Abstract
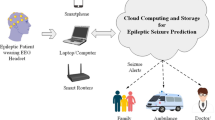
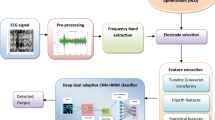
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an indispensable part of the healthcare system since it creates a link between the doctor and the patient for remote medical consultations. IoT-based seizure prediction detects seizures and monitors the health of patients remotely. The disease seizure is classified as the sudden and repeated malfunction of the neurons of the brain. To protect patients’ lives, it’s critical to recognise the risk of an epileptic seizure. In this research, a hybrid cuckoo finch optimisation is proposed using a tuned Deep-CNN (Deep-Convolutional Neural Network) classifier to recognise and predict the occurrence of epileptic seizures using electroencephalogram (EEG) signal data obtained through IoT. Initially, the gathered data is pre-processed and subjected to frequency band generation. Then there are the notable characteristics, such as statistical features, wavelet features, entropy-based features, spectral features, CPR (common spatial patterns), and logarithmic band power, which are extracted and concatenated. The optimal electrode selection is done by using the proposed hybrid cuckoo finch optimisation that inherits the characteristics of intrusive and attentive search agents. The data is finally normalised and fed to the proposed hybrid cuckoo finch optimisation tuned to Deep-CNN to classify the seizure disease. The specificity, accuracy, and sensitivity of the proposed model are 92.5212%, 97.7648%, and 95.6324%, which demonstrate the efficient performance of the proposed seizure prediction model.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets used for experimental analysis in this study are publically available and cited within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ioannou, P., Foster, D.L., Sander, J.W., Dupont, S., Gil-Nagel, A., Drogon O’Flaherty, E., Alvarez-Baron, E., Medjedovic, J.: The burden of epilepsy and unmet need in people with focal seizures. Brain Behav. 12(9), e2589 (2022)
Kato, M., Kada, A., Shiraishi, H., Tohyama, J., Nakagawa, E., Takahashi, Y., Akiyama, T., Kakita, A., Miyake, N., Fujita, A., Saito, A.M.: Sirolimus for epileptic seizures associated with focal cortical dysplasia type II. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 9(2), 181–192 (2022)
Yu, Y., Hasegawa, D., Kanazono, S., Saito, M.: Clinical characterization of epileptic seizures in Pomeranians with idiopathic epilepsy or epilepsy of unknown cause. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 36(6), 2113–2122 (2022)
B. Kapoor and B. Nagpal, "EEG Signals Acquisition, Analysis and Modeling for Classification in Healthcare," 2021 8th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 2021, pp. 468–473.
Ahmed, M.I.B., Alotaibi, S., Dash, S., Nabil, M., AlTurki, A.O.: A Review on machine learning approaches in identification of pediatric epilepsy. SN Comput. Sci. 3(6), 437 (2022)
Wu, J., Wang, Y., Xiang, L., Yixue, Gu., Yan, Y., Li, L., Tian, X., Jing, W., Wang, X.: Machine learning model to predict the efficacy of antiseizure medications in patients with familial genetic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 181, 106888 (2022)
Sánchez-Hernández, S.E., Salido-Ruiz, R.A., Torres-Ramos, S., Román-Godínez, I.: Evaluation of feature selection methods for classification of epileptic seizure EEG signals. Sensors 22(8), 3066 (2022)
Usman, S.M., Khalid, S., Bashir, Z.: Epileptic seizure prediction using scalp electroencephalogram signals. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 41(1), 211–220 (2021)
Le Van Quyen, M., Martinerie, J., Navarro, V., Boon, P., D’Havé, M., Adam, C., Renault, B., Varela, F., Baulac, M.: Anticipation of epileptic seizures from standard EEG recordings. The Lancet 357(9251), 183–188 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03591-1
Kapoor, B., Nagpal, B., Jain, P.K., Abraham, A., Gabralla, L.A.: Epileptic seizure prediction based on hybrid seek optimization tuned ensemble classifier using EEG signals. Sensors 23(1), 423 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010423
Boonyakitanont, P., Lek-Uthai, A., Chomtho, K., Songsiri, J.: A review of feature extraction and performance evaluation in epileptic seizure detection using EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 57, 101702 (2020)
Pandey, S.K., Janghel, R.R., Verma, A., Varma, K., Mishra, P.K.: automated epilepsy seizure detection from EEG signals using deep CNN model. In: Artificial intelligence and machine learning in 2D/3D medical image processing, pp. 15–30. CRC Press, Boca RAton (2020)
Zhang, T., Chen, W., Li, M.: AR based quadratic feature extraction in the VMD domain for the automated seizure detection of EEG using random forest classifier. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 31, 550–559 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2016.10.001
Bandarabadi, Mojtaba, Antonio Dourado, Cesar A. Teixeira, Theoden I. Netoff, and Keshab K. Parhi, "Seizure prediction with bipolar spectral power features using Adaboost and SVM classifiers", In proceedings of 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, pp. 6305–6308, 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610995
Chaovalitwongse, W.A., Fan, Y.J., Sachdeo, R.C.: On the time series k-nearest neighbor classification of abnormal brain activity. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, and Cybern A 37(6), 1005–1016 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2007.897589
Sharmila, A., Geethanjali, P.: DWT based detection of epileptic seizure from EEG signals using naive Bayes and k-NN classifiers. IEEE Access 4, 7716–7727 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2585661
Usman, S.M., Khalid, S., Aslam, M.H.: Epileptic seizures prediction using deep learning techniques. IEEE Access 8, 39998–40007 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2976866
Liu, C.-L., Xiao, B., Hsaio, W.-H., Tseng, V.S.: Epileptic seizure prediction with multi-view convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2955285
Saminu, S., Xu, G., Shuai, Z., Abd El Kader, I., Jabire, A.H., Ahmed, Y.K., Karaye, I.A., Ahmad, I.S.: A recent investigation on detection and classification of epileptic seizure techniques using EEG signal. Brain Sci. 11(5), 668 (2021)
Büyükçakır, B., Elmaz, F., Mutlu, A.Y.: Hilbert vibration decomposition-based epileptic seizure prediction with neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 119, 103665 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103665
Praveena, H.D., Subhas, C., Ramaaidu, K.: Automatic epileptic seizure recognition using relief feature selection and long short term memory classifier. J. Ambient Intell. Humanized Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02185-7
Ein Shoka, A.A., Alkinani, M.H., El-Sherbeny, A.S., El-Sayed, A., Dessouky, M.M.: Automated seizure diagnosis system based on feature extraction and channel selection using EEG signals. Brain Inf. 8(1), 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-021-00123-7
Borhade, R.R., Nagmode, M.S.: Modified atom search optimization-based deep recurrent neural network for epileptic seizure prediction using electroencephalogram signals. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 40(4), 1638–1653 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2020.10.001
Prathaban, B.P., Balasubramanian, R.: Prediction of epileptic seizures using grey wolf optimized model driven mathematical approach. Microprocessors Microsyst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103370
Sameer, M., Gupta, B.: Detection of epileptical seizures based on alpha band statistical features. Wireless Pers. Commun. 115, 909–925 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07542-5
Thara, D.K., PremaSudha, B.G., Xiong, F.: Epileptic seizure detection and prediction using stacked bidirectional long short term memory. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 128, 529–535 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.10.034
Savadkoohi, M., Oladunni, T., Thompson, L.: A machine learning approach to epileptic seizure prediction using electroencephalogram (EEG) Signal. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 40(3), 1328–1341 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2020.07.004
Kapoor, B., Nagpal, B., Alharbi, M.: Secured healthcare monitoring for remote patient using energy-efficient IoT sensors. Comput. Electr. Eng. 106, 108585 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2023.108585
Samie, Farzad, Sebastian Paul, Lars Bauer, and Jorg Henkel, "Highly efficient and accurate seizure prediction on constrained iot devices", In proceedings of Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), IEEE, pp. 955–960, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.23919/DATE.2018.8342147
Al-Janabi, Thair A., and Hamed S. Al-Raweshidy, "Optimised clustering algorithm-based centralised architecture for load balancing in IoT network", In proceeding of International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), IEEE, pp. 269–274, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ISWCS.2017.8108123
Islam, M.S., El-Hajj, A.M., Alawieh, H., Dawy, Z., Abbas, N., El-Imad, J.: EEG mobility artifact removal for ambulatory epileptic seizure prediction applications. Biomed. Signal Processing Control 55, 101638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101638
Hu, L., Zhiguo, Z.: EEG signal processing and feature extraction. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9113-2
Prathap, Parvathy, and T. Aswathy Devi, "EEG spectral feature based seizure prediction using an efficient sparse classifier", In proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), IEEE, pp. 721–725, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICICT1.2017.8342653
Aljalal, Majid, Ridha Djemal, Khalil AlSharabi, and Sutrisno Ibrahim, "Feature extraction of EEG based motor imagery using CSP based on logarithmic band power, entropy and energy", In proceedings of 1st International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS), IEEE, pp. 1–6, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CAIS.2018.8441995
Calvo, H., Paredes, J.L., Figueroa-Nazuno, J.: Measuring concept semantic relatedness through common spatial pattern feature extraction on EEG signals. Cognitive Syst. Res. 50, 36–51 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.03.004
Martis, R.J., Acharya, U.R., Tan, J.H., Petznick, A., Tong, L., Chua, C.K., Ng, E.Y.K.: Application of intrinsic time-scale decomposition (ITD) to EEG signals for automated seizure prediction. Int. J. Neural Syst. 23(05), 1350023 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065713500238
Yang, X.S., Deb, S.: Cuckoo search: recent advances and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 24(1), 169–174 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1367-1
Xue, J., Shen, B.: A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 8(1), 22–34 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/21642583.2019.1708830
Ebiaredoh-Mienye, S.A., Swart, T.G., Esenogho, E., Mienye, I.D.: A machine learning method with filter-based feature selection for improved prediction of chronic kidney disease. Bioengineering 9(8), 350 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080350
Obaido, G., Ogbuokiri, B., Swart, T.G., Ayawei, N., Kasongo, S.M., Aruleba, K., Mienye, I.D., Aruleba, I., Chukwu, W., Osaye, F., Egbelowo, O.F.: An interpretable machine learning approach for hepatitis B diagnosis. Appl. Sci. 12(21), 11127 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app122111127
Ebiaredoh-Mienye, S.A., Esenogho, E., Swart, T.G.: Integrating enhanced sparse autoencoder-based artificial neural network technique and softmax regression for medical diagnosis. Electronics 9(11), 1963 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9111963
Esenogho, E., Djouani, K., Kurien, A.M.: Integrating artificial intelligence internet of things and 5G for next-generation smartgrid: a survey of trends challenges and prospect. IEEE Access 10, 4794–4831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3140595
CHB-MIT Scalp EEG Database, “https://physionet.org/content/chbmit/1.0.0/”, accessed on March 2022.
Seina Database, “https://lib.siena.edu/az.php” accessed on March 2022.
Li, X., Wang, L., Sung, E.: AdaBoost with SVM-based component classifiers. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 21(5), 785–795 (2008)
Aydemir, O., Kayikcioglu, T.: Decision tree structure based classification of EEG signals recorded during two dimensional cursor movement imagery. J. Neurosci. Methods 229, 68–75 (2014)
Zolghadr-Asli, B., Bozorg-Haddad, O., Chu, X.: Crow search algorithm (CSA). Adv. Optim. Nat.-Inspired Algorithms (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5221-7_14
Jain, M., Singh, V., Rani, A.: A novel nature-inspired algorithm for optimization: squirrel search algorithm. Swarm Evol. Comput. 44, 148–175 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.02.013
Devarajan, K., Jyostna, E., Jayasri, K., Balasampath, V.: EEG-based epilepsy detection and prediction. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 6(3), 212 (2014). https://doi.org/10.7763/IJET.2014.V6.698
Akashah, P.E., Shita, A.N.: An IoT platform for seizure alert wearable device. In IOP Conf. Series 767(1), 012012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/767/1/012012
Dhinakaran, M., Phasinam, K., Alanya-Beltran, J., Srivastava, K., Babu, D.V., Singh, S.K.: A system of remote patients’ monitoring and alerting using the machine learning technique. J. Food Quality (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6274092
Sharma, N., Mangla, M., Mohanty, S.N., Gupta, D., Tiwari, P., Shorfuzzaman, M., Rawashdeh, M.: A smart ontology-based IoT framework for remote patient monitoring. Biomed. Signal Processing Control 68, 102717 (2021)
Nancy, A.A., Dakshanamoorthy Ravindran, P.M., Vincent, D.R., Srinivasan, K., Reina, D.G.: Iot-cloud-based smart healthcare monitoring system for heart disease prediction via deep learning. Electronics 11(15), 2292 (2022)
Rathod, N., Wankhade, S.: Optimizing neural network based on cuckoo search and invasive weed optimization using extreme learning machine approach. Neurosci. Inform. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuri.2022.100075
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Idea and Implementation by BK, Original manuscript preparation and results analysis by BK, manuscript editing by BK and BN, the entire work have been done under the supervision of BN. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kapoor, B., Nagpal, B. Hybrid cuckoo finch optimisation based machine learning classifier for seizure prediction using EEG signals in IoT network. Cluster Comput 27, 2239–2260 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-04059-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-04059-x