Abstract
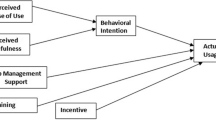
The main objective of this article is to study the factors that affect university students’ acceptance of E-learning systems. To achieve this objective, we have proposed a new model that aims to investigate the impact of innovativeness, quality, trust, and knowledge sharing on E-learning acceptance. Data collection has taken place through an online questionnaire survey, which was carried out at The British University in Dubai (BUiD) and University of Fujairah (UOF) in the UAE. There were 251 students participated in this study. Data were analyzed using SmartPLS and SPSS. The Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) has been used to validate the proposed model. The outcomes revealed that knowledge sharing and quality in the universities have a positive influence on E-learning acceptance among the students. Innovativeness and trust were found not to significantly affect the E-learning system acceptance. By identifying the factors that influence the E-learning acceptance, it will be more useful to provide better services for E-learning. Other implications are also presented in the study.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Abbas, M., Shahid Nawaz, M., Ahmad, J., & Ashraf, M. (2017). The effect of innovation and consumer related factors on consumer resistance to innovation. Cogent Business and Management, 4(1), 1312058.
Abu-Al-Aish, A. (2014). Toward mobile learning deployment in higher education (Doctoral dissertation, Brunel University, School of Information Systems, Computing and Mathematics).
Abu-Al-Aish, A., & Love, S. (2013). Factors influencing students’ acceptance of m-learning: an investigation in higher education. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 14(5).
Adel, R. (2017). Manage perceived e-learning quality in Egyptian context. Total Quality Management and Business Excellence, 28(5), 600–613.
Akter, S., D'Ambra, J., & Ray, P. (2011). An evaluation of PLS based complex models: The roles of power analysis, predictive relevance and GoF index.
Al Emran, M., & Shaalan, K. (2014a). A survey of intelligent language tutoring systems. In Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI, 2014 International Conference on (pp. 393-399). IEEE.
Al Emran, M., & Shaalan, K. F. (2014b). E-podium technology: A medium of managing knowledge at Al Buraimi University college via M-learning. In BCS International IT Conference.
Al-Emran, M., & Malik, S. I. (2016). The impact of google apps at work: higher educational perspective. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 10(4), 85–88.
Al-Emran, M., & Salloum, S. A. (2017). Students' attitudes towards the use of mobile technologies in e-evaluation. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 11(5), 195–202.
Al-Emran, M., & Shaalan, K. (2015). Attitudes towards the use of mobile learning: a case study from the gulf region. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 9(3), 75–78.
Al-Emran, M., & Shaalan, K. (2017). Academics’ awareness towards mobile learning in Oman. International Journal of Computing and Digital Systems, 6(1).
Al-Emran, M., Elsherif, H. M., & Shaalan, K. (2016). Investigating attitudes towards the use of mobile learning in higher education. Computers in Human Behavior, 56, 93–102.
Alkandari, B. (2015). An investigation of the factors affecting students’ acceptance and intention to use E-learning systems at Kuwait University: Developing a technology acceptance model in E-learning environments (Doctoral dissertation, Cardiff Metropolitan University).
Alkhalaf, S., Drew, S., & Alhussain, T. (2012). Assessing the impact of e-learning systems on learners: A survey study in the KSA. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 47, 98–104.
Al-rahmi, W. M., Othman, M. S., & Yusuf, L. M. (2015). Exploring the factors that affect student satisfaction through using e-learning in Malaysian higher education institutions. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(4), 299.
Ashill, N. J., & Jobber, D. (2010). Measuring state, effect, and response uncertainty: Theoretical construct development and empirical validation. Journal of Management, 36(5), 1278–1308.
Bakeman, R. (2005). Recommended effect size statistics for repeated measures designs. Behavior Research Methods, 37(3), 379–384.
Barclay, D., Higgins, C., & Thompson, R. (1995). The partial least squares (pls) approach to casual modeling: Personal computer adoption Ans use as an illustration.
Behera, S. K. (2013). E-and M-learning: A comparative study. International Journal on New Trends in Education and Their Implications, 4(3), 65–78.
Cakir, R., & Solak, E. (2014). Exploring the factors influencing E-learning of Turkish EFL learners through TAM. TOJET: The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology, 13(3).
Calvo-Mora, A., Leal, A., & Roldán, J. L. (2005). Relationships between the EFQM model criteria: a study in Spanish universities. Total Quality Management and Business Excellence, 16(6), 741–770.
Campbell, C., & Ma, J. J. (2015). Looking forward, looking back: Drawing on the past to shape the future of marketing. In Proceedings of the 2013 World Marketing Congress.
Chang, W. L., & Lee, C. Y. (2013). Trust as a learning facilitator that affects students' learning performance in the Facebook community: An investigation in a business planning writing course. Computers & Education, 62, 320–327.
Chen, H. R., & Tseng, H. F. (2012). Factors that influence acceptance of web-based E-learning systems for the in-service education of junior high school teachers in Taiwan. Evaluation and Program Planning, 35(3), 398–406.
Cheng, W. Y. T., & Chen, C. C. (2015). The impact of e-learning on workplace on-the-job training. International Journal of e-Education, e-Business, e-Management and e-Learning, 5(4), 212.
Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Modern Methods for Business Research, 295(2), 295–336.
Chin, W. W. (2010). How to write up and report PLS analyses. In Handbook of partial least squares (pp. 655–690). Berlin:Springer.
Chou, H. K., Lin, I. C., Woung, L. C., & Tsai, M. T. (2012). Engagement in e-learning opportunities: An empirical study on patient education using expectation confirmation theory. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(3), 1697–1706.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Dečman, M. (2015). Modeling the acceptance of E-learning in mandatory environments of higher education: The influence of previous education and gender. Computers in Human Behavior, 49, 272–281.
Delone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30.
Dreheeb, A. E., Basir, N., & Fabil, N. (2016). Impact of system quality on Users' satisfaction in continuation of the use of E-learning system. International Journal of e-Education, e-Business, e-Management and E-learning, 6(1), 13–25.
Eid, M. I., & Al-Jabri, I. M. (2016). Social networking, knowledge sharing, and student learning: The case of university students. Computers & Education, 99, 14–27.
El-Masri, M., & Tarhini, A. (2017). Factors affecting the adoption of e-learning systems in Qatar and USA: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology 2 (UTAUT2). Educational Technology Research and Development, 1–21.
Falk, R. F., & Miller, N. B. (1992). A primer for soft modeling. University of Akron Press.
Faqih, K. M. (2016)Which is more important in e-learning adoption, perceived value or perceived usefulness? Examining the moderating influence of perceived compatibility.
Farahat, T. (2012). Applying the technology acceptance model to online learning in the Egyptian universities. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 64, 95–104.
Fong, S. K. C. J., & Wang, W. F. F. L. (2013) Hybrid learning and continuing education.
Fook, C. Y., Sidhu, G. K., Narasuman, S., Fong, L. L., & Rahman, S. B. A. (Eds.). (2015). 7th International conference on university learning and teaching (InCULT 2014) Proceedings: Educate to innovate. Springer.
Fornell, C., & Bookstein, F. L. (1982). Two structural equation models: LISREL and PLS applied to consumer exit-voice theory. Journal of Marketing Research, 440–452.
Geisser, S. (1974). A predictive approach to the random effects model. Biometrika, 61, 101–107.
Hair Jr, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage Publications.
Harun, A., Liew, T. S., Kassim, A. W. M., & Sulong, R. S. (2015). Smartphone dependency and its impact on purchase behavior. Asian Social Science, 11(26), 196.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2012). Using partial least squares path modeling in advertising research: Basic concepts and recent issues. Handbook of research on international advertising, 252.
Islam, A. N. (2012). Understanding e-learning system usage outcomes in hybrid courses. In System Science (HICSS), 2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on (pp. 118-127). IEEE.
Jaradat, M. I. R. M. (2014). Understanding individuals' perceptions, determinants and the moderating effects of age and gender on the adoption of mobile learning: Developing country perspective. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 8(3–4), 253–275.
Joo, Y. J., Lee, H. W., & Ham, Y. (2014). Integrating user interface and personal innovativeness into the TAM for mobile learning in Cyber University. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 26(2), 143–158.
Kanwal, F., & Rehman, M. (2017). Factors affecting E-learning adoption in developing countries–empirical evidence from Pakistan’s higher education sector. IEEE Access.
Kundu, S. C., & Gahlawat, N. (2016). Ability–motivation–opportunity enhancing human resource practices and firm performance: Evidence from India. Journal of Management & Organization, 1–18.
Lee, Y. C. (2006). An empirical investigation into factors influencing the adoption of an E-learning system. Online Information Review, 30(5), 517–541.
Lee, Y. H., Hsieh, Y. C., & Chen, Y. H. (2013). An investigation of employees' use of e-learning systems: Applying the technology acceptance model. Behaviour & Information Technology, 32(2), 173–189.
Liao, C. H., & Huang, W. L. (2009). Community adaptability, computer and internet self-efficacy, and intention of blended e-learning. International Journal of Society Systems Science, 1(3), 209–226.
Lin, C. S., Tzeng, G. H., Chin, Y. C., & Chang, C. C. (2010). Recommendation sources on the intention to use e-books in academic digital libraries. The Electronic Library, 28(6), 844–857.
Liu, Y., & Wu, Y. (2010). A survey on trust and trustworthy E-learning system. In Web Information Systems and Mining (WISM), 2010 International Conference on (Vol. 1, pp. 118-122). IEEE.
Liu, I. F., Chen, M. C., Sun, Y. S., Wible, D., & Kuo, C. H. (2010). Extending the TAM model to explore the factors that affect intention to use an online learning community. Computers & Education, 54(2), 600–610.
Lu, H. P., & Chiou, M. J. (2010). The impact of individual differences on e-learning system satisfaction: A contingency approach. British Journal of Educational Technology, 41(2), 307–323.
Luo, X., Li, H., Zhang, J., & Shim, J. P. (2010). Examining multi-dimensional trust and multi-faceted risk in initial acceptance of emerging technologies: An empirical study of mobile banking services. Decision Support Systems, 49(2), 222–234.
Ma, W., & Yuen, A. (2011). 11. E-learning system acceptance and usage pattern. Technology acceptance in education: Research and issues, 201.
Mahmodi, M. (2017). The analysis of the factors affecting the acceptance of E-learning in higher education. Interdisciplinary Journal of Virtual Learning in Medical Sciences, (In Press).
Masa'd, F. M. S. (2017). Implementation of E-training in developing country: Empirical evidence from Jordan. International Business Research, 10(4), 42.
Matias-Reche, F., Garcia-Morales, V. J., & Rueda-Manzanares, A. (2008). Entrepreneurial size, complexity and decentralization of decision-making in the use of temporary help workers in Spain. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 19(1), 169–187.
Migdadi, M. M., Abu Zaid, M. K. S., Al-Hujran, O. S., & Aloudat, A. M. (2016). An empirical assessment of the antecedents of electronic-business implementation and the resulting organizational performance. Internet Research, 26(3), 661–688.
Milošević, I., Živković, D., Manasijević, D., & Nikolić, D. (2015). The effects of the intended behavior of students in the use of M-learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 51, 207–215.
Misra, B. M. S., Torre, A. M. A. R. C., Falcão, J. G. R. M. I., Apduhan, D. T. B. O., &Gervasi, O. (2014). Computational Science and Its Applications–ICCSA 2014.
Mtebe, J. (2014). Acceptance and use of eLearning Technologies in Higher Education in East Africa.
Ngafeeson, M. N., & Sun, J. (2015). The effects of technology innovativeness and system exposure on student acceptance of e-textbooks. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 14, 55–71.
Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). The theory of measurement error. Psychometric theory, 209–247.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40(3), 879–891.
Purnomo, S. H., & Lee, Y. H. (2013). E-learning adoption in the banking workplace in Indonesia: An empirical study. Information Development, 29(2), 138–153.
Rahman, I. A., Memon, A. H., Abdullah, N. H., & Azis, A. A. A. (2013). Application of PLS-SEM to assess the influence of construction resources on cost overrun. In Applied Mechanics and Materials (Vol. 284, pp. 3649-3656). Trans Tech Publications.
Robinson Jr, L. (Ed.). (2014). Marketing Dynamism & Sustainability: Things Change, Things Stay the Same...: Proceedings of the 2012 Academy of Marketing Science (AMS) Annual Conference. Springer.
Rodríguez-Ardura, I., & Meseguer-Artola, A. (2016). What leads people to keep on e-learning? An empirical analysis of users' experiences and their effects on continuance intention. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1030–1053.
Roky, H., & Al Meriouh, Y. (2015). Evaluation by users of an industrial information system (XPPS) based on the DeLone and McLean model for IS success. Procedia Economics and Finance, 26, 903–913.
Salloum, S. A., Al-Emran, M., Monem, A. A., & Shaalan, K. (2017). A survey of text mining in social media: Facebook and twitter perspectives. Advances in Science Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, 2(1), 127–133.
Santos-Vijande, M. L., López-Sánchez, J. Á., & Rudd, J. (2016). Frontline employees’ collaboration in industrial service innovation: Routes of co-creation’s effects on new service performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44(3), 350–337.
Senapathi, M., & Srinivasan, A. (2014). An empirical investigation of the factors affecting agile usage. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering (p. 10). ACM.
Skersys, T., Butleris, R., Nemuraite, L., & Suomi, R. (Eds.). (2011). Building the E-World Ecosystem: 11th IFIP WG 6.11 Conference on E-Business, E-Services, and E-Society, I3E 2011, Kaunas, Lithuania, October 12-14, 2011, Revised Selected Papers (Vol. 353). Springer.
Stone, M. (1974). Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the royal statistical society. Series B (Methodological), 111–147.
Storey, C., & Kahn, K. B. (2010). The role of knowledge management strategies and task knowledge in stimulating service innovation. Journal of Service Research, 13(4), 397–410.
Tarhini, A., Hone, K., & Liu, X. (2013). Factors affecting students' acceptance of E-learning environments in developing countries: A structural equation modeling approach. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 3(1), 54.
Tarhini, A., Mohammed, A. B., & Maqableh, M. (2016). Modeling factors affecting Student’s usage behaviour of E-learning Systems in Lebanon. International Journal of Business and Management, 11(2), 299.
Tarhini, A., Hone, K., Liu, X., & Tarhini, T. (2017). Examining the moderating effect of individual-level cultural values on users’ acceptance of E-learning in developing countries: A structural equation modeling of an extended technology acceptance model. Interactive Learning Environments, 25(3), 306–328.
Tenenhaus, M., Vinzi, V. E., Chatelin, Y. M., & Lauro, C. (2005). PLS path modeling. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 48(1), 159–205.
Van Raaij, E. M., & Schepers, J. J. (2008). The acceptance and use of a virtual learning environment in China. Computers & Education, 50(3), 838–852.
Vinzi, V. E., Chin, W. W., Henseler, J., & Wang, H. (Eds.). (2010). Handbook of partial least squares: Concepts, methods and applications. Springer Science & Business Media.
Wang, Y. D. (2014). Building trust in E-learning. Athens Journal of Education, 1(1), 9–18.
Wetzels, M., Odekerken-Schröder, G., & Van Oppen, C. (2009). Using PLS path modeling for assessing hierarchical construct models: Guidelines and empirical illustration. MIS Quarterly, 33, 177–195.
Wu, B., & Zhang, C. (2014). Empirical study on continuance intentions towards E-learning 2.0 systems. Behaviour & Information Technology, 33(10), 1027–1038.
Yatigammana, M. R. K. N., Johar, M. D. G. M. D., & Gunawardhana, C. (2013). Impact of Innovations attributes on E-learning acceptance among Sri Lankan postgraduate students.
Yee-Loong Chong, A., Ooi, K. B., Bao, H., & Lin, B. (2014). Can e-business adoption be influenced by knowledge management? An empirical analysis of Malaysian SMEs. Journal of Knowledge Management, 18(1), 121–136.
Yilmaz, R. (2016). Knowledge sharing behaviors in E-learning community: Exploring the role of academic self-efficacy and sense of community. Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 373–382.
Yuen, A. H., & Ma, W. W. (2004). Knowledge sharing and teacher acceptance of web based learning system. In C. McBeath, Atkinson, D. Jonas-Dwyer, and R. Phillips, editors, Beyond the comfort zone: Proceedings of the 21st ASCILITE Conference (pp. 975-983).
Yusof, Z. M., Ismail, M. B., Ahmad, K., & Yusof, M. M. (2012). Knowledge sharing in the public sector in Malaysia: A proposed holistic model. Information Development, 28(1), 43–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salloum, S.A., Al-Emran, M., Shaalan, K. et al. Factors affecting the E-learning acceptance: A case study from UAE. Educ Inf Technol 24, 509–530 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9786-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9786-3