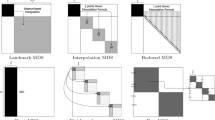
Abstract
Due to the large difference between seek time and transfer time in current disk technology, it is advantageous to perform large I/O using a single sequential access rather than multiple small random I/O accesses. However, prior optimal cost and data placement approaches for processing range queries over two-dimensional datasets do not consider this property. In particular, these techniques do not consider the issue of sequential data placement when multiple I/O blocks need to be retrieved from a single device. In this paper, we reevaluate the optimal cost of range queries by declustering two-dimensional datasets over multiple devices, and prove that, in general, it is impossible to achieve the new optimal cost. This is because disks cannot facilitate two-dimensional sequential access which is required by the new optimal cost. Then we revisit the existing data allocation schemes under the new optimal cost, and show that none of them can achieve the new optimal cost. Fortunately, MEMS-based storage is being developed to reduce I/O cost. We first show that the two-dimensional sequential access requirement can not be satisfied by simply modeling MEMS-based storage as conventional disks. Then we propose a new placement scheme that exploits the physical properties of MEMS-based storage to solve this problem. Our theoretical analysis and experimental results show that the new scheme achieves almost optimal I/O costs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CMU CHIP project, 2002, http://www.lcs.ece.cmu.edu/research/MEMS.
Hewlett-packard laboratories atomic resolution storage, 2003, http://www.hpl.hp.com/research/storage.html.
K.A.S. Abdel-Ghaffar and A. El Abbadi, “Optimal allocation of two-dimensional data,” in International Conference on Database Theory, 1997, pp. 408–418.
M.J. Atallah and S. Prabhakar, “(Almost) optimal parallel block access for range queries,” in Nineteenth ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems, PODS, 2000, pp. 205–215.
R. Bhatia, R.K. Sinha, and C.M. Chen, “Declustring using golden ratio sequences,” in Proc. of International Conference on Data Engineering, 2000, pp. 271–280.
C. Chen and C.T. Cheng, “From discrepancy to declustering: Near-optimal multidimensional declustering strategies for range queries,” Journal of the ACM, vol. 51, no. 1, 2004.
H.C. Du and J.S. Sobolewski, “Disk allocation for cartesian product files on multiple-disk systems,” ACM Transactions of Database Systems, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 82–101, 1982.
C. Faloutsos and P. Bhagwat, “Declustring using fractals,” in Proc. of the 2nd Int. Conf. on Parallel and Distributed Information Systems, 1993, pp. 18–25.
C. Faloutsos and Y. Rong, “Spatial access methods using fractals: Algorithms and performance evaluation,” in Tech. Report. UMIACS-TR-89-31, CR-TR-2214, Department of Computer Science, University of Maryland, 1989.
K. Frikken, M.J. Atallah, S. Prabhakar, and R. Safavi-Naini, “Optimal parallel I/O for range queries through replication,” in Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Applications, 2002, pp. 669–678.
J. Griffin, S. Schlosser, G. Ganger, and D. Nagle, “Modeling and performance of MEMSBased storage devices,” in Proceedings of ACM SIGMETRICS, 2000, pp. 56–65.
J. Griffin, S. Schlosser, G. Ganger, and D. Nagle, “Operating systems management of MEMS based storage devices,” in Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI), 2000.
H.V. Jagadish, “Linear clustering of objects with multiple attributes,” in Proc. Int. Conf. on Management of Data (SIGMOD), 1990, pp. 332–342.
M.H. Kim and S. Pramanik, “Optimal file distribution for partial match retrieval,” in Proc. Int. Conf. on Management of Data (SIGMOD), 1988, pp. 173–182.
S. Prabhakar, K.A.S. Abdel-Ghaffar, D. Agrawal, and A. El Abbadi, “Cyclic allocation of two-dimensional data,” in International Conference on Data Engineering, 1998, pp. 94–101.
B. Seeger, “An analysis of schedules for performing multi-page requests,” Information Systems, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 387–407, 1996.
P. Vettider, M. Despont, U. Durig, W. Haberle, M.I. Lutwyche, H.E. Rothuizen, R. Stuz, R. Widmer, and G.K. Binnig, “The “millipede”-more than one thousand tips for future afm storage,” IBM Journal of Research and Development, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 323–340, 2000.
H. Yu, D. Agrawal, and A. El Abbadi, “Tabular placement of relational data on MEMS based storage devices,” in 29th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, 2003, pp. 680–693.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by: Sunil Prabhakar
This research is supported by the NSF grants under IIS-0220152 and CNF-0423336.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Agrawal, D. & Abbadi, A.E. Exploiting sequential access when declustering data over disks and MEMS-based storage. Distrib Parallel Databases 19, 147–168 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-006-8485-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-006-8485-z