Abstract
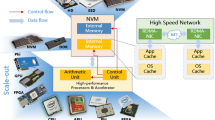
The CPU-Accelerator heterogeneous systems have demonstrated performance and efficiency benefits on DBMSs. However, the CPU-Cache-DRAM architecture can not fully utilize the bandwidth of DRAMs such that in-memory approach get limited improvement. To overcome this drawback, it is non-trivial to customize efficient domain-specific accelerators and efficiently shuttle data between the host memory space and accelerator. But even if high-performance accelerators are available for DBMS, it is challenging to integrate the software with accelerator non-intrusively. To address these problems, we propose a hardware-software co-designed system, database offloading engine (DOE), which contains hardware accelerator architecture—Conflux for effective SQL operation offloading, and a software DOE programming platform—DP2 for application integration and seamless harness of the computing power. We subtly partition each well-known relational operator, such as filter, join, group by, aggregate, and sort, and dynamically map these operators on multiple kernels in parallel. The DOE kernels work in streaming processing mode, over which the microarchitecture aggressively exploits data parallelism and memory bandwidth. The experiment results show that DOE achieves more than 100x and 10x performance improvement compared with PostgreSQL and MonetDB respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe, S., Fujimoto, K., Saeki, Y., et al.: Column-oriented database acceleration using FPGAS. In: ICDE, pp. 686–697. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2019.00067
Sirin, U., Ailamaki, A.: Micro-architectural analysis of olap: limitations and opportunities. Proc. VLDB Endow. 13(6), 840–853 (2020). https://doi.org/10.14778/3380750.3380755
Yuan, Y., Lee, R., Zhang, X.: The yin and yang of processing data warehousing queries on GPU devices. Proc. VLDB Endow. 6(10), 817–828 (2013). https://doi.org/10.14778/2536206.2536210
Lee, R., Zhou, M., Li, C., et al.: The art of balance: a rateupdb\(^{{\rm TM}}\) experience of building a CPU/GPU hybrid database product. Proc. VLDB Endow. 14(12), 2999–3013 (2021). https://doi.org/10.14778/3476311.3476378
Yan, G., Lu, W., Li, X., et al.: Comparative study of the domain-specific processors. Scientia Sinica Informationis (2022)
Lu, W., Chen, Y., Wu, J., et al.: Doe: database offloading engine for accelerating SQL processing. In: ICDEW, pp. 129–134. IEEE (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDEW55742.2022.00026
Wu, L., Lottarini, A., Paine, T.K., et al.: The q100 database processing unit. IEEE Micro. 35(3), 34–46 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/MM.2015.51
Sukhwani, B., Min, H., Thoennes, M.: et al.: Database analytics acceleration using FPGAS. In: PACT, pp. 411–420. IEEE (2012)
HeteroDB. Pg-strom. [EB/OL], https://github.com/heterodb/pg-strom (2021). Accessed 20 Feb 2023
Bakkum, P., Skadron, K.: Accelerating SQL database operations on a GPU with cuda. In: GPGPU-3, pp. 94–103 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1145/1735688.1735706
Kim, C., Chhugani, J., Satish, N., et al.: Fast: fast architecture sensitive tree search on modern CPUS and GPUS. In: SIGMOD, pp. 339–350 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1145/1807167.1807206
Sitaridi, E.A., Ross, K.A.: Gpu-accelerated string matching for database applications. VLDB J. 25(5), 719–740 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-015-0409-y
Kara, K., Alonso, G.: Fast and robust hashing for database operators. In: FPL, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/FPL.2016.7577353
Zhou, Z., Yu, C., Nutanong, S., et al.: A hardware-accelerated solution for hierarchical index-based merge-join. IEEE TKDE 31(1), 91–104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2018.2822707
Manev, K., Vaishnav, A., Kritikakis, C., et al.: Scalable filtering modules for database acceleration on FPGAS. In: HEART (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3337801.3337810
Xu, S., Bourgeat, T., Huang, T., et al.: Aquoman: an analytic-query offloading machine. In: MICRO, pp. 386–399. IEEE (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/MICRO50266.2020.00041
Balkesen, C., Kunal, N., Giannikis, G., et al.: Rapid: in-memory analytical query processing engine with extreme performance per watt. In: SIGMOD. ACM, pp. 1407–1419. (2018) https://doi.org/10.1145/3183713.3190655
Hemmatpour, M., Montrucchio, B., Rebaudengo, M., et al.: Analyzing in-memory nosql landscape. TKDE 34(4), 1628–1643 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2020.3002908
Najafi, M., Zhang, K., Sadoghi, M., et al.: Hardware acceleration landscape for distributed real-time analytics: virtues and limitations. In: ICDCS, pp. 1938–1948. IEEE (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDCS.2017.194
Sukhwani, B., Min, H., Thoennes, M., et al.: Database analytics: a reconfigurable-computing approach. IEEE Micro. 34(1), 19–29 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/MM.2013.107
Najafi, M., Sadoghi, M., Jacobsen, H.A.: Flexible query processor on FPGAS. Proc. VLDB Endow. 6(12), 1310–1313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.14778/2536274.2536303
Drumond, M., Daglis, A., Mirzadeh, N., et al.: The mondrian data engine. SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 45(2), 639–651 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3140659.3080233
Acknowledgements
Extension of Conference Paper [6]. This paper is supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 62002340, 61872336 and 62090020, in part by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDB44030100, and in part by Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS No. Y201923. The corresponding author is Wenyan Lu, Guihai Yan and Xiaowei Li.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HK and WL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, H., Lu, W., Chen, Y. et al. DOE: database offloading engine for accelerating SQL processing. Distrib Parallel Databases 41, 273–297 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-023-07427-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10619-023-07427-z