Abstract
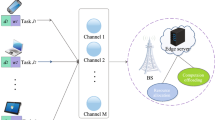
The method of charging mobile devices with wireless power transfer (WPT) from the base station (BS) integrated with mobile edge computing (MEC) increases the potential of MEC. The increasing demand for intelligent computation offloading requires effective decisions among local or remote computation specifically in wireless fading channels of the dynamic environment. Our main aim is to generate an effective offloading decision between local and remote computation in a real-time environment for each wireless channel while preserving optimal computation rate. In this article, we consider a wireless powered MEC system that governs a binary offloading decision to execute the task locally at the edge devices or the remote server. We propose a reinforcement learning based intelligent online offloading (RLIO) framework that adopts an optimal offloading action based on reinforcement methods. This framework acquires a worthy decision among local or remote computation for the time varying wireless channel conditions in dense networks. Numerical results show that the proposed framework can achieve optimal performance while preserving the computation time compared with existing optimization methods. Second, the average execution cost of RLIO is less than 0.4 ms per channel, which enables real-time and optimal offloading in dynamic and large-scale networks.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Notes
Details of product specifications are available at the website of Powercast Co. (http://www.powercastco.com).
References
Shuja, J., et al.: Analysis of vector code offloading framework in heterogeneous cloud and edge architectures. IEEE Access 5, 24542–24554 (2017)
Othman, M., et al.: Computation offloading cost estimation in mobile cloud application models. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 97(3), 4897–4920 (2017)
Kottursamy, K., Sadayappillai, B., Raja, G.: Optimized D-RAN aware data retrieval for 5G information centric networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 124, 1–22 (2021)
Chaudhry, S.A., et al.: An improved anonymous authentication scheme for distributed mobile cloud computing services. Clust. Comput. 22(1), 1595–1609 (2019)
Posner, J., et al.: Federated learning in vehicular networks: opportunities and solutions. IEEE Netw. 35(2), 152–159 (2021)
Ayyub, M., et al.: A comprehensive survey on clustering in vehicular networks: current solutions and future challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 124, 102729 (2022)
Abreha, H.G., Hayajneh, M., Serhani, M.A.: Federated learning in edge computing: a systematic survey. Sensors 22(2), 450 (2022)
Kaur, M.J., et al.: Futuristic communication systems using mobile edge computing. In: Energy Conservation Solutions for Fog-Edge Computing Paradigms, pp. 267–281. Springer, Singapore (2022)
Maray, M., Shuja, J.: Computation offloading in mobile cloud computing and mobile edge computing: survey, taxonomy, and open issues. Mob. Inf. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1121822
Ranaweera, P., Jurcut, A.D., Liyanage, M.: Survey on multi-access edge computing security and privacy. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 23(2), 1078–1124 (2021)
Atieh, A.T.: The next generation cloud technologies: a review on distributed cloud, fog and edge computing and their opportunities and challenges. ResearchBerg Rev. Sci. Technol. 1(1), 1–15 (2021)
Jararweh, Y.: Enabling efficient and secure energy cloud using edge computing and 5G. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 145, 42–49 (2020)
Al Ridhawi, I., et al.: Enabling intelligent IoCV services at the edge for 5G networks and beyond. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(8), 5190–5200 (2021)
Zhai, D., et al.: Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer at 5G new frequencies: channel measurement and network design. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 37(1), 171–186 (2018)
Mustafa, E., et al.: Joint wireless power transfer and task offloading in mobile edge computing: a survey. Clust. Comput. 25(4), 2429–2448 (2022)
Mazouzi, H., Achir, N., Boussetta, K.: DM2-ECOP: an efficient computation offloading policy for multi-user multi-cloudlet mobile edge computing environment. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 19(2), 1–24 (2019)
Mao, Y., Zhang, J., Letaief, K.B.: Joint task offloading scheduling and transmit power allocation for mobile-edge computing systems. In: 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC). IEEE (2017)
Bi, S., Zeng, Y., Zhang, R.: Wireless powered communication networks: an overview. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 23(2), 10–18 (2016)
Feng, J., et al.: Computation offloading and resource allocation for wireless powered mobile edge computing with latency constraint. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 8(5), 1320–1323 (2019)
Wang, F., et al.: Joint offloading and computing optimization in wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 17(3), 1784–1797 (2017)
Jehangiri, A.I., et al.: LiMPO: lightweight mobility prediction and offloading framework using machine learning for mobile edge computing. Clust. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03518-7
Qiu, X., et al.: Online deep reinforcement learning for computation offloading in blockchain-empowered mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68(8), 8050–8062 (2019)
Li, J., et al.: Deep reinforcement learning based computation offloading and resource allocation for MEC. In: 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC). IEEE (2018)
Zhou, S., Jadoon, W., Shuja, J.: Machine learning-based offloading strategy for lightweight user mobile edge computing tasks. Complexity (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6455617
Yan, J., Bi, S., Zhang, Y.J.A.: Offloading and resource allocation with general task graph in mobile edge computing: a deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 19(8), 5404–5419 (2020)
Jehangiri, A.I., et al.: Mobility-aware computational offloading in mobile edge networks: a survey. Clust. Comput. 24(4), 2735–2756 (2021)
Wang, J., et al.: Computation offloading in multi-access edge computing using a deep sequential model based on reinforcement learning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 57(5), 64–69 (2019)
Huang, L., Bi, S., Zhang, Y.-J.A.: Deep reinforcement learning for online computation offloading in wireless powered mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 19(11), 2581–2593 (2019)
Yu, Y., Zhang, J., Letaief, K.B.: Joint subcarrier and CPU time allocation for mobile edge computing. In: 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). IEEE (2016)
Mao, Y., et al.: Stochastic joint radio and computational resource management for multi-user mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 16(9), 5994–6009 (2017)
Bi, S., Zhang, Y.J.: Computation rate maximization for wireless powered mobile-edge computing with binary computation offloading. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 17(6), 4177–4190 (2018)
Zhou, F., Hu, R.Q.: Computation efficiency maximization in wireless-powered mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 19(5), 3170–3184 (2020)
Chen, X., et al.: Optimized computation offloading performance in virtual edge computing systems via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4005–4018 (2018)
Nduwayezu, M., Pham, Q.-V., Hwang, W.-J.: Online computation offloading in NOMA-based multi-access edge computing: a deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Access 8, 99098–99109 (2020)
Mahmood, A., et al.: Partial offloading in energy harvested mobile edge computing: a direct search approach. IEEE Access 8, 36757–36763 (2020)
Psomas, C., Krikidis, I.: Wireless powered mobile edge computing: offloading or local computation? IEEE Commun. Lett. 24(11), 2642–2646 (2020)
Wang, F.: Computation rate maximization for wireless powered mobile edge computing. In: 2017 23rd Asia–Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC). IEEE (2017)
Zhou, F., et al.: Computation rate maximization in UAV-enabled wireless-powered mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 36(9), 1927–1941 (2018)
Bi, S., et al.: Lyapunov-guided deep reinforcement learning for stable online computation offloading in mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 20(11), 7519–7537 (2021)
Chen, W., et al.: DRL based offloading of industrial IoT applications in wireless powered mobile edge computing. IET Commun. 16(9), 951–962 (2022)
Wang, J., et al.: Optimization for computational offloading in multi-access edge computing: a deep reinforcement learning scheme. Comput. Netw. 204, 108690 (2022)
Guo, S., et al.: Energy-efficient dynamic offloading and resource scheduling in mobile cloud computing. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2016—The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications. IEEE (2016)
Guo, Y., et al.: Distributed machine learning for multiuser mobile edge computing systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 16(3), 460–473 (2022)
Li, C., et al.: Dynamic offloading for multiuser multi-CAP MEC networks: a deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 70(3), 2922–2927 (2021)
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
This is the authors own work not submitted anywhere else.
Informed consent
NA.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, E., Shuja, J., Bilal, K. et al. Reinforcement learning for intelligent online computation offloading in wireless powered edge networks. Cluster Comput 26, 1053–1062 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03700-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03700-5