Abstract
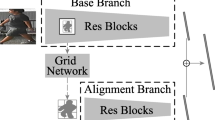
Person re-identification is a challenging task due to its large variations on pedestrian pose, camera view, lighting and background. To solve pedestrian misalignment problem, most of the existing works assume that the pedestrian images are horizontally aligned so that the extracted features can be compared correspondingly. However, such assumption is not necessarily true in reality because the pedestrians may be misaligned vertically. To address the misalignment problem, we propose a dynamic locally connected (DLC) layer based on convolutional neural network (CNN). We use human parsing tool to get parsing results of pedestrian images, then map the results to the last feature map of our CNN. By doing this, proposed model is able to locate the human body parts dynamically within DLC layer, thus leads to a more accurate matching on local features. Furthermore, we adopt pre-training with two-step fine-tuning strategy on the small person re-identification datasets, which again boost the model performance. According to the experiments, proposed model achieves competitive results among the state-of-the-art models on four popular person re-identification datasets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song, B., Kamal, A.T., Soto, C., Ding, C., Farrell, J.A., Roychowdhury, A.K.: Tracking and activity recognition through consensus in distributed camera networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(10), 2564–2579 (2010)
Gong, S., Cristani, M., Loy, C.C., Hospedales, T.M.: The Reidentification Challenge in Person Re-identification. Springer, London (2014)
Vezzani, R., Davide, B., Cucchiara, R.: People reidentification in surveillance and forensics: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1145/2543581.2543596
Mignon, A., Jurie, F.: PCCA: a new approach for distance learning from sparse pairwise constraints. In: CVPR (2016)
Li, W., Wang, X.: Locally aligned feature transforms across views. In: CVPR (2013)
Zheng, W., Gong, S., Xiang, T.: Reidentification by relative distance comparison. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(3), 653–668 (2013)
Liao, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, X., Li, S.: Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: CVPR (2015)
Paisitkriangkrai, S., Shen, C., Hengel, A.: Learning to rank in person re-identification with metric ensembles. In: CVPR (2015)
Zhang, L., Xiang, T., Gong, S.: Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2016)
Zhang, Y., Li, B., Lu, H., Irie, A., Ruan, X.: Sample-specific SVM learning for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2016)
Chen, D., Yuan, Z., Chen, B., Zheng, N.: Similarity learning with spatial constraints for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2016)
Liao, S., Li, S.: Efficient PSD constrained asymmetric metric learning for person re-identification. In: ICCV (2015)
Li, W., Zhao, R., Xiao, T., Wang, X.: DeepReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2014)
Yi, D., Lei, Z., Liao, S., Li, S.: Deep metric learning for person re-identification. In: ICPR (2014)
Ahmed, E., Jones, M., Marks, T.: An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2015)
Wang, F., Zuo, W., Lin, L., Zhang, D., Zhang, L.: Joint learning of single-image and cross-image representations for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2016)
Xiao, T., Li, H., Ouyang, W., Wang, X.: Learning deep feature representations with domain guided dropout for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2016)
Varior, R., Haloi, M., Wang, G.: Gated siamese convolutional neural network architecture for human re-identification. In: ECCV (2016)
Sun, Y., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. In: CVPR (2014)
Taigman, Y., Yang, M., Ranzato, M.A., Wolf, L.: DeepFace: closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification. In: CVPR (2014)
Cheng, D., Gong, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, J., Zheng, N.: Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function. In: CVPR (2016)
Luo, P., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Pedestrian parsing via deep decompositional network. In: ICCV (2013)
Yang, Y., Yang, J., Yan, J., Liao, S., Yi, D., Li, S.: Salient color names for person re-identification. In: ECCV (2014)
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., Wang, X.: Learning mid-level filters for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2014)
Li, W., Wang, X.: Locally aligned feature transforms across views. In: CVPR (2013)
Ma, B., Su, Y., Jurie, F.: A novel image representation for person re-identification and face verification. In: BMVC (2012)
Khamis, S., Kuo, C.-H., Singh, V., Shet, V., Davis, L.: Joint learning for attribute-consistent person re-identification. In: ECCV (2014)
Li, Z., Chang, S., Liang, F., Huang, T.S., Cao, J.R.: Learning locally-adaptive decision functions for person verification. In: CVPR, Liangliang and Smith (2013)
Kostinger, M., Hirzer, M., Wohlhart, P., Roth, P.M., Bischof, H.: Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In: CVPR (2012)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Sun, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Tang, X.: Deep learning face representation by joint identification-verification. In: NIPS (2014)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: CVPR (2014)
Varior, R., Shuai, B., Lu, J., Xu, D., Wang, G.: A siamese long short-term memory architecture for human re-identification. In: ECCV (2016)
Shi, H., Yang, Y., Zhu, X., Liao, S., Lei, Z., Zheng, W., Li, S.: Embedding deep metric for person re-identification: a study against large variations. In: ECCV (2016)
Wu, L., Shen, C., Hengel, A.V.D.: PersonNet: person re-identification with deep convolutional neural networks (2016). arXiv:1601.07255
Geng, M., Wang, Y., Xiang, T., Tian, Y.: Deep transfer learning for person re-identification (2016). arxiv:1611.05244
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person re-identification (2016). arXiv:1611.05666
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Deng, W., Wang, S.: Svdnet for pedestrian retrieval (2017). arXiv:1703.05693
Chung, D., Tahboub, K., Delp, E.J.: A two stream siamese convolutional neural network for person re-identification. In: CVPR (2017)
Yu, H.X., Wu, A., Zheng, W.S.: Cross-view asymmetric metric learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR (2017)
Jia, Y., Shelhamer, E., Donahue, J., Karayev, S., Long, J., Girshick, R.B., Guadarrama, S., Darrell, T.: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In: ACMMM, Caffe (2014)
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: ICCV (2015)
Liu, H., Feng, J., Qi, M., Jiang, J., Yan, S.: End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(7), 3492–3506 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Scientific Research Project of Chongqing Education Commission (No. KJ1729408) and Teaching Reform Research Project of Chongqing Education Commission (No. 162071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Li, F. & Chen, H. Dynamic locally connected layer for person re-identification. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 4), 8975–8984 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2033-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2033-2