Abstract
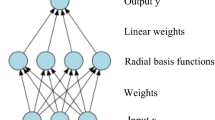
After the occurrence of major accidents, the people in the buildings should be evacuated to safe areas within the shortest time. It is the important part of safe evacuation and reduction of mass mortality accidents. Therefore, the research of fire evacuation problem has highly theoretical and practical values. In the fire evacuation scene, the individual attributes are affected by psychology and behavior among individuals. Based on radial basis function neural network, we used the principal component analysis to determine six main factors affecting evacuation time. These factors are taken as the input of neural network; the evacuation time as the output of neural network. The network was trained by 125 sets of survey data. The quadratic sum error of the model was similar to 0, thus better achieving simulation of actual situation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helbing, D., Illes, J., Farkas, P.: Simulation of Pedestrian Crowds in Normal and Evacuation Situations. Pedestrain and Evacuation Dynamics, pp. 21–58. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Helbing, D.: Traffic and related self-driven many-particle systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 1067–1141 (2001)
Galea, E.R., Blake, S.: Collection and Analysis of Human Behaviour Data Appearing in the Mass Media Relating To The Evacuation of The World Trade Centre Towers of 11 September 2001, pp. 4–6. Office of the Deputy Prime Minister, London (2004)
Helbing, D., Farkas, I., Vicsek, T.: Simulating dynamical features of escape panic. Nature 407, 487–490 (2000)
Helbing, D., Schonhof, M., Kern, D.: Volatile decision dynamics: experiments, stochastic description, intermittency control, and traffic optimization. New J. Phys. 4(33), 1–33 (2002)
Helbing, D., Platkowski, T.: Self-organization in space and induced by fluctuations. Int. J. Chaos Theory Appl. 5(2), 25–38 (2000)
Helbing, D.: A fluid dynamics model for movement of pedestrians. Complex Syst. 6(1), 391–415 (1992)
Henderson, F.: The statistics of crowd fluids. Nature 229, 381–383 (1971)
Henderson, F.: Sexual differences in human crowd notion. Nature 240(8), 353–355 (1972)
Mitchell, H., MacGregor, J.: Topological network design of pedestrian networks. Transp. Res. B 35, 107–135 (2001)
Lovas, G.: Modeling and simulation of pedestrian traffic flow. Transp. Res. B 28, 429–443 (1994)
Murakami, Y., Minami, K., Kawasoe, T., et al.: Multi-agent simulation for crisis management. In: KMN’02 Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Knowledge Media Networking. Washington: IEEE Computer Society, pp. 135–139 (2002)
Society of Fire Protection Engineers. SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering (2002 Edition).Quincy, MA: National fire protection association (NFPA),2003-01
Smith, A.: Density velocity and flow relationships for closely packed crowds. Saf. Sci. 18, 321–327 (1995)
Matthew, O.: The EXODUS evacuation model applied to building evacuation scenarios. Fire Eng. J. 20(7), 27–30 (1996)
Gwynne, S., Galea, E.R., Owen, M.: An investigation of the aspects of occupant behavior required for evacuation modeling. Appl. Fire Sci. 8(1), 19–59 (1988)
Wolfram, S.: Theory and Applications of Cellular Automata, pp. 41–44. World Scientific, Singapore (1986)
Helbing, D.: A mathematical model for behavioral changes by pair interactions and its relation to game theory. Angewandte Sozialforschung 18(3), 117–132 (1994)
Wang, X.H., Yan, M.: An emergency evacuation elgorithm in large building fire. Software 32(2), 112–114 (2011)
Cui, X.H., Li, Q., Chen, J., Chen, C.X.: Study on occupant evacuation model in large public place: to consider individual character and following behavior. J. Nat. Disasters 14(6), 133–140 (2005)
Nguyen, V.Q., Nguyen, M.T., Nguyen, V.N.: Sliding mode control of a three phase induction motor based on RBF neural network. System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), 2017, July: 21–23
Sandeep, K., Satchidananda, D., Alok, K.: ABC optimized RBF network for classification of EEG signal for epileptic seizure identification. Egypt. Inform. J. 18(1), 55–66 (2017)
Zhou, Qingyuan, Luo, Jianjian: Artificial neural network based grid computing of E-government scheduling for emergency management. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 30(5), 327–335 (2015)
Zhou, Q., Luo, J.: The study on evaluation method of urban network security in the big data era. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/10798587.2016.1267444
Zhou, Qingyuan, Luo, Jianjian: The risk management using limit theory of statistics on extremes on the big data era. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 12, 6237–6243 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2015.4661
Liu, R., Pan, T., Li, Z.: Multi-model recursive identification for nonlinear systems with non-uniformly sampling. Clust. Comput. 20(1), 25–32 (2017)
Liu, R., Xu, H., Zheng, E., et al.: Adaptive filtering for intelligent sensing speech based on multi-rate LMS algorithm. Clust. Comput. 20(2), 1493–1509 (2017)
Fathi, M., Mohebbi, M., Razavi, S.M.A.: Application of image analysis and artificial neural network to predict mass transfer kinetics and color changes of osmotically dehydrated kiwifruit. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 4(8), 1357–1366 (2011)
Kashaninejad, M., Dehghani, A.A., Kashiri, M.: Modeling of wheat soaking using two artificial neural networks (MLP and RBF). J. Food Eng. 91(4), 602–607 (2009)
Li, G., Song, Z.: RBF neural network prediction model based on particle swarm optimization for internet-based teleoperation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Seventh International Symposium onComputational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), pp. 34–37 (2014)
Zhou, Q.: Multi-layer affective computing model based on emotional psychology. Electron. Commer. Res. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-017-9265-8
Xie, J., Luo, J., Zhou, Q.: Data mining based quality analysis on informants involved applied research. Clust. Comput. 19(4), 1885–1893 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0657-7
Acknowledgements
National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. 61374137, 61773106, 61703086), the IAPI Fundamental Research Funds (2013ZCX02-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Liu, J. & Tan, S. The radial basis function analysis of fire evacuation model based on RBF neural network. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 3), 6417–6424 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2159-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2159-2