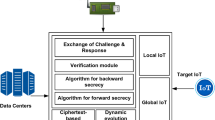
Abstract
Internet of Things (IoT) is a heterogeneous environment where multiple devices/consumers can interest/request for the same chunk of content at the same time with the need for source authenticity. According to the current NDN policy, only one user can verify the content authenticity using a digital signature. However, the digital signature is generated for one particular user whose public key and identity have been used. As the content can be cached and multicast to all the users whose interest is awaiting in the Pending Interest Table (PIT). Unfortunately, only one user is able to verify the content authenticity while the rest can just receive the content. To solve this, we designed a novel multi-cast signature solution for NDN-based IoT networks in which the consumers can verify the source of the content provider. The proposed scheme obeys the forwarding and caching policy of NDN. Besides, the designed scheme can prevent cache pollution attacks, content poisoning attacks, denial of service attacks, and interest flooding attacks. For efficiency, we compared our newly designed scheme with some Identity-Based Signature (IBS) in terms of computation time and communication overhead. The results show significant improvements in both computation time and communication overhead. In addition, we also validate the designed scheme using the familiar security validation tool AVISPA. Finally, we provide a robust application scenario of the designed scheme on NDN-based IoT.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated/analyzed during this are included in this article.
References
Datta, S.K., Bonnet, C.: Integrating named data networking in internet of things architecture. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), pp. 1–2 (2016)
Nour, B., Khedher, H.I., Moungla, H., Afifi, H., Li, F., Sharif, K., Khelifi, H., Guizani, M.: Internet of things mobility over information-centric/named-data networking. IEEE Internet Comput. 24(1), 14–24 (2019)
Nour, B., Khelifi, H., Hussain, R., Mastorakis, S., Moungla, H.: Access control mechanisms in named data networks: a comprehensive survey (2020). https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.04624
Shi, W., Cao, J., Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Xu, L.: Edge computing: vision and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 3(5), 637–646 (2016)
Pan, J., Paul, S., Jain, R.: A survey of the research on future internet architectures. IEEE Commun. Mag. 49(7), 26–36 (2011)
Ullah, S.S., Hussain, S., Gumaei, A., AlSalman, H.: A secure ndn framework for internet of things enabled healthcare. Comput. Mater. Contin. 67(1), 223–240 (2021)
Aceves, G.L., Barijough, M.M.M.: Efficient multicasting in content-centric networks using datagrams. In: 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 1–6 (2016)
Zhang, L., Afanasyev, A., Burke, J., Jacobson, V., Claffy, K.C., Crowley, P.P., et al.: Named data networking. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 44(3), 66–73 (2014)
Tourani, R., Misra, S., Mick, T., Panwar, G.: Security, privacy, and access control in information-centric networking: a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 20(1), 566–600 (2017)
Ullah, S.S., Ullah, I., Khattak, H., Khan, M.A., Adnan, M., Hussain, S., Amin, N.U., Khattak, M.A.K.: A lightweight identity-based signature scheme for mitigation of content poisoning attack in named data networking with internet of things. IEEE Access 8, 98910–98928 (2020)
Yu, L., Ai, H., Hhoi, D.O.: Countermeasures of interest flooding attack in named data networking: a survey. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0020720920983518
Nguyen, T., Marchal, X., Doye, G., Cholez, T., Cogranne, R., Content poisoning in named data networking: comprehensive characterization of real deployment. In: 2017 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM), pp. 72–80 (2017)
Khelifi, H., Luo, S., Nour, B., Shah, S.C.: Security and privacy issues in vehicular named data networks: an overview. Mob. Inf. Syst. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5672154
Rehman, M., Khattakh, H., Alzahrani, A.S., Ullah, I., Adnan, M., Ullah, S.S., Amin, N.U., Hussain, H., Khattak, S.J.: A lightweight nature heterogeneous generalized signcryption (HGSC) scheme for named data networking-enabled internet of things. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 1–20 (2020)
Bellare, M., Boldyreva, A., Kurosawa, K., Staddon, J.: Multi-recipient encryption schemes: how to save on bandwidth and computation without sacrificing security. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 53(11), 3927–3943 (2007)
Han, Y., Gui, X.: Multi-recipient signcryption for secure group communication. In: 2009 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, pp. 161–165 (2009)
Shamir, A.: Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes. Advances in Cryptology, Proceedings of CRYPTO’84, Santa Barbara, California, USA, 19–22 August 1984, vol. 196, pp. 47–53 (1984)
Boneh, D., Franklin, M.: Identity based encryption from the weil pairing. Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2001, 21st Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, California, USA, 19–23 August 2001, Proceedings, Springer, New York, USA, vol. 2139, pp. 213–229 (2001)
Tseng, Y.H., Huang, Y.M., Chang, Y.J.: Privacy-preserving multireceiver ID-based encryption with provable security. Int. J. Commun. Syst. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.2395
Han, W., Zhu, Z.: An ID-based mutual authentication with key agreement protocol for multiserver environment on elliptic curve cryptosystem. Int. J. Commun. Syst. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.2405
Barreto, P., Libert, B., McCullagh, N.: Efficient and provably-secure identity-based signature and signcryption from bilinear maps. In: Advances in Cryptology ASIACRYPT’05. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3788, pp. 515–532 (2005)
Chuang, Y.H., Tseng, Y.M.: Towards generalized ID-based user authentication for mobile multi-server environment. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 25(4), 447–460 (2012)
Delos, O., Quisquater, J.J.: An identity-based signature scheme with bounded life-span. In: Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO’94, 14th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, California, USA, 21–25 August 1994, Proceedings, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, New York, USA, vol. 839, pp. 83–994 (1994)
Han, K., Chan, Y.Y., Shon, T., Park, J., Kim, K.: A scalable and efficient key escrow model for lawful interception of IDBC-based secure communication. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 24(4), 461–472 (2011)
Smart, N.P.: An identity based authenticated key agreement protocol based on the weil pairing. Electron. Lett. 38, 630–632 (2001)
Popescu, C.: An efficient ID-based group signature scheme. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Inform. 47(2), 29–36 (2002)
Zhang, F., Kim, K.: ID-based blind signature and ring signature from pairings. In: Advances in Cryptology-ASIACRYPT 2002, 8th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Queenstown, New Zealand, 1–5 December 2002, Proceedings, Springer, New York, USA, vol. 2501, pp. 533–547 (2002).
Zhang, F., Kim, K.: Efficient id-based blind signature and proxy signature from bilinear pairings. In: ACISP’03 Proceedings of the 8th Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, vol. 2727, pp. 312–323, Springer, Berlin (2003)
Ullah, S., Din, N.: Blind signcryption scheme based on hyper elliptic curves cryptosystem. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14, 917–932 (2021)
Zhang, L., Hu, Y., Wu, Q.: Short signature from the bilinear pairing. Information Computing and Applications (ICICA 2010), LNCS, pp. 111–118. Springer , Berlin (2010)
Yasmin, R.: An efficient authentication framework for wireless sensor networks. Ph.D. thesis: School of Computer Science College of Engineering and Physical Sciences, The University of Birminghams (2012). http://etheses.bham.ac.uk/id/eprint/3774
Sharma, N., Sharma, B.K.: Identity-based signature scheme using random oracle model. J. Comput. Math. Sci. 9(4), 254–263 (2018)
Yuan, E., Wang, L., Cheng, S., Ao, H., Guo, Q.: A key management scheme based on pairing-free identity based digital signature algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Sensors 20(6), 1543 (2020)
Liu, J.K., Baek, J., Zhou, J., Yang, Y.: Efficient online/offline identity-based signature for wireless sensor network. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 9(4), 287–296 (2010)
Sharma, G., Bala, S., Verma, A.K.: PF-IBS: pairing-free identity based digital signature algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 97, 1185–1196 (2017)
Debiao, H., Jianhua, C., Jin, H.: Identity-based digital signature scheme without bilinear pairings. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2011/079 (2011). https://ia.cr/2011/079
Bashirpour, H., Bashirpour, S., Shamshirband, S., Chronopoulos, A.T.: An imprsensors. ital signature protocol to multi-user broadcast authentication based on elliptic curve cryptography in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Math. Comput. Appl. 23(2), 1–17 (2018)
Rao, R.R.V.K., Gayathri, N.B., Reddy, P.V.: Identity-based directed signature scheme without bilinear pairings. J. Mech. Math. Sci. 14(2), 335–353 (2019)
Watro, R.J., Kong, D., Cuti, S.F., Gardiner, C., Lynn, C., Kruus, P.: Tinypk: Securing sensor networks with public key technology. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Workshop on Security of Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks, pp. 59–64. Washington DC, USA (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1029102.1029113
Rivest, R.L., Shamir, A., Adleman, L.M.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 21(2), 120–126 (1978)
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22(6), 44–654 (1976)
Wong, K.H.M., Zheng, Y., Cao, J., Wang, S.: A dynamic user authentication scheme for wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Sensor Networks, Ubiquitous, and Trustworthy Computing (SUTC'06). Taichung, Taiwan (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/SUTC.2006.1636182
Das, M.L.: Two-factor user authentication in wireless sensor networks”. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 8(3), 1086–1090 (2009)
Sharma, G., Bala, S., Verma, A.K.: PF-IBS: pairing-free identity based digital signature algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 7, 185–1196 (2017)
James, S., Gayathri, N.B., Reddy, P.V.: New and efficient ID-based signature scheme with message recovery using bilinear pairings over elliptic curves. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 120(5), 1405–1422 (2018)
Yaduvanshi, R., Mishra, S.: An efficient and secure pairing free short ID-based signature scheme over elliptic curve. SSRN Electron. J. (2019). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3351027
Mishra, S., Yaduvanshi, R., Dubey, K., Rajpoot, P.: ESS‐IBAA: Efficient, short, and secure ID‐based authentication algorithm for wireless sensor network. Int. J. Commun. Syst. (2021). https://www.x-mol.com/paper/1371008734268440576
Dolev, D., Yao, A.: On the security of public key protocols. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 29(2), 198–208 (1983)
Sahoo, S.S., Mohanty, S., Majhi, B.: An improved and secure two-factor dynamic id based authenticated key agreement scheme for multiserver environment. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 101, 1307–1333 (2018)
Armando, A., Basin, D., Boichut, Y., Chevalier, Y., Compagna, L., Cuéllar, J., Drielsma, P.H., Héam, P.-C., Kouchnarenko, O., Mantovani, J., Mödersheim, S., von Oheimb, D., Rusinowitch, M., Santiago, J., Turuani, M., Viganò, L., Vigneron, L.: The avispa tool for the automated validation of internet security protocols and applications. In: International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, pp. 281–285, Springer (2005)
A.A. V.: Internet security protocols and applications (2015). http://www.avispa-project.org/
Cao, X., Kou, W., Du, X.: A pairing-free identity-based authenticated key agreement protocol with minimal message exchanges. Inf. Sci. 180(15), 28952903 (2010)
Hussain, S., Ullah, I., Khattak, H., Khan, M.A., Chen, C.M., Kumari, S.: A lightweight and provable secure identity-based generalized proxy signcryption (IBGPS) scheme for Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 58, 102625 (2021)
Khan, M.A., Ullah, I., Kumar, N., Oubbati, O.S., Qureshi, I., Noor, F., Ullah, F.: An efficient and secure certificate-based access control and key agreement scheme for flying ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 70, 4839–4851 (2021)
Funding
This work is also supported by the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, University of Malaya under Postgraduate Research Grant (PG035-2016A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, S., Ullah, S.S. & Ali, I. An efficient content source verification scheme for multi-receiver in NDN-based Internet of Things. Cluster Comput 25, 1749–1764 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03384-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03384-3