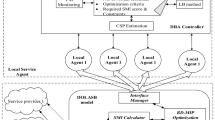
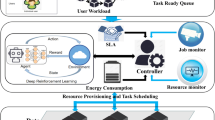
Abstract
Big data processing, scientific calculations, and multimedia operations are some applications that require very complex time-consuming computations which cannot be performed on personal computers. Utilizing powerful cloud resources is a common method to address this problem. The amount of energy consumption of cloud data centers is an important challenge in these complex calculations, and reducing the energy consumption of cloud data centers is one of the most important goals of the researches in this area. The proposed method of this paper, called multi-agent deep Q-network with coral reefs optimization (MDQ-CR), combines the coral reefs optimization algorithm and multi-agent deep Q-network to reduce the energy consumption of data centers and cloud resources using the dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) technique. The MDQ-CR has two main phases. The first phase exploits coral reefs optimization algorithm with a short-term view, and the second phase uses deep Q-network with a long-term view. The Markov game model is used to lead the learning agents to converge to the global optimal solution. Since processors consume the highest amount of energy of cloud compared to the other resources, the proposed method focuses on reducing the processors’ energy consumption. Reducing the voltage and frequency of processors, considering expiration times of their tasks, can reduce their energy consumption significantly. The empirical experiments show that the proposed method can save energy about 89% compared to completely randomized methods, and about 20% compared to the two recent methods of the literature.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
My manuscript has no associated data.
References
Ahmad, R.W., Gani, A., Ab, S.H., Shiraz, H.M., Yousafzai, A., Xia, F.: A survey on virtual machine migration and server consolidation frameworks for cloud data centers. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 52, 11–25 (2015)
Alkhanak, E.N., Lee, S.P., Khan, S.U.: Cost-aware challenges for workflow scheduling approaches in cloud computing environments: taxonomy and opportunities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 50, 3–21 (2015)
Manvi, S.S., Shyam, G.K.: Resource management for Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in cloud computing: a survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 41, 424–440 (2014)
Ghomi, E.J., Rahmani, A.M., Qader, N.N.: Load-balancing algorithms in cloud computing: a survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 88, 50–71 (2017)
Singh, S., Jeong, Y.-S., Park, J.H.: A survey on cloud computing security: Issues, threats, and solutions. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 75, 200–222 (2016)
Hameed, A., Khoshkbarforoushha, A., Ranjan, R., Jayaraman, P.P., Kolodziej, J., Balaji, P., Zeadally, S., Malluhi, Q.M., Tziritas, N., Vishnu, A., Khan, S.U.: A survey and taxonomy on energy efficient resource allocation techniques for cloud computing systems. Computing 98, 751–774 (2016)
Ebrahimi, K., Jones, G.F., Fleischer, A.S.: A review of data center cooling technology, operating conditions and the corresponding low-grade waste heat recovery opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 31, 622–638 (2014)
Mishra, S.K., Puthal, D., Sahoo, B., Jena, S.K., Obaidat, M.S.: An adaptive task allocation technique for green cloud computing. J. Supercomput. 74, 370–385 (2018)
Cisco Global Cloud Index. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/global-cloud-index-gci/Cloud_Index_White_Paper
Khattar, N., Sidhu, J., Singh, J.J.: Toward energy-efficient cloud computing: a survey of dynamic power management and heuristics-based optimization techniques. J. Supercomput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-02764-2
Khan, A.A., Zakarya, M., Khan, R.: Energy-aware dynamic resource management in elastic cloud datacenters. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 92, 82–99 (2019)
Chunxia, Y., Shunfu, J.: An energy-saving strategy based on multi-server vacation queuing theory in cloud data center. J. Supercomput. 74, 6766–6784 (2018)
Zhong, W., Zhuang, Y., Sun, J., Gu, J.: A load prediction model for cloud computing using PSO-based weighted wavelet support vector machine. Appl. Intell. 48, 4072–4083 (2018)
Sofia, A.S., GaneshKumar, P.: Multi-objective task scheduling to minimize energy consumption and makespan of cloud computing using NSGA-II. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 26, 463–485 (2018)
Chaabouni, T., Khemakhem, M.: Energy management strategy in cloud computing: a perspective study. J. Supercomput. 74, 6569–6597 (2018)
Salcedo-Sanz, S., Del Ser, J., Landa-Torres, I., Gil-López, S., Portilla-Figueras, J.A.: The coral reefs optimization algorithm: a novel metaheuristic for efficiently solving optimization problems. Sci. World J. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/739768
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Graves, A., Antonoglou, I., Wierstra, D., Riedmiller, M.: Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. In: NIPS Deep Learning Workshop. 2013
Etinski, M., Corbalan, J., Labarta, J., Valero, M.: Understanding the future of energy-performance trade-off via DVFS in HPC environments. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 72, 579–590 (2012)
Mahmoud, H., Thabet, M., Khafagy, M.H., Omara, F.A.: An efficient load balancing technique for task scheduling in heterogeneous cloud environment. Clust. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03334-z
Muteeh, A., Sardaraz, M., Tahir, M.: MrLBA: multi-resource load balancing algorithm for cloud computing using ant colony optimization. Clust. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03322-3
Zhang, X., Wu, T., Chen, M., Wei, T., Zhou, J., Hu, S., Buyya, R.: Energy-aware virtual machine allocation for cloud with resource reservation. J. Syst. Softw. 147, 147–161 (2019)
Al-Dulaimy, A., Itani, W., Zantout, R., Zekri, A.: Type-aware virtual machine management for energy efficient cloud data centers. Sustain. Comput. 19, 185–203 (2018)
Kumar, N., Vidyarthi, D.P.: A novel energy-efficient scheduling model for multi-core systems. Clust. Comput. 24, 643–666 (2021)
Safari, M., Khorsand, R.: PL-DVFS: combining power-aware list-based scheduling algorithm with DVFS technique for real-time tasks in cloud computing. J. Supercomput. 74, 5578–5600 (2018)
Juiz, C., Bermejo, B.: The CiS2: a new metric for performance and energy trade-off in consolidated servers. Clust. Comput. 23, 2769–2788 (2020)
Sharma, Y., Si, W., Sun, D., Javadi, B.: Failure-aware energy-efficient VM consolidation in cloud computing systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 94, 620–633 (2019)
Dimiduk, D.M., Holm, E.A., Niezgoda, S.R.: Perspectives on the impact of machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence on materials, processes, and structures engineering. Integr. Mater. Manuf. Innov. 7(3), 157–172 (2018)
Ding, D., Fan, X., Zhao, Y., Kang, K., Yin, Q., Zeng, J.: Q-learning based dynamic task scheduling for energy-efficient cloud computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 108, 361–371 (2020)
Zhang, Q., Lin, M., Yang, L.T., Chen, Z., Li, P.: Energy-efficient scheduling for real-time systems based on deep Q-learning model. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 4(1), 132–141 (2017)
Peng, Z., Lin, J., Cui, D., Li, O., He, J.: A multi-objective trade-off framework for cloud resource scheduling based on the Deep Q-network algorithm. Clust. Comput. 23, 2753–2767 (2020)
Zhang, Q., Lin, M., Yang, L.T., Chen, Z., Khan, S.U., Li, P.: A double deep Q-learning model for energy-efficient edge scheduling. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 12(5), 739–749 (2018)
Shamshirband, S., Fathi, M., Chronopoulos, A.T., Montieri, A., Palumbo, F., Pescapè, A.: Computational intelligence intrusion detection techniques in mobile cloud computing environments: review, taxonomy, and open research issues. J. Inf. Security Appl. 55, 102582 (2020)
Wang, J., Jiang, C., Zhang, K., Hou, X., Ren, Y., Qian, Y.: Distributed Q-learning aided heterogeneous network association for energy-efficient IIoT. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 16(4), 2756–2764 (2019)
Jena, U.K., Das, P.K., Kabat, M.R.: Hybridization of meta-heuristic algorithm for load balancing in cloud computing environment. J. King Saud Univ. (2020)
Shaw, R., Howley, E., Barrett, E.: Applying Reinforcement Learning towards automating energy efficient virtual machine consolidation in cloud data centers. Inf. Syst. 2021, 101722 (2021)
Liu, N., Li, Z., Xu, J., Xu, Z., Lin, S., Qiu, O., Tang, J., Wang, Y., A hierarchical framework of cloud resource allocation and power management using deep reinforcement learning. In 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), pp. 372–382. IEEE, 2017
Jaiswal, A., Kumar, S., Dohare, U. Green Computing in Heterogeneous Internet of Things: Optimizing Energy Allocation Using SARSA-based Reinforcement Learning. In 2020 IEEE 17th India Council International Conference (INDICON), pp. 1–6. IEEE, 2020
Zhao, R., Wang, X., Xia, J., Fan, L.: Deep reinforcement learning based mobile edge computing for intelligent Internet of Things. Phys. Commun. 43, 101184 (2020)
Duggan, M., Flesk, K., Duggan, J., Howley, E., Barrett. E. A reinforcement learning approach for dynamic selection of virtual machines in cloud data centres. In 2016 Sixth International Conference on Innovative Computing Technology (INTECH), pp. 92–97. IEEE, 2016
Lin, X., Wang, Y., Pedram, M. A reinforcement learning-based power management framework for green computing data centers. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Engineering (IC2E), pp. 135–138. IEEE, 2016
Asghari, A., Sohrabi, M.K., Yaghmaee, F.: Online scheduling of dependent tasks of cloud’s workflows to enhance resource utilization and reduce the makespan using multiple reinforcement learning-based agents. Soft. Comput. 24(21), 16177–16199 (2020)
Asghari, A., Sohrabi, M.K., Yaghmaee, F.: A cloud resource management framework for multiple online scientific workflows using cooperative reinforcement learning agents. Computer Networks (2020): 107340
Asghari, A., Sohrabi, M.K., Yaghmaee, F.: Task scheduling, resource provisioning, and load balancing on scientific workflows using parallel SARSA reinforcement learning agents and genetic algorithm. J. Supercomput. 77(3), 2800–2828 (2021)
Yang, J., Jiang, B., Lv, Z., Choo, K.-K.R.: A task scheduling algorithm considering game theory designed for energy management in cloud computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 105, 985–992 (2020)
Sofia, A.S., GaneshKumar, P.: Multi-objective task scheduling to minimize energy consumption and makespan of cloud computing using NSGA-II. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 26(2), 463–485 (2018)
Li, K.: Scheduling parallel tasks with energy and time constraints on multiple manycore processors in a cloud computing environment. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 82, 591–605 (2018)
Jararweh, Y., Issa, M.B., Daraghmeh, M., Al-Ayyoub, M., Alsmirat, M.A.: Energy efficient dynamic resource management in cloud computing based on logistic regression model and median absolute deviation. Sustain. Comput. 19, 262–274 (2018)
Han, S., Min, S., Lee, H.: Energy efficient VM scheduling for big data processing in cloud computing environments. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01361-8
Safari, M., Khorsand, R.: Energy-aware scheduling algorithm for time-constrained workflow tasks in DVFS-enabled cloud environment. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 87, 311–326 (2018)
Moghaddam, M.J., Esmaeilzadeh, A., Ghavipour, M., Khadem-Zadeh, A.: Minimizing virtual machine migration probability in cloud computing environments. Clust. Comput. 23, 3029–3038 (2020)
Lu, Y., Sun, N.: An effective task scheduling algorithm based on dynamic energy management and efficient resource utilization in green cloud computing environment. Clust. Comput. 22(1), 513–520 (2019)
Garg, R., Mittal, M.: Reliability and energy efficient workflow scheduling in cloud environment. Clust. Comput. 22(4), 1283–1297 (2019)
Dong, S., Jain, R.: Energy-efficient scheme based on user task characteristic in virtual cloud platform. Clust. Comput. 23, 1125–1135 (2020)
Kumar, G.G., Vivekanandan, P.: Energy efficient scheduling for cloud data centers using heuristic based migration. Clust. Comput. 22, 14073–14080 (2019)
Garg, N., Singh, D., Goraya, M.S.: Energy and resource efficient workflow scheduling in a virtualized cloud environment. Clust. Comput. 24, 767–797 (2021)
Ibrahim, H., Aburukba, R.O., El-Fakih, K.: An integer linear programming model and adaptive genetic algorithm approach to minimize energy consumption of cloud computing data centers. Comput. Electr. Eng. 67, 551–565 (2018)
Fard, S.Y.Z., Sohrabi, M.K., Ghods, V.: Energy-aware and proactive host load detection in virtual machine consolidation. Inf. Technol. Control 50(2), 332–341 (2021)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement learning: an introduction. MIT Press, New York (2018)
Barto, A.G., Mahadevan, R.: Recent advances in hierarchical reinforcement learning. Discret. Event Dyn. Syst. 13(1–2), 41–77 (2003)
Watkins, C.J.C.H., Dayan, C.P.: Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 8(3–4), 279–292 (1992)
Abbasi, A.A., Javed, S., Shamshirband, S.: An intelligent memory caching architecture for data-intensive multimedia applications. Multimed.Tools Appl. 80, 16743–16761 (2021)
Wang, Y., Liu, H., Zheng, W., Xia, Y., Li, Y., Chen, P., Guo, K., Xie, H.: Multi-objective workflow scheduling with deep-Q-network-based multi-agent reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 7, 39974–39982 (2019)
Rahmani, F., Joloudari, J.H., Shamshirband, S., Mostafavi, S.A.: Game theory and Evolutionary-optimization methods applied to resource allocation problems in emerging computing environments: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.11355 (2020)
Littman, M.L.: Value-function reinforcement learning in Markov games. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2(1), 55–66 (2001)
Sohrabi, M.K., Azgomi, H.A.: Survey on the combined use of optimization methods and game theory. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 27, 59–80 (2020)
Arroba, P., Moya, J.M., Ayala, J.L., Buyya, R.: Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling-aware dynamic consolidation of virtual machines for energy efficient cloud data centers. Concurr. Comput. 29, e4067 (2017)
Tang, Z., Qi, L., Cheng, Z., et al.: An energy-efficient task scheduling algorithm in DVFS-enabled cloud environment. J. Grid Comput. 14, 55–74 (2016)
Mishra, S.K., Parida, P.P., Sahoo, S., Sahoo, B., Jena, S.K.: Improving energy usage in cloud computing using DVFS. In: Progress in Advanced Computing and Intelligent Engineering, pp. 623–632. Singapore, Springer (2018)
Shirvani, M.H., Rahmani, A.M., Sahafi, A.: A survey study on virtual machine migration and server consolidation techniques in DVFS-enabled cloud datacenter: taxonomy and challenges. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 32(3), 267–286 (2020)
Wu, T., Gu, H., Zhou, J., Wei, T., Liu, X., Chen, M.: Soft error-aware energy-efficient task scheduling for workflow applications in DVFS-enabled cloud. J. Syst. Architect. 84, 12–27 (2018)
Azgomi, H., Sohrabi, M.K.: A novel coral reefs optimization algorithm for materialized view selection in data warehouse environments. Appl. Intell. 49, 3965–3989 (2019)
Asghari, A., Sohrabi, M.K.: Combined use of coral reefs optimization and reinforcement learning for improving resource utilization and load balancing in cloud environments. Computing 103, 1545–1567 (2021)
Ahuja, S.P., Muthiah, K.: Advances in green cloud computing. In: Green computing strategies for competitive advantage and business sustainability, pp. 1–16. IGI Global (2018)
Zakarya, M., Gillam, L.: Energy efficient computing, clusters, grids and clouds: a taxonomy and survey. Sustain. Comput. 14, 13–33 (2017)
Ali, S.A., Affan, M., Alam, M. A study of efficient energy management techniques for cloud computing environment. 2019 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), 2019, pp. 13–18
Clark, C., Fraser, K., Hand, S., Hansen, J.G., Jul, E., Limpach, C., Pratt, I., Warfield, A.: Live migration of virtual machines. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Symposium on Networked Systems Design & Implementation-Volume 2, pp. 273–286. 2005
Davis, L.: Applying adaptive algorithms to epistatic domains. In: IJCAI: Proceedings of the 9th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 162–164 (1985)
Xu, F., Yang, F., Zhao, C., Wu, S.: Deep reinforcement learning based joint edge resource management in maritime network. China Commun. 17(5), 211–222 (2020)
Saadatfar, H., Khosravi, S., Joloudari, J.H., Mosavi, A., Shamshirband: S. A new K-nearest neighbors classifier for big data based on efficient data pruning. Mathematics 8(2), 286 (2020)
Badshah, A., Ghani, A., Shamshirband, S., Aceto, G., Pescapè, A.: Performance-based service-level agreement in cloud computing to optimise penalties and revenue. IET Commun. 14(7), 1102–1112 (2020)
Calheiros, R.N., Ranjan, R., Beloglazov, A., De Rose, A.F., Buyya, C.: CloudSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Software 41(1), 23–50 (2011)
Chen, W., Deelman, E., Workflowsim: A toolkit for simulating scientific workflows in distributed environments. In: IEEE 8th International Conference on E-science (e-science), 2012, pp. 1–8. IEEE, 2012
https://confluence.pegasus.isi.edu/display/pegasus/WorkflowGenerator. Accessed 5 Jan 2020
Juve, G., Chervenak, A., Deelman, E., Bharathi, S., Mehta, G., Vahi, K.: Characterizing and profiling scientific workflows. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 29(3), 682–692 (2013)
Vasile, M.-A., Pop, F., Tutueanu, R.I., Cristea, V., Kołodziej, J.: Resource-aware hybrid scheduling algorithm in heterogeneous distributed computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 51, 61–71 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asghari, A., Sohrabi, M.K. Combined use of coral reefs optimization and multi-agent deep Q-network for energy-aware resource provisioning in cloud data centers using DVFS technique. Cluster Comput 25, 119–140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03368-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03368-3