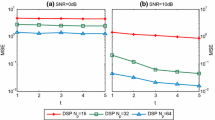
Abstract
Massive MIMO systems with a large number of antennas at the base station (BS) may significantly boost spectrum and energy efficiency. In massive MIMO systems, it’s important to have accurate channel state information (CSI) to get the most out of the large number of antennas and make sure the system works well. But because there are so many antennas at the base station (BS), the massive MIMO system has a lot of pilot overhead, which hurts system performance a lot. The spatial correlations between the signal sources in MIMO systems are low. This pattern of distribution makes it possible to use compressive sensing in massive MIMO systems to solve the channel estimation problem. In this study, we used the Shannon entropy function to come up with a new way to estimate the channel in the downlink of an FDD massive MIMO system. The Shannon entropy function is used as a sparsity regularizer for downlink channel estimation in the presented method to reduce the amount of work done by the pilot. The simulation results show that the proposed system outperforms existing compressive sensing (CS)-based channel estimation techniques in terms of NMSE performance and effectively lowers pilot overhead.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Larsson, E.G., Edfors, O., Tufvesson, F., Marzetta, T.L.: Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 52(2), 186–195 (2014)
Yang, B., Yunxue, Xu., Tong, J., Zhang, Y., Feng, Y., Yafei, Hu.: Tri-port antenna with shared radiator and self-decoupling characteristic for 5G smartphone application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70(6), 4836–4841 (2022)
Marzetta, T.L.: Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 9(11), 3590–3600 (2010)
Lappalainen, A., Rosenberg, C.: Can 5G fixed broadband bridge the rural digital divide? IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 6(2), 79–84 (2022)
Rusek, F., et al.: Scaling up MIMO: opportunities and challenges with very large arrays. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30(1), 40–60 (2013)
Conceição, F., Antunes, C.H., Gomes, M., Silva, V., Dinis, R.: Max-min fairness optimization in uplink cell-free massive MIMO using meta-heuristics. IEEE Trans. Commun. 70(3), 1792–1807 (2022)
Xu, Y., Yue, G., Mao, S.: User grouping for massive MIMO in FDD systems: new design methods and analysis. IEEE Access 2, 947–959 (2014)
Albataineh, Z., Hayajneh, K., Salameh, H.B., Dang, C., Dagmseh, A.: Robust massive MIMO channel estimation for 5G networks using compressive sensing technique. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 120, 153197 (2020)
Albataineh, Z., Andrawes, A., Abdullah, N.F., Nordin, R.: Energy-efficient beyond 5G multiple access technique with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer for the factory of the future. Energies 15, 6059 (2022)
Albataineh, Z.: Low-complexity near-optimal iterative signal detection based on MSD-CG method for uplink massive MIMO systems. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 116, 2549–2563 (2021)
Zammit, J., Wassell, I.J.: Adaptive block compressive sensing: toward a real-time and low-complexity implementation. IEEE Access 8, 120999–121013 (2020)
Albataineh, Z., Salem, F.: Two pairwise iterative schemes for high dimensional blind source separation. Int. J. Speech Technol. 24, 957–968 (2021)
Guo, J., Wang, L., Li, F., Xue, J.: CSI feedback with model-driven deep learning of massive MIMO systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 26(3), 547–551 (2022)
Albataineh, Z.: Blind decoding of massive MIMO uplink systems based on the higher order cumulants. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 103, 1835–1847 (2018)
Shi, Y., Zhu, X.X., Bamler, R.: Nonlocal compressive sensing-based SAR tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 57(5), 3015–3024 (2019)
Albataineh, Z., Salem, F.: New blind multiuser detection DS-CDMA algorithm using simplified fourth order cumulant matrices. IEEE Int. Symp. Circ. Syst. 2013, 1946–1949 (2013)
Bany Salameh, H., Shamekh, A.: Adaptive packet-size control for improved throughput in dynamic access networks. Clust. Comput. 24, 1935–1944 (2021)
Cao, H., Chan, Y.T., So, H.C.: Efficient sensing for compressive estimation of frequency of a real sinusoid. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 57(1), 744–750 (2021)
Ahmed, I., Khalil, A., Ahmed, I., Frnda, J.: Sparse signal representation, sampling, and recovery in compressive sensing frameworks. IEEE Access 10, 85002–85018 (2022)
Qi, C., Huang, Y., Jin, S., Wu, L.: Sparse channel estimation based on compressed sensing for massive MIMO systems. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (2015)
Gao, Z., Dai, L., Dai, W., Shim, B., Wang, Z.: Structured compressive sensing-based spatio-temporal joint channel estimation for FDD massive MIMO. IEEE Trans. Commun. 64(2), 601–617 (2016)
Abdel-Razeq, S., Al-Obiedollah, H., Bany Salameh, H.: Efficient user-channel pairing with power-domain sum-rate maximization in opportunistic hybrid OFDMA-NOMA IoT systems. Clust. Comput. 25, 2501–2514 (2022)
Xu, X., Liu, M., Xiong, J., et al.: Key technology and application of millimeter wave communications for 5G: a survey. Clust. Comput. 22(Suppl 5), 12997–13009 (2019)
Nandhini, S.A., Radha, S., Kishore, R.: Efficient compressed sensing based object detection system for video surveillance application in WMSN. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(2), 1905–1925 (2018)
Dai, L., Gao, Z., Wang, Z., Yang, Z.: Spectrum-efficient superimposed pilot design based on structured compressive sensing for downlink large-scale MIMO systems. In: 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), pp. 1–4 (2014)
Kapula, P.R., Sridevi, P.V.: Channel estimation in 5G multi input multi output wireless communication using optimized deep neural framework. Clust. Comput. 25, 3517–3530 (2022)
Dai, L., Wang, J., Wang, Z., Tsiaflakis, P., Moonen, M.: Spectrum- and energy-efficient OFDM based on simultaneous multi-channel reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(23), 6047–6059 (2013)
Subitha, D., Mathana, J.M.: A novel low complexity downlink linear precoding algorithm for massive MIMO systems. Clust. Comput. 22(Suppl 6), 13645–13652 (2019)
Barbotin, Y., Hormati, A., Rangan, S., Vetterli, M.: Estimation of sparse MIMO channels with common support. IEEE Trans. Commun. 60(12), 3705–3716 (2012)
Qiu, Z., Zhou, S., Zhao, M., Zhou, W.: Low-complexity precoding by exploiting spatial sparsity in massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 21(7), 4740–4753 (2022)
Stanković, L., Sejdić, E., Stanković, S., Daković, M., Orović, I.: A tutorial on sparse signal reconstruction and its applications in signal processing. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 38(3), 1206–1263 (2018)
Fascista, A., De Monte, A., Coluccia, A., Wymeersch, H., Seco-Granados, G.: Low-complexity downlink channel estimation in mmWave multiple-input single-output systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 11(3), 518–522 (2022)
Albreem, M.A., Alhabbash, A.H., Shahabuddin, S., Juntti, M.: Deep learning for massive MIMO uplink detectors. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 24(1), 741–766 (2022)
Tropp, J.A., Gilbert, A.C.: Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 53(12), 4655–4666 (2007)
Needell, D., Tropp, J.A.: CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 26(3), 301–321 (2009)
Wang, Y., Yin, W.: Sparse signal reconstruction via iterative support detection. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 3(3), 462–491 (2010)
Huang, S., Tran, D.N., Tran, T.D.: Sparse signal recovery based on nonconvex entropy minimization. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3867–3871.https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2016 (2016)
Li, H., Lin, Z.: Accelerated proximal gradient methods for nonconvex programming. Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 28, 379–387 (2015)
Huang, S., Tran, T.D.: Sparse signal recovery via generalized entropy functions minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67(5), 1322–1337 (2019)
Al-Salihi, H., Al-Gharbawi, M., Said F.: Optimal pilot sequence design for machine learning based channel estimation in FDD massive mimo systems. In: 2021 ITU Kaleidoscope: Connecting Physical and Virtual Worlds (ITU K), pp. 1–5 (2021)
Sadeghi, N., Azghani, M.: Channel estimation using block sparse joint orthogonal matching pursuit in massive MIMO systems. In: 2021 26th International Computer Conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC), pp. 1–5 (2021)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZA and NA-Z wrote the main manuscript text and NA-Z prepared all figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. ZA and AM supervise the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Albataineh, Z., Al-Zoubi, N. & Musa, A. Channel estimation for massive MIMO system using the shannon entropy function. Cluster Comput 26, 3793–3801 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03783-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03783-0