Abstract
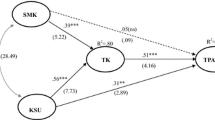
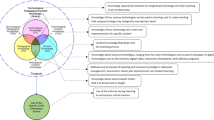
This study examined Indonesian pre-service language teachers’ use of information and communication technology (UICT) during teaching practices. We used technological pedagogical and content knowledge (TPACK) framework to predict the UICT. The objective of the study is to determine if the TPACK is a valid model to explain Indonesian pre-service language teachers’ UICT during teaching practices. 287 pre-service language teachers from three Indonesian universities completed a 38-item survey instruments based on the TPACK and UICT. The development of the survey instruments was done mainly through content validity index (CVI) and exploratory factor analysis (EFA). Findings of the study that were obtained through partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) informed 13 hypotheses. Overall, the TPACK components are interconnected and also reported to be a valid model to help explain Indonesian pre-service language teachers’ UICT during teaching practices.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The dataset can be accessed at Mendeley dataset repository https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/s6brgxxktt/4
References
Agyei, D. D., & Voogt, J. (2012). Developing technological pedagogical content knowledge in pre-service mathematics teachers through collaborative design. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 28(4), 547–564. https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.827.
Angeli, C., & Valanides, N. (2009). Epistemological and methodological issues for the conceptualization, development, and assessment of ICT–TPCK: Advances in technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPCK). Computers & Education, 52(1), 154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2008.07.006.
Archambault, L. M., & Barnett, J. H. (2010). Revisiting technological pedagogical content knowledge: Exploring the TPACK framework. Computers & Education, 55(4), 1656–1662. https://doi.org/10.1016/je.compedu.2010.07.009.
Arrosagaray, M., González-Peiteado, M., Pino-Juste, M., & Rodríguez-López, B. (2019). A comparative study of Spanish adult students’ attitudes to ICT in classroom, blended and distance language learning modes. Computers & Education, 134, 31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.01.016.
Aslan, A., & Zhu, C. (2017). Investigating variables predicting Turkish pre-service teachers’ integration of ICT into teaching practices. British Journal of Educational Technology, 48(2), 552–570. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12437.
Bernhardt, E. B. (2010). Teaching other languages. Educational Practices Series, 20, 1–29.
Bustamante, C. (2019). TPACK and teachers of Spanish: Development of a theory-based joint display in a mixed methods research case study. Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 13(2), 163–178. https://doi.org/10.1177/15586898177121199.
Castro, R. (2012). Blended learning in higher education: Trends and capabilities. Education and Information Technologies, 24(4), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09886-3.
Chai, C. S., Koh, J. H. L., Ho, J. H. N., & Tsai, C. C. (2012). Examining preservice teachers’ perceived knowledge of TPACK and Cyberwellness through structural equation Modelling. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 28(6), 1000–1019. https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.807.
Chen, C. P. (2018). Understanding mobile English-learning gaming adopters in the self-learning market: The uses and gratification expectancy model. Computers & Education, 126, 217–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.07.055.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). A concise introduction to mixed methods research. Sage Publications.
Dong, Y., Chai, C. S., Sang, G. Y., Koh, J. H. L., & Tsai, C. C. (2015). Exploring the profiles and interplays of pre-service and in-service teachers' technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) in China. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 18(1), 158–169.
Fleiss, J. L., Levin, B., & Paik, M. C. (2004). The measurement of interrater agreement. In W. Shewart & S. Wilks (Eds.), Statistical methods for rates and proportions (pp. 598–626). John Hoboken: Wiley & Sons.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(3), 382–388. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378101800313
Golonka, E. M., Bowles, A. R., Frank, V. M., Richardson, D. L., & Freynik, S. (2014). Technologies for foreign language learning: A review of technology types and their effectiveness. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 27(1), 70–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2012.700315.
Graham, C. R. (2011). Theoretical considerations for understanding technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK). Computers & Education, 57(3), 1953–1960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.04.010.
Habibi, A., Mukminin, A., Riyanto, Y., Prasojo, L. D., Sulistiyo, U., Sofwan, M., & Saudagar, F. (2018). Building an online community: Student teachers’ perceptions on the advantages of using social networking services in a teacher education program. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 19(1), 46–61.
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Babin, B. J., & Black, W. C. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: A global perspective (7th ed.). New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squaress structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). London: Sage publications.
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review, 31(1), 2–24. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203.
Halek, M., Holle, D., & Bartholomeyczik, S. (2017). Development and evaluation of the content validity, practicability and feasibility of the innovative dementia-oriented assessment system for challenging behaviour in residents with dementia. BMC Health Services Research, 17(1), 554 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28806934.
Hayduk, L. A., & Littvay, L. (2012). Should researchers use single indicators, best indicators, or multiple indicators in structural equation models? BMC Medical Research Methodology, 12(1), 159. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-12-159.
Joo, Y. J., Park, S., & Lim, E. (2018). Factors influencing preservice teachers’ intention to use technology: TPACK, teacher self-efficacy, and technology acceptance model. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 21(3), 48–59.
Kabilan, M. K., Ahmad, N., & Abidin, M. J. Z. (2010). Facebook: An online environment for learning of English in institutions of higher education? The Internet and Higher Education, 13(4), 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2010.07.003.
Keane, T., & Keane, W. (2019). A vision of the digital future-government funding as a catalyst for 1 to 1 computing in schools. Education and Information Technologies, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09988-y.
Koh, J. H. L., Chai, C. S., & Tsai, C. C. (2010). Examining technological pedagogical content knowledge of Singapore pre-service teachers with a large-scale survey. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 26(6), 563–573. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2729.2010.00372.x.
Liu, Y., Holden, D., & Zheng, D. (2016). Analyzing students’ language learning experience in an augmented reality mobile game: An exploration of an emergent learning environment. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 228, 369–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.06.016.
Luik, P., Taimalu, M., & Suviste, R. (2018). Perceptions of technological, pedagogical and content knowledge (TPACK) among pre-service teachers in Estonia. Education and Information Technologies, 23(2), 741–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-017-9633-y.
Lynn, M. R. (1986). Determination and quantification of content validity. Nursing Research, 35(6), 382–385.
Mei, B., Brown, G. T., & Teo, T. (2018). Toward an understanding of preservice English as a foreign language teachers’ acceptance of computer-assisted language learning 2.0 in the People’s republic of China. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 56(1), 74–104. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117700144.
Mishra, P., & Koehler, M. J. (2006). Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A framework for teacher knowledge. Teachers College Record, 108(6), 1017–1054. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2006.00684.x.
(2018). Grafik [Active student graphic based on majors]. Retrieved from https://forlap.ristekdikti.go.id/mahasiswa/homegraphbidang.
Mumcu, F. K., & Usluel, Y. K. (2010). A scale development study of integration of ICT into learning and teaching process according to TPACK. In A. Isman (Ed.), International educational technology conference 2010 (pp. 1419–1423). Turkey: Istanbul.
Niemelä, P., Isomöttönen, V., & Lipponen, L. (2016). Successful design of learning solutions being situation aware. Education and Information Technologies, 21(1), 105–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-014-9311-2.
Özgün-Koca, S. A., Meagher, M., & Edwards, M. T. (2010). Preservice teachers' emerging TPACK in a technology-rich methods class. The Mathematics Educator, 19(2), 10–20.
Pallant, J. (2011). Survival manual. A step by step guide to data analysis using SPSS. 4th edition, Crows Nest, NSW: Allen & Unwin.
Pamuk, S., Ergun, M., Cakir, R., Yilmaz, H. B., & Ayas, C. (2015). Exploring relationships among TPACK components and development of the TPACK instrument. Education and Information Technologies, 20(2), 241–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-013-9278-4.
Polit, D. F., & Beck, C. T. (2009). Essentials of nursing research: Appraising evidence for nursing practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Prasojo, L. D., Habibi, A., Yaakob, M. F. M., Mukminin, A., Haswindy, S., & Sofwan, M. (2019). An explanatory sequential study on Indonesian principals' perceptions on ICT integration barriers. Electronic Journal of e-Learning, 17(1), 1–10.
Reyes Jr., V. C., Reading, C., Doyle, H., & Gregory, S. (2017). Integrating ICT into teacher education programs from a TPACK perspective: Exploring perceptions of university lecturers. Computers & Education, 115, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.07.009.
Scherer, R., Tondeur, J., & Siddiq, F. (2017). On the quest for validity: Testing the factor structure and measurement invariance of the technology-dimensions in the technological, pedagogical, and content knowledge (TPACK) model. Computers & Education, 112, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.04.012.
Schmidt, D. A., Baran, E., Thompson, A. D., Mishra, P., Koehler, M. J., & Shin, T. S. (2009). Technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) the development and validation of an assessment instrument for preservice teachers. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 42(2), 123–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2009.10782544.
Shulman, L. S. (1986). Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Educational Researcher, 15(2), 4–14. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X015002004.
Tai, S. J. D. (2015). From TPACK-in-action workshops to classrooms: CALL competency developed and integrated. Language Learning & Technology, 19(1), 139–164.
Taimalu, M., & Luik, P. (2019). The impact of beliefs and knowledge on the integration of technology among teacher educators: A path analysis. Teaching and Teacher Education, 79, 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2018.12.012.
Teo, T., Sang, G., Mei, B., & Hoi, C. K. W. (2018). Investigating pre-service teachers’ acceptance of web 2.0 technologies in their future teaching: A Chinese perspective. Interactive Learning Environments, 27(4), 530–546. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1489290.
Tondeur, J., Pareja Roblin, N., van Braak, J., Voogt, J., & Prestridge, S. (2017). Preparing beginning teachers for technology integration in education: Ready for take-off? Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 26(2), 157–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/1475939X.2016.11935566.
Tseng, J. J. (2018). Exploring TPACK-SLA interface: Insights from the computer-enhanced classroom. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 31(4), 390–412. https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2017.1412324.
Valtonen, T., Sointu, E., Kukkonen, J., Kontkanen, S., Lambert, M. C., & Mäkitalo-Siegl, K. (2017). TPACK updated to measure pre-service teachers’ twenty-first century skills. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 33(3).
Valtonen, T., Sointu, E., Kukkonen, J., Mäkitalo, K., Hoang, N., Häkkinen, P., Järvelä, S., Näykki, P., Virtanen, A., Pöntinen, S., Kostiainen, E., & Tondeur, J. (2019). Examining pre-service teachers' technological pedagogical content knowledge as evolving knowledge domains: A longitudinal approach. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12353.
Vinzi, V. E., Trinchera, L., & Amato, S. (2010). PLS path modeling: From foundations to recent developments and open issues for model assessment and improvement. In Handbook of partial least squares (pp. 47–82). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Acknowledgements
We thank all respondents for their time and willingness to participate. Financing was fully provided by LPDP Indonesia (No. FR13102018159279).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, A., Yusop, F.D. & Razak, R.A. The role of TPACK in affecting pre-service language teachers’ ICT integration during teaching practices: Indonesian context. Educ Inf Technol 25, 1929–1949 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-10040-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-10040-2