Abstract
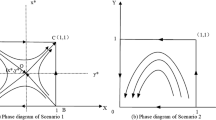
Risk factors have a significant influence on corporate investing and financing behavior. Based on agency theory, this paper analyzes conflicts of interest that are involved in the process of corporate investing and financing under the influence of risk, and it conducts this analysis using the evolutionary game model for investing and financing behavior. The evolutionary simulation analysis is conducted using the system dynamics method to explore the investing and financing behavior of corporate entities that are influenced by different risks. The results of this analysis show that the risks that impact the debt financing strategies of corporations are usually investment risk and interest rate risk, and that internal governance risk does not appear to change the financing structure of corporate behavior. Risks that impact the excessive investment strategy choices of corporations are mainly investment risk and internal governance risk, while interest rate risk does not appear to have any effect on the excessive investment tendencies of certain managers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, X.S., Tan, Y.C., Liu, J.M.: Non-financial information, external financing and investment efficiency-research based on external institutional constraint. Manag. World 7(137), 150–188 (2012)
Frank, M.Z., Goyal, V.K.: Testing the pecking order theory of capital structure. J. Financ. Econ. 67(2), 217–248 (2003)
D’Mello, R., Miranda, M.: Long-term debt and overinvestment agency problem. J. Bank. Financ. 34(2), 324–335 (2010)
Fama, E.F., French, K.R.: Taxes, financing decisions, and firm value. J. Financ. 53(3), 819–843 (1998)
Hennessy, C.A., Leland, H.E.: Can the trade-off theory explain debt structure? Rev. Financ. Stud. 20(5), 1389–1428 (2007)
Bertomeu, J., Beyer, A., Dye, R.A.: Capital structure, cost of capital, and voluntary disclosures. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 86(3), 857–886 (2011)
Berger, A.N., Marco Espinosa-Vega, W., Frame, S., Miller, N.: Debt, maturity, risk, and asymmetric information. J. Financ. 60, 2895–2923 (2005)
Datta, S., Mai, I.D., Raman, K.: Managerial stock ownership and the maturity structure of corporate debt. J. Financ. 60(5), 2333–2350 (2005)
Akhtar, S.: The determinants of capital structure for australian multinational and domestic corporations. Aust. J. Manag. 30(2), 321–339 (2005)
Nguyen, T.D.K., Ramachandran, N.: Capital structure in small and medium-sized enterprises: the case of Vietnam. ASEAN Econ. Bull. 23(2), 192–211 (2006)
Pao, H.-T.: Capital structure in Taiwan’s high tech dot companies. J. Am. Acad. Bus. 12(1), 133–138 (2007)
Harford, J., Li, K., Zhao, X.: Corporate boards and the leverage and debt maturity choices. Int. J. Corp. Gov. 1, 3–27 (2008)
Cai, K., Fairchild, R., Guney, Y.: Debt maturity structure of chinese companies. Pac. Basin Financ. J. 16(3), 268–297 (2008)
Flavin, T., O’Connor, T.: The sequencing of stock market liberalization events and corporate financing decisions. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 11, 183–204 (2010)
Cook, D.O., Tang, T.: Macroeconomic conditions and capital structure adjustment speed. J. Corp. Financ. 16(1), 73–87 (2010)
Sun, J., Ding, L., Guo, J.M., Li, Y.: Ownership, capital structure and financing decision: evidence from the UK. Br. Account. Rev. 48(4), 448–463 (2015)
Wang, Y.T., Wang, L.L., Peng, Y.: Nature of property right, debt shield and capital structure. Econ. Res. 2010(9), 122–136 (2010)
Ma, W.C., Hu, S.Y.: Monetary policy, credit channel and capital structure. Account. Res. (11), 39–48 (2012) (94–95, in Chinese)
Fosberg, R.H.: Capital structure and the financial crisis. J. Financ. Account. 11, 1 (2012)
Allayannis, G., Brown, G.W., Klapper, L.F.: Capital structure and financial risk: evidence from foreign debt use in east asia. J. Financ. 58(6), 2667–2710 (2010)
Liu, X., Li, N., Zhang, C.: Competition within banks, ultimate control and debt allocation structure. Account. Res. 10:44-50+96 (2015)
Bai, J.J., Li, B.X.: Influence of monetary compensation structure on managerial entrenchment behavior: an experimental study. China Soft Sci. 10, 88–103 (2012)
Wang, Y.H., Wang, H.: Study on the choice model of enterprise debt term structure based on evolutionary game simulation. Modern. Manag. 03, 5–8 (2016)
Daniel, F.: Evolutionary games in economics. Econometrica 59(3), 637–666 (1991)
Zeng, Y.R., Zeng, Y., Choi, B., Wang, L.: Multifactor-influenced energy consumption forecasting using enhanced back-propagation neural network. Energy 127, 381–396 (2017)
Zeng, Y.R., Peng, L., Zhang, J., Wang, L.: An effective hybrid differential evolution algorithm incorporating simulated annealing for joint replenishment and delivery problem with trade credit. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 9(6), 1001–1015 (2016)
Wang, L., Zeng, Y., Chen, T.: Back propagation neural network with adaptive differential evolution algorithm for time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(2), 855–863 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported by the fundamental research funds for the central universities (Program No. 2662016QD054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wang, B. Evolutionary game simulation of corporate investing and financing behavior from a risk perspective. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 3), 5955–5964 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1734-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1734-x