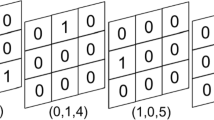
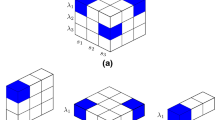
Abstract
Two-dimensional optical orthogonal codes (2-D OOCs) are of current practical interest in fiber-optic code-division multiple-access networks as they enable optical communication at lower chip rate to overcome the drawbacks of nonlinear effects in large spreading sequences of one-dimensional codes. A 2-D OOC is said to be optimal if its cardinality is the largest possible. In this paper, we develop some constructions for optimal 2-D OOCs using combinatorial design theory. As an application, these constructions are used to construct an infinite family of new optimal 2-D OOCs with auto-correlation 1 and cross-correlation 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel R.J.R., Buratti M.: Some progress on (v, 4, 1) difference families and optical orthogonal codes. J. Combin. Theory A 106, 59–75 (2004)
Baker C.: Extended Skolem sequences. J. Comb. Des. 3, 363–379 (1995)
Beth T., Jungnickel D., Lenz H.: Design Theory. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK (1999)
Bitan S., Etzion T.: Constructions for optimal constant weight cyclically permutable codes and difference families. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 41, 77–87 (Jan. 1995).
Brickell E.F., Wei V.K.: Optical orthogonal codes and cyclic block designs. Congr. Numer. 58, 175–192 (1987)
Buratti M.: A powerful method for constructing difference families and optimal optical orthogonal codes. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 5, 13–25 (1995)
Buratti M.: Recursive constructions for difference matrices and relative difference families. J. Comb. Des. 6, 165–182 (1998)
Buratti M.: Cyclic designs with block size 4 and related optimal optical orthogonal codes. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 26, 111–125 (2002)
Cao H., Wei R., Su Y.: Combinatorial constructions for optimal optical two-dimensional orthogonal codes. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 55, 1387–1394 (2009)
Chang Y.: Some cyclic BIBDs with block size four. J. Comb. Des. 12, 177–183 (2004)
Chang Y., Fuji-Hara R., Miao Y.: Combinatorial constructions of optimal optical orthogonal codes with weight 4. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 49, 1283–1292 (2003)
Chang Y., Ji L.: Optimal (4up, 5, 1) optical orthogonal codes. J. Comb. Des. 12, 346–361 (2004)
Chang Y., Miao Y.: Constructions for optimal optical orthogonal codes. Discrete Math. 261, 127–139 (2003)
Chang Y., Yin J.: Further results on optimal optical orthogonal codes with weight 4. Discrete Math. 279, 135–151 (2004)
Chu W., Colbourn C.J.: Optimal (v, 4, 2)-OOC of small orders. Discrete Math. 279, 163–172 (2004)
Chu W., Colbourn C.J.: Recursive constructions for optimal (v, 4, 2)-OOCs. J. Comb. Des. 12, 333–345 (2004)
Chu W., Golomb S.W.: A new recursive construction for optical orthogonal codes. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 49, 3072–3076 (2003)
Chung H., Kumar P.V.: Optical orthogonal codes—new bounds and an optimal construction. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 36, 866–873 (1990)
Chung F.R.K., Salehi J.A., Wei V.K.: Optimal optical orthogonal codes: Design, analysis, and applications. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 35, 595–604 (1989); correction, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 38, 1429 (May 1992).
Colbourn C.J., Dinitz J.H.: The CRC Handbook of Combinatorial Designs. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (2007)
Colbourn C.J., Hoffman D.G., Rees R.: A new class of divisible designs with block size three. J. Combin. Theory A 59, 73–89 (1992)
Fuji-Hara R., Miao Y.: Optimal optical orthogonal codes: Their bounds and new optimal constructions. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 46, 2396–2406 (2000)
Fuji-Hara R., Miao Y., Yin J.: Optimal (9v, 4, 1) optical orthogonal codes. SIAM J. Discrete Math. 14, 256–266 (2001)
Gallant R.P., Jiang Z., Ling A.C.H.: The spectrum of cyclic group divisible designs with block size three. J. Comb. Des. 7, 95–105 (1999)
Ge G., Yin J.: Constructions for optimal (v, 4, 1) optical orthogonal codes. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 47, 2998–3004 (2001)
Hall M. Jr.: Combinatorial Theory, 2nd edn. Wiley (1986).
Hanani H.: Balanced incomplete block designs and related designs. Discrete Math. 11, 255–369 (1975)
Kwong W.C., Yang G.C.: Extended carrier-hopping prime codes for wavelength-time optical code-division multiple access. IEEE Trans. Commun. 52, 1084–1091 (2004)
Ma S., Chang Y.: A new class of optimal optical orthogonal codes with weight five. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 50, 1848–1850 (2004)
Ma S., Chang Y.: Constructions of optimal optical orthogonal codes with weight five. J. Comb. Des. 13, 54–69 (2005)
Maric S.V., Lau V.K.N.: Multirate fiber-optic CDMA: system design and performance analysis. J. Lightwave Technol. 16, 9–17 (1998)
Maric S.V., Moreno O., Corrada C.: Multirate transmission in fiber-optic LAN’s using optical CDMA. J. Lightwave Technol. 14, 2149–2153 (1996)
Mendez A.J., Gagliardi R.M., Feng H.X.C., Heritage J.P., Morookian J.M.: Strategies for realizing optical cdma for dense, high-speed, long span, optical network applications. J. Lightwave Technol. 168, 1685–1695 (2000)
Mendez A.J., Gagliardi R.M., Hernandez V.J., Bennett C.V., Lennon W.j.: Design and performance analysis of wavelength/time (W/T) matrix codes for optical CDMA. J. Lightwave Technol. 21, 2524–2533 (2003)
Miyamoto N., Mizuno H., Shinohara S.: Optical orthogonal codes obtained from conics on finite projective planes. Finite Fields Th. App. 10, 405–411 (2004)
Omrani R., Kummar P.V.: Codes for optical CDMA. In: Proc. of SETA 2006. Springer-Verlags Lecture Notes in Computer Science Series, vol. 4086, pp. 34–46 (2006).
Peltesohn R.: Eine Losung der beiden Heffterschen Differenzenprobleme. Comp. Math. 6, 251–257 (1939)
Salehi J.A., Brackett C.A.: Code-division multiple access techniques in optical fiber networks: part 1 and part 2. IEEE Trans. Commun. 37, 824–842 (1989)
Shivaleela E.S., Selvarajan A., Srinivas T.: Two-dimensional optical orthogonal codes for fiber-optic cdma networks. J. Lightwave Technol. 23, 647–654 (2005)
Shivaleela E.S., Sivarajan K.N., Selvarajan A.: Design of a new family of two-dimensional codes for fiber-optic cdma networks. J. Lightwave Technol. 16, 501–508 (1998)
Tan̆evski L., Andonovic I.: Hybrid wavelength hopping/time spreading schemes for use in massive optical networks with increased security. J. Lightwave Technol. 14, 2636–2647 (1996)
Tan̆evski L., Andonovic I., Tur M., Budin J.: Massive optical LANs using wavelength hopping/time spreading with increased security. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 8, 935–937 (1996)
Tang Y., Yin J.: The combinatorial construction for a class of optimal optical orthogonal codes. Sci. China A 45, 1268–1275 (2002)
Yang G.C., Kwong W.C.: Two-dimensional spatial signature patterns. IEEE Trans. Commun. 44, 184–191 (1996)
Yang G.C., Kwong W.C.: Performance comparison of multiwavelength CDMA and WDMA+CDMA for fiber-optic networks. IEEE Trans. Communun. 45, 1426–1434 (1997)
Yim R.M.H., Chen L.R., Bajcsy J.: Design and performance of 2-D codes for wavelength-time optical CDMA. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 14, 714–716 (2002)
Yin J.: Some combinatorial constructions for optical orthogonal codes. Discrete Math. 185, 201–219 (1998)
Yin J.: A general construction for optimal cyclic packing designs. J. Combin. Theory A 97, 272–284 (2002)
Yin J.: Cyclic difference packing and covering arrays. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 37, 281–292 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Charles J. Colbourn.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Shan, X. & Yin, J. On constructions for optimal two-dimensional optical orthogonal codes. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 54, 43–60 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-009-9308-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10623-009-9308-9