Abstract
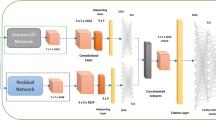
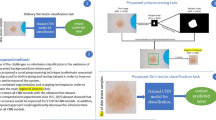
Skin cancer is a commonly occurring disease, which affects people of all age groups. Automated detection of skin cancer is needed to decrease the death rate by identifying the diseases at the initial stage. The visual inspection during the medical examination of skin lesions is a tedious process as the resemblance among the lesions exists. Recently, imaging-based Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) model is widely used to screen and detect the skin cancer. This paper is designed with automated Deep Learning with a class attention layer based CAD model for skin lesion detection and classification known as DLCAL-SLDC. The goal of the DLCAL-SLDC model is to detect and classify the different types of skin cancer using dermoscopic images. During image pre-processing, Dull razor approach-based hair removal and average median filtering-based noise removal processes take place. Tsallis entropy based segmentation technique is applied to detect the affected lesion areas in the dermoscopic images. Also, a DLCAL based feature extractor is used for extracting the features from the segmented lesions using Capsule Network (CapsNet) along with CAL and Adagrad optimizer. The CAL layer incorporated into the CapsNet is intended to capture the discriminative class-specific features to cover the class dependencies and effectively bridge the CapsNet for further process. Finally, the classification is carried out by the Swallow Swarm Optimization (SSO) algorithm based Convolutional Sparse Autoencoder (CSAE) known as SSO-CSAE model. The proposed DLCAL-SLDC technique is validated using a benchmark ISIC dataset. The proposed framework has accomplished promising results with 98.50% accuracy, 94.5% sensitivity and 99.1% specificity over the other methods interms of different measures.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ünver, H.M., Ayan, E.: Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic images with combination of YOLO and grabcut algorithm. Diagnostics 9(3), 72 (2019)
Karimkhani, C., Green, A., Nijsten, T., Weinstock, M., Dellavalle, R., Naghavi, M., Fitzmaurice, C.: The global burden of melanoma: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Br. J. Dermatol. 177, 134–140 (2017)
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Hao, Y., Xu, J., Thun, M.J.: Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69, 7–34 (2019)
Neelakandan, S., Paulraj, D.: A gradient boosted decision tree-based sentiment classification of twitter data. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut. Inf. Process. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219691320500277
Paulraj, D.: An automated exploring and learning model for data prediction using balanced CA-Svm. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01937-9
Kamalraj, R., Neelakandan, S., Ranjith Kumar, M., Chandra Shekhar Rao, V., Anand, R., Singh, H.: Interpretable filter based convolutional neural network (IF-CNN) for glucose prediction and classification using PD-SS algorithm. Measurement (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109804
Okur, E., Turkan, M.: A survey on automated melanoma detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 73, 50–67 (2018)
Satpathy, S., Das, S., Debbarma, S.: A new healthcare diagnosis system using an IoT-based fuzzy classifier with FPGA. J. Supercomput. 76(8), 5849–5861 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-03013-2
Berlin, M.A., Tripathi, S., et al.: IoT-based traffic prediction and traffic signal control system for smart city. Soft. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05896-x
Hasan, M.K., Elahi, M.T.E., Alam, M.A., Jawad, M.T.: DermoExpert: skin lesion classification using a hybrid convolutional neural network through segmentation, transfer learning and augmentation. medRxiv (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.02.21251038
Acosta, M.F.J., Tovar, L.Y.C., Garcia-Zapirain, M.B., Percybrooks, W.S.: Melanoma diagnosis using deep learning techniques on dermatoscopic images. BMC Med. Imaging 21(1), 1–11 (2021)
Seeja, R.D., Suresh, A.: Deep learning based skin lesion segmentation and classification of melanoma using support vector machine (SVM). Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev.: APJCP 20(5), 1555 (2019)
Li, Y., Shen, L.: Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors 18(2), 556 (2018)
Yap, J., Yolland, W., Tschandl, P.: Multimodal skin lesion classification using deep learning. Exp. Dermatol. 27(11), 1261–1267 (2018)
Khan, M.A., Akram, T., Zhang, Y.D., Sharif, M.: Attributes based skin lesion detection and recognition: a mask RCNN and transfer learning-based deep learning framework. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 143, 58–66 (2021)
Srinivasu, P.N., SivaSai, J.G., Ijaz, M.F., Bhoi, A.K., Kim, W., Kang, J.J.: Classification of skin disease using deep learning neural networks with MobileNet V2 and LSTM. Sensors 21(8), 2852 (2021)
Gazioğlu, B.S.A., Kamaşak, M.E.: Effects of objects and image quality on melanoma classification using deep neural networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 67, 102530 (2021)
Lee, T., Ng, V., Gallagher, R., Coldman, A., McLean, D.: Dullrazor®: a software approach to hair removal from images. Comput. Boil. Med. 27, 533–543 (1997)
Manikantan, K., Arun, B.V., Yaradoni, D.K.S.: Optimal multilevel thresholds based on Tsallis entropy method using golden ratio particle swarm optimization for improved image segmentation. Procedia Eng. 30, 364–371 (2012)
Toraman, S., Alakus, T.B., Turkoglu, I.: Convolutional CapsNet: a novel artificial neural network approach to detect COVID-19 disease from X-ray images using capsule networks. Chaos Solitons Fract. 140, 110122 (2020)
Hua, Y., Mou, L., Zhu, X.X.: Recurrently exploring class-wise attention in a hybrid convolutional and bidirectional LSTM network for multi-label aerial image classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 149, 188–199 (2019)
Saravanan, S., Hailu, M., Gouse, G.M., Lavanya, M., Vijaysai, R.: Optimized secure scan flip flop to thwart side channel attack in crypto-chip. Adv. Sci. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15357-1_34
Luo, W., Li, J., Yang, J., Xu, W., Zhang, J.: Convolutional sparse autoencoders for image classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(7), 3289–3294 (2017)
Hodashinsky, I., Sarin, K., Shelupanov, A., Slezkin, A.: Feature selection based on swallow swarm optimization for fuzzy classification. Symmetry 11(11), 1423 (2019)
Subbulakshmi, P.: Mitigating eavesdropping by using fuzzy based MDPOP-Q learning approach and multilevel Stackelberg game theoretic approach in wireless CRN. Cogn. Syst. Res. 52, 853–861 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.09.021
Połap, D., Winnicka, A., Serwata, K., Kęsik, K., Woźniak, M.: An intelligent system for monitoring skin diseases. Sensors 18(8), 2552 (2018)
Sikkandar, M.Y., Alrasheadi, B.A., Prakash, N.B., Hemalakshmi, G.R., Mohanarathinam, A., Shankar, K.: Deep learning based an automated skin lesion segmentation and intelligent classification model. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02537-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adla, D., Reddy, G.V.R., Nayak, P. et al. Deep learning-based computer aided diagnosis model for skin cancer detection and classification. Distrib Parallel Databases 40, 717–736 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-021-07360-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-021-07360-z