Abstract
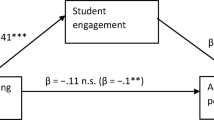
Connection and communication via social networking applications are now one of the most important features in college students’ lives. Text and graphical messaging and generating, sharing, and viewing visual messages may affect students’ academic life, especially their academic performance. In this regard, reports about the effect of social networking on academic performance have been inconsistent and also explanations for the possible causes of the negative effects of social networks have been incomplete. The current study focuses on this gap and investigates the role of social networking on the academic performance of students regarding the mediating role of study approaches by using descriptive-correlational research method and analyzing the data of 380 college students through the regression and mediation analysis. Findings revealed that social networking negatively affects academic performance. Moreover, we found that strategic study approach could not mediate the negative effect of social networking on academic performance. These findings were discussed and recommendations were presented for further research.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Abedin, N. F. Z., Jaafar, Z., Husain, S., & Abdullah, R. (2013). The validity of ASSIST as a measurement of learning approach among MDAB students. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 90, 549–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.07.125.
Alwagait, E., Shahzad, B., & Alim, S. (2015). Impact of social media usage on students academic performance in Saudi Arabia. Computers in Human Behavior, 51(Part B), 1092–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.09.028.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173–1182.
Bellur, S., Nowak, K. L., & Hull, K. S. (2015). Make it our time: In class multitaskers have lower academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 53, 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.06.027.
Bonsaksen, T., Sadeghi, T., & Thørrisen, M. M. (2017). Associations between self-esteem, general self-efficacy, and approaches to studying in occupational therapy students: A cross-sectional study. Occupational Therapy in Mental Health, 33(4), 326–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/0164212X.2017.1295006.
Chen, Q., & Yan, Z. (2016). Does multitasking with mobile phones affect learning? A review. Computers in Human Behavior, 54, 34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.047.
Cheston, C. C., Flickinger, T. E., & Chisolm, M. S. (2013). Social media use in medical education: A systematic review. Academic Medicine, 88(6), 893–901.
Cheung, C. M., Chiu, P.-Y., & Lee, M. K. (2011). Online social networks: Why do students use facebook? Computers in Human Behavior, 27(4), 1337–1343.
Dede, C. (2005). Planning for neomillennial learning styles. Educause Quarterly, 28(1), 7–12.
Dindar, M., & Akbulut, Y. (2016). Effects of multitasking on retention and topic interest. Learning and Instruction, 41, 94–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2015.10.005.
Egenti, H. N. (2012). Relationships of approaches to studying, metacognition, and intellectual development of general chemistry students. University of north texas.
Entwistle, N., & Ramsden, P. (1983). Understanding student learning. London, UK: Croom Helm.
Entwistle, N., & Smith, C. (2002). Personal understanding and target understanding: Mapping influences on the outcomes of learning. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 72(3), 321–342.
Floyd, K. S., Harrington, S. J., & Santiago, J. (2009). The effect of engagement and perceived course value on deep and surface learning strategies. Informing Science: The International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline, 12, 181–190.
Gall, M. D., Borg, W. R., & Gall, J. P. (1996). Educational research: An introduction: Longman publishing.
Gallardo-Echenique, E. E., Marqués-Molías, L., Bullen, M., & Strijbos, J.-W. (2015). Let’s talk about digital learners in the digital era. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 16(3), 156–187.
Hameed, Z., Maqbool, A., Aslam, N., Hassan, E. u., & Anwar, M. (2013). An empirical study to investigate the impact of social networking sites on student’s academic performance and attitude in case of Pakistan. Asian Journal of Empirical Research, 3(6), 775–784.
Hassanbeigi, A., Askari, J., Nakhjavani, M., Shirkhoda, S., Barzegar, K., Mozayyan, M. R., & Fallahzadeh, H. (2011). The relationship between study skills and academic performance of university students. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 30, 1416–1424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.276.
Hung, H.-T., & Yuen, S. C.-Y. (2010). Educational use of social networking technology in higher education. Teaching in Higher Education, 15(6), 703–714. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562517.2010.507307.
Jacobsen, W. C., & Forste, R. (2010). The wired generation: Academic and social outcomes of electronic media use among university students. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 14(5), 275–280. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2010.0135.
Jansen, E. P. W. A., & Suhre, C. J. M. (2010). The effect of secondary school study skills preparation on first-year university achievement. Educational Studies, 36(5), 569–580. https://doi.org/10.1080/03055691003729070.
Judd, T. (2014). Making sense of multitasking: The role of Facebook. Computers & Education, 70, 194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.08.013.
Junco, R. (2012a). In-class multitasking and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(6), 2236–2243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.06.031.
Junco, R. (2012b). Too much face and not enough books: The relationship between multiple indices of Facebook use and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(1), 187–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2011.08.026.
Junco, R., Heiberger, G., & Loken, E. (2011). The effect of twitter on college student engagement and grades. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 27(2), 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2729.2010.00387.x.
Jungert, T. (2008). A longitudinal study of engineering students’ approaches to their studies. Higher Education Research and Development, 27(3), 201–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360802183770.
Karin, B., Marina, K., Rolien, K., & Bernice, B. (2016). Factors influencing students’ learning approaches in auditing. Meditari Accountancy Research, 24(3), 390–413. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEDAR-06-2013-0018.
Karpinski, A. C., Kirschner, P. A., Ozer, I., Mellott, J. A., & Ochwo, P. (2013). An exploration of social networking site use, multitasking, and academic performance among United States and European university students. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 1182–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.10.011.
Kaya, T., & Bicen, H. (2016). The effects of social media on students’ behaviors; Facebook as a case study. Computers in Human Behavior, 59, 374–379.
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607–610.
Kutlu, M. O., & Korkmaz, Ş. (2014). Relationship between the high school students perspectives on study skills and the types of state high School in Terms of some variables. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 152, 1029–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.09.268.
Lin, K.-Y., & Lu, H.-P. (2011). Why people use social networking sites: An empirical study integrating network externalities and motivation theory. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(3), 1152–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.12.009.
Magogwe, J. M., Ntereke, B., & Phetlhe, K. R. (2015). Facebook and classroom group work: A trial study involving University of Botswana Advanced Oral Presentation students. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(6), 1312–1323. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12204.
Michikyan, M., Subrahmanyam, K., & Dennis, J. (2015). Facebook use and academic performance among college students: A mixed-methods study with a multi-ethnic sample. Computers in Human Behavior, 45, 265–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.033.
Moneta, G. B., Spada, M. M., & Rost, F. M. (2007). Approaches to studying when preparing for final exams as a function of coping strategies. Personality and Individual Differences, 43(1), 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.12.002.
Nor, S. A. K., & Amelia, H. (2007). Reading habits and attitude in the digital age: Analysis of gender and academic program differences in Malaysia. The Electronic Library, 25(3), 285–298. https://doi.org/10.1108/02640470710754805.
Ogedebe, P., Emmanuel, J., & Musa, Y. (2012). A survey on Facebook and academic performance in Nigeria universities. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, 2(4), 788–797.
Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(6), 2117–2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.06.016.
Pepe, K. (2012). Study skills of students studying at different departments. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 47, 1040–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.776.
Shi, Y., Luo, Y. L., Yang, Z., Liu, Y., & Cai, H. (2014). The development and validation of the social network sites (SNSs) usage questionnaire. Paper presented at the International Conference on Social Computing and Social Media, The Development and Validation of the Social Network Sites (SNSs) Usage Questionnaire.
Spada, M. M., Nikcevic, A. V., Moneta, G. B., & Ireson, J. (2006). Metacognition as a mediator of the effect of test anxiety on a surface approach to studying. Educational Psychology, 26(5), 615–624. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410500390673.
Speth, C. A., Namuth, D. M., & Lee, D. J. (2007). Using the ASSIST short form for evaluating an information technology application: Validity and reliability issues. Informing Science (10), 107–119
Subrahmanyam, K., Michikyan, M., Clemmons, C., Carrillo, R., Uhls, Y. T., & Greenfield, P. M. (2013). Learning from paper, learning from screens: Impact of screen reading and multitasking conditions on reading and writing among college students. International Journal of Cyber Behavior, Psychology and Learning (IJCBPL), 3(4), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijcbpl.2013100101.
Tait, H., Entwistle, N., & McCune, V. (1998). ASSIST: A reconceptualisation of the approaches to studying inventory. In C. Rust (Ed.), In Improving students as learners (pp. 262–271). Oxford: Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development.
Tarabashkina, L., & Lietz, P. (2011). The impact of values and learning approaches on student achievement: Gender and academic discipline influences. Issues in Educational Research, 21(2), 210–231.
Trigwell, K., Prosser, M., & Waterhouse, F. (1999). Relations between teachers' approaches to teaching and students' approaches to learning. Higher Education, 37(1), 57–70.
Valadas, S. C. A. T. S., Gonçalves, F. R., & Faísca, L. M. (2010). Approaches to studying in higher education Portuguese students: A Portuguese version of the approaches and study skills inventory for students. Higher Education, 59(3), 259–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-009-9246-5.
Walker, R., Spronken-Smith, R., Bond, C., McDonald, F., Reynolds, J., & McMartin, A. (2010). The impact of curriculum change on health sciences first year students’ approaches to learning. Instructional Science, 38(6), 707–722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-009-9092-y.
Walsh, J. L., Fielder, R. L., Carey, K. B., & Carey, M. P. (2013). Female college students’ media use and academic outcomes: Results from a longitudinal cohort study. Emerging Adulthood, 1(3), 219–232.
West, C., & Sadoski, M. (2011). Do study strategies predict academic performance in medical school? Medical Education, 45(7), 696–703.
Yu, A. Y., Tian, S. W., Vogel, D., & Chi-Wai Kwok, R. (2010). Can learning be virtually boosted? An investigation of online social networking impacts. Computers & Education, 55(4), 1494–1503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.06.015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostaminezhad, M.A., Porshafei, H. & Ahamdi, A.A. Can effective study approaches mediate the negative effect of social networking on academic performance?. Educ Inf Technol 24, 205–217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9770-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9770-y