicle loading, in particular changes of mass associated with changes in traffic loading are observed, providing the ability for verification and/or improvement of bridge design and modelling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yi, T.H., Li, H.N., Gu, M.: Experimental assessment of high-rate GPS receivers for deformation monitoring of bridge. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 46(1), 420–432 (2013)
Gikas, V.: Ambient vibration monitoring of slender structures by microwave interferometer remote sensing. J. Appl. Geod. 6(3–4), 167–176 (2012)
Costa, B.J.A., Figueiras, J.A.: Fiber optic based monitoring system applied to a centenary metallic arch bridge: design and installation. Eng. Struct. 44(6), 271–280 (2012)
He, X.H., Hua, X.G., Chen, Z.Q., et al.: EMD-based random decrement technique for modal parameter identification of an existing railway bridge. Eng. Struct. 33(4), 1348–1356 (2011)
Kumberg, T., Schneid, S., Reindl, L.: A wireless sensor network using GNSS receivers for a short-term assessment of the modal properties of the Neckartal bridge. Appl. Sci. 7(6), 626 (2017)
Boscato, G., Russo, S., Ceravolo, R., et al.: Global sensitivity-based model updating for heritage structures. Comput.-Aided Civil Infrastruct. Eng. 30(8), 620–635 (2015)
García-Palencia, A.J., Santini-Bell, E.: A two-step model updating algorithm for parameter identification of linear elastic damped structures. Comput.-Aided Civil Infrastruct. Eng. 28(7), 509–521 (2013)
Eckl, M.C., Snay, R.A., Soler, T., et al.: Accuracy of GPS-derived relative positions as a function of interstation distance and observing-session duration. J. Geod. 75(12), 633–640 (2001)
Firuzabadì, D., King, R.W.: GPS precision as a function of session duration and reference frame using multi-point software. GPS Solut. 16(2), 191–196 (2012)
Psimoulis, P., Pytharouli, S., Karambalis, D., et al.: Potential of global positioning system (GPS) to measure frequencies of oscillations of engineering structures. J. Sound Vib. 318(3), 606–623 (2008)
Zhang, X.: Study on precise point positioning based on combined GPS and GLONASS. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 35(1), 9–12 (2010)
Tolman, B.W., Kerkhoff, A., Rainwater, D., et al.: Absolute precise kinematic positioning with GPS and GLONASS. In: Proceedings of International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (2010)
Bos, M.S., Bastos, L., Fernandes, R.M.S.: The influence of seasonal signals on the estimation of the tectonic motion in short continuous GPS time-series. J. Geodyn. 49(3–4), 205–209 (2010)
Geoffrey, B., David, L.: Effect of annual signals on geodetic velocity. J. Geophys. Res. 107, ETG 9-1–ETG 9-11 (2010)
Ogundipe, O., Roberts, G.W., Brown, C.J.: GPS monitoring of a steel box girder viaduct. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 10(1), 25–40 (2014)
Demir, D.O., Dogan, U.: Determination of crustal deformations based on GPS observing-session duration in Marmara region, Turkey. Adv. Space Res. 53(3), 452–462 (2014)
Kaloop, M.R., Hu, J.W., Elbeltagi, E.: Adjustment and assessment of the measurements of low and high sampling frequencies of GPS real-time monitoring of structural movement. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 5(12), 222 (2016)
Tu, R., Liu, J., Lu, C., et al.: Cooperating the BDS, GPS, GLONASS and strong-motion observations for real-time deformation monitoring. Geophys. J. Int. 209(3), 1408–1417 (2017)
Shi, C., Zhao, Q., Hu, Z., et al.: Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut. 17(1), 103–119 (2013)
Yang, Y.X., Li, J.L., Xu, J.Y., et al.: Contribution of the compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chin. Sci. Bull. 56(26), 2813 (2011)
He, H., Li, J., Yang, Y., et al.: Performance assessment of single- and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut. 18(3), 393–403 (2014)
Deng, C., Tang, W., Liu, J., et al.: Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system. GPS Solut. 18(3), 375–386 (2014)
Teunissen, P.J.G., Odolinski, R., Odijk, D.: Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J. Geod. 88(4), 335–350 (2014)
Han, H., Wang, J., Meng, X., et al.: Analysis of the dynamic response of a long span bridge using GPS/accelerometer/anemometer under typhoon loading. Eng. Struct. 2016(122), 238–250 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Q., Zhou, J., Ullah, S. et al. Operational modal analysis of rigid frame bridge with data from navigation satellite system measurements. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 3), 5535–5545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1360-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1360-z