Abstract
In recent years, a trend for accelerating the economic, social and environmental development of cities through associations, organization and creation of synergies has been identified. Our investigation applies a grouping model in order to identify municipalities that could create optimal synergies towards the construction of competitive advantages. In order to achieve this task, we use tools of Fuzzy Logic to evaluate subjective and qualitative characteristic elements of different municipalities under Galois’ group theory. Results conclude on 32 different groups ordered in 7 different levels, relating 12 municipalities of a specific region according to 8 competitive variables. This work seeks to shed light in the conformation of groups under uncertain conditions and the deep examination of the characteristic competitive elements in a specific region for further policy and decision-making processes.

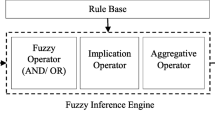
Source: Retrieved from Keropyan and Gil-Lafuente (2013)

Source: Self-elaborated
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Alfaro V, Gil-Lafuente A (2012) New methodological structure for the development of creative cities: the case of morelia-michoacán méxico. soft computing in management and business economics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 195–205
Alfaro V, Gil-Lafuente A, Alfaro G (2014) Methodological structure for the aggregation of municipalities under uncertain conditions. Inceptum Revista de Investigación en Ciencias de la Administración 7(13):215–228
Artin E (1998) Galois theory. Dover, New York
Begg I (1999) Cities and competitiveness. Urban stud 36(5–6):795–809
Bellman E, Zadeh L (1970) Decision-making in a fuzzy environment. Manag Sci 17(4):B-141
Budd L, Hirmis A (2004) Conceptual framework for regional competitiveness. Reg Stud 38(9):1015–1028
Caragliu A, Del Bo C, Nijkamp P (2011) Smart cities in Europe. J Urban Technol 18(2):65–82
Chapain C, Cooke P, De Propris L, MacNeill S, Mateos-Garcia J (2010) Creative clusters and innovation. http://www.nesta.org.uk/publications/creative-clusters-and-innovation-report#sthash.Zby2xjgh.dpuf. Accessed 7 September 2014
Chen C (2001) A fuzzy approach to select the location of the distribution center. Fuzzy Sets Syst 118(1):65–73
Compete Network (2010) Messages for Competitive European Cities. https://www.ljmu.ac.uk/EIUA/EIUA_Docs/COMPETE_Final_Report.pdf/. Last Accessed 21 June 2014
Creative Metropoles (2010) How to support creative industries. http://www.creativemetropoles.eu/. Last Accessed 7 December 2013
Delgado M, Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Martínez L (1998) Combining numerical and linguistic information in group decision making. Inf Sci 107(1):177–194
Denecke K, Ernâe M, Wismath S (2004) Galois connections and applications, vol 565. Springer, Newyork
Edwards S, Tardieu O (1984). Galois theory
Florida R (2008) Who’s your city?. Basic Books, USA
Gardiner B, Martin R, Tyler P (2006) Competitiveness, productivity and economic growth across the European regions. Reg Compet 30:55
Gil-Aluja J (1999) Elements for a theory of decision in uncertainty. Kluwer Academic Publishers, London
Gil-Aluja J, Gil-Lafuente A, Klimova A (2009) M-attributes algorithm for the selection of a company to be affected by a public offering. Inter J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl-Based Syst 17(03):333–343
Gil-Aluja J, Gil-Lafuente A, Merigó J (2011) Using homogeneous groupings in portfolio management. Expert Syst Appl 38(9):10950–10958
Gil-Lafuente J (2002) Algoritmos para la excelencia: claves para el éxito en la gestión deportiva. Milladoiro, Spain
Gil-Lafuente A, Paula L (2013) Algorithm applied in the identification of stakeholders. Kybernetes 42(5):674–685
Hansen T, Winther L (2011) Innovation, regional development and relations between high-and low-tech industries. European Urban Reg Stud 18(3):321–339
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E (2000) Linguistic decision analysis: steps for solving decision problems under linguistic information. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115(1):67–82
INAFED (2010) Encyclopedia of the Municipalities of Mexico. http://www.e-local.gob.mx/wb/ELOCALNew/municipios Last Accessed 21 August 2013
INEGI (2014) México en Cifras. http://www3.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/mexicocifras/default.aspx?e=16 Last Accessed 20 September 2014
Jiang Y, Fan Z, Ma J (2008) A method for group decision making with multi-granularity linguistic assessment information. Inf Sci 178(4):1098–1109
Kaufmann A, Gil-Aluja J (1988) Modelos para la investigación de los efectos olvidados. Milladoiro, Vigo (Spain)
Keropyan A, Gil-Lafuente A (2013) A personal selection model using galois group theory. Kybernetes 42(5):711–719
Ketels C (2013) Recent research on competitiveness and clusters: what are the implications for regional policy? Cambridge J Regions, Econ Soc 6(2):269–284
Malecki E (2007) Cities and regions competing in the global economy: knowledge and local development policies. Environ Plan 25(5):638
Nation J (1985) Some varieties of semi distributive lattices, universal algebra and lattice theory. Comer S, Lecture Notes in Mathematics Vol. 1149. Springer. NewYork, NY
Parkinson M, Clark G, Hutchins M, Simmie J, Verdonk H (2004) Competitive European cities: where do the core cities stand?. Office of the Deputy Prime Minister, London
Porter M (1996) What is strategy? Harvard Bus Rev 74(6):61–78
Porter M (1998) Clusters and the new economics of competition. Business Econ 76(6):77–90
Porter M (2000) Location, competition, and economic development: local clusters in a global economy. Econ Dev Q 14(1):15–34
Porter M (2003) The economic performance of regions. Reg Stud 37(6–7):545–546
Ribeiro R (1996) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making: a review and new preference elicitation techniques. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78(2):155–181
Rogerson R (1999) Quality of life and city competitiveness. Urban studies 36(5–6):969–985
Turok I (2004) Cities, regions and competitiveness. Reg Stud 38(9):1069–1083
UNDP (2014) Índice de Desarrollo Humano Municipal en México: nueva metodología. http://www.mx.undp.org Accessed 27 November 2014
Zadeh L (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–353
Zadeh L (1997) Toward a theory of fuzzy information granulation and its centrality in human reasoning and fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 90(2):111–127
Acknowledgments
The first author expresses his gratitude to the Mexican Council of Science and Technology (CONACYT) for the financial support given to this research project with the scholarship no. 381436 to graduate studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfaro-García, V.G., Gil-Lafuente, A.M. & Alfaro Calderón, G.G. A fuzzy approach to a municipality grouping model towards creation of synergies. Comput Math Organ Theory 23, 391–408 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10588-016-9233-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10588-016-9233-1