Abstract
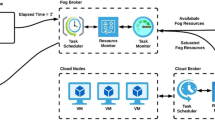
We present an energy-efficient thermal-aware real-time global scheduler for a set of hard real-time (HRT) tasks running on a multiprocessor system. This global scheduler fulfills the thermal and temporal constraints by handling two independent variables, the task allocation time and the selection of clock frequency. To achieve its goal, the proposed scheduler is split into two stages. An off-line stage, based on a deadline partitioning scheme, computes the cycles that the HRT tasks must run per deadline interval at the minimum clock frequency to save energy while honoring the temporal and thermal constraints, and computes the maximum frequency at which the system can run below the maximum temperature. Then, an on-line, event-driven stage performs global task allocation applying a Fixed-Priority Zero-Laxity policy, reducing the overhead of quantum-based or interval-based global schedulers. The on-line stage embodies an adaptive scheduler that accepts or rejects soft RT aperiodic tasks throttling CPU frequency to the upper lowest available one to minimize power consumption while meeting time and thermal constraints. This approach leverages the best of two worlds: the off-line stage computes an ideal discrete HRT multiprocessor schedule, while the on-line stage manage soft real-time aperiodic tasks with minimum power consumption and maximum CPU utilization.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed R, Ramanathan P, Saluja KK (2016) Necessary and sufficient conditions for thermal schedulability of periodic real-time tasks under fluid scheduling model. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS) 15(3):49
Anderson JH, Srinivasan A (2001) Mixed pfair/erfair scheduling of asynchronous periodic tasks. In: Real-time systems, 13th euromicro conference on, 2001. IEEE, pp 76–85
ARINC (1997) Specification 651: Design guide for integrated modular avionics
AUTOSAR (2017) Specification of rte software
Baker TP (2005) A comparison of global and partitioned edf schedulability tests for multiprocessors. In: International conf. on real-time and network systems. Citeseer
Baruah S, Bertogna M, Butazzo G (2015) Multiprocessor Scheduling for Real-Time Systems. Springer, New York. ISBN 978-3-319-08695-8
Baruah SK, Cohen NK, Plaxton CG, Varvel DA (1996) Proportionate progress: a notion of fairness in resource allocation. Algorithmica 15(6):600–625
Baruah SK, Gehrke JE, Plaxton CG (1995) Fast scheduling of periodic tasks on multiple resources. In: Ipps. IEEE, p 280
Bertogna M, Cirinei M (2007) Response-time analysis for globally scheduled symmetric multiprocessor platforms. In: 28th IEEE international real-time systems symposium, 2007. RTSS 2007. IEEE, pp 149–160
Bertogna M, Cirinei M, Lipari G (2005) Improved schedulability analysis of edf on multiprocessor platforms. In: Proceedings of the 17th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems, ECRTS ’05. ISBN 0-7695-2400-1. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 209–218
Bini E, Buttazzo GC (2005) Measuring the performance of schedulability tests. Real-Time Systems 30(1-2):129–154
Brandenburg BB, Mahircan G (2016) Global scheduling not required: Simple, near-optimal multiprocessor real-time scheduling with semi-partitioned reservation. In: IEEE real-time systems symposium (RTSS 2016), pp 99–110
Calandrino JM, Anderson JH, Baumberger DP (2007) A hybrid real-time scheduling approach for large-scale multicore platforms. In: Proceedings of the 19th Euromicro conference on real-time systems, ECRTS ’07. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 247–258
Cardona J, Hernandez C, Mezzetti E, Abella J, Cazorla FJ (2018) Noco: Ilp-based worst-case contention estimation for mesh real-time manycores. In: 2018 IEEE Real-time systems symposium (RTSS), pp 265–276
Casini D, Biondi A, Giorgio B (2017) Semi-partitioned scheduling of dynamic real-time workload: A practical approach based on analysis-driven load balancing. In: Bertogna M (ed) 29th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems (ECRTS 2017), volume 76 of Leibniz International Proceedings in Informatics (LIPIcs), pp 13:1–13:23
Chantem T, Hu XS, Dick RP (2011) Temperature-aware scheduling and assignment for hard real-time applications on MPSoCs. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst 19(10):1884–1897. ISSN 1063-8210
Chen J-J, Hung C-M, Kuo T-W (2007) On the minimization fo the instantaneous temperature for periodic real-time tasks. In: 13Th IEEE real time and embedded technology and applications symposium (RTAS’07). IEEE, pp 236–248
Chen J-J, Kuo T-W (2007) Procrastination determination for periodic real-time tasks in leakage-aware dynamic voltage scaling systems. In: IEEE/ACM international conference on computer-aided design, 2007. ICCAD 2007, pp 289–294
Davis RI, Burns A (2011a) Fpzl schedulability analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2011 17th IEEE real-time and embedded technology and applications symposium, RTAS ’11. ISBN 978-0-7695-4344-4. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 245–256
Davis RI, Burns A (2011b) A survey of hard real-time scheduling for multiprocessor systems. ACM computing surveys (CSUR) 43(4):35
Desel J, Esparza J (1995) Free choice petri nets. Cambridge Tracts in Theoretical Computer Science, 40
Desirena G, Rubio L, Ramirez A, Briz JL (2019) Thermal-aware hrt scheduling simulation framework. https://www.gdl.cinvestav.mx/art/uploads/TCPN-Thermal-Aware_Real-Time_Scheduling.zip
Desirena-Lopez G, Briz JL, Vázquez CR, Ramírez-Treviño A, Gómez-Gutiérrez D (2016) On-line scheduling in multiprocessor systems based on continuous control using timed continuous petri nets. In: 13Th international workshop on discrete event systems, pp 278–283
Desirena-Lopez G, Ramírez-Treviño A, Briz JL, Vázquez CR, Gómez-Gutiérrez D (2019) Thermal-aware real-time scheduling using timed continuous petri nets. ACM Transactions on embedded computing systems. To appear, accepted Apr. 2019)
Desirena-Lopez G, Vázquez CR, Ramírez-Treviño A, Gómez-Gutiérrez D (2014) Thermal modelling for temperature control in MPSoc’s using fluid Petri nets. In: IEEE conference on control applications part of multi-conference on systems and control
Diniz N, Rufino J (2005) Arinc 653 in space
Donald J, Martonosi M (2006) Techniques for multicore thermal management: Classification and new exploration. In: ACM SIGARCH computer architecture news, vol 34. IEEE Computer Society, pp 78–88
Fernandez G, Jalle J, Abella J, Quiñones E, Vardanega T, Cazorla FJ (2017) Computing safe contention bounds for multicore resources with round-robin and fifo arbitration. IEEE Trans Comput 66(4):586–600
Fisher N, Goossens J, Baruah S (2010) Optimal online multiprocessor scheduling of sporadic real-time tasks is impossible. Real-Time Syst 45(1-2):26–71
Fu X, Wang X, Puster E (2009) Dynamic thermal and timeliness guarantees for distributed real-time embedded systems. In: 2009 15th IEEE international conference on embedded and real-time computing systems and applications. IEEE, pp 403–412
Fu Y, Kottenstette N, Chen Y, Lu C, Koutsoukos XD, Wang H (2010) Feedback thermal control for real-time systems. In: 2010 16Th IEEE real-time and embedded technology and applications symposium. IEEE, pp 111–120
Fu Y, Kottenstette N, Lu C, Koutsoukos XD (2012) Feedback thermal control of real-time systems on multicore processors. In: Proceedings of the tenth ACM international conference on embedded software. ACM, pp 113–122
Funk S, Levin G, Sadowski C, Pye I, Brandt S (2011) Dp-fair: a unifying theory for optimal hard real-time multiprocessor scheduling. Real-Time Systems 47 (5):389–429
Gerard S (2001) Linear and integer programming: Theory and practice. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Goossens JL, Funk S (2003) Priority-driven scheduling of periodic task systems on multiprocessors. Real-Time Systems, pp 2–3
Hettiarachchi PM, Fisher N, Ahmed M, Wang LY, Wang S, Shi W (2014) A design and analysis framework for thermalresilent hard real-time systems. ACM Trans Embed Comput Syst 13(5s):146:1–146:25
Kong J, Chung SW, Skadron K (2014) Recent thermal management techniques for microprocessors. ACM Computing Surveys 44(3):13:1–13:42
Mahulea C, Ramirez-Trevino A, Recalde L, Silva M (2008) Steady-state control reference and token conservation laws in continuous Petri net systems. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 5(2):307–320. ISSN 1545-5955
MATLAB (2018) version 9.4 (R2018a) . The MathWorks Inc., Natick
Moulik S, Devaraj R, Sarkar A, Shaw A (2017) A deadline-partition oriented heterogeneous multi-core scheduler for periodic tasks. In: 2017 18Th international conference on parallel and distributed computing, applications and technologies (PDCAT), pp 204–210
Oh D-I, Bakker TP (1998) Utilization bounds for n-processor rate monotone scheduling with static processor assignments. Real-Time Systems 15(2):183–192
Rubio-Anguiano L, Desirena-López G, Ramírez-Treviño A, Briz JL (2018) Energy-efficient thermal-aware scheduling for rt tasks using tcpn. IFAC-PapersOnLine 51(7):236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.06.307. 14th IFAC Workshop on Discrete Event Systems WODES 2018
Schor L, Bacivarov I, Yang H, Thiele L (2012) Worst-case temperature guarantees for real-time applications on multi-core systems. In: 2012 IEEE 18Th real time and embedded technology and applications symposium. IEEE, pp 87–96
Silva M, Júlvez J, Mahulea C, Renato Vázquez C (2011) On fluidization of discrete event models: observation and control of continuous Petri nets. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems 21(4)(3):427–497
Silva M, Recalde L (2007) Redes de Petri continuas: Expresividad, análisis y control de una clase de sistemas lineales conmutados. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e informática Industrial 4(3):5–33. ISSN 1697-7912
Zanini F, Atienza D, De Micheli G (2009) A control theory approach for thermal balancing of mpsoc. In: 2009 Asia and south pacific design automation conference. IEEE, pp 37–42
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades and the European ERDF under Grant TIN2016-76635-C2-1-R (AEI/ERDF, EU), and by the Aragon Government (T58_17R research group) and ERDF 2014-2020 Construyendo Europa desde Aragón.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Theory-2020
Guest Editors: Francesco Basile, Jan Komenda, and Christoforos Hadjicostis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubio-Anguiano, L., Desirena-López, G., Ramírez-Treviño, A. et al. Energy-efficient thermal-aware multiprocessor scheduling for real-time tasks using TCPN. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 29, 237–264 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10626-019-00285-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10626-019-00285-x