Abstract
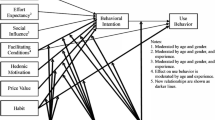
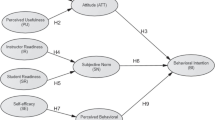
Mobile phone is increasingly widespread among University students, while different factors can affect students’ behavior towards the use and acceptance of mobile technology. One of the methods to measure these factors is the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the Behavioral Intention of University students for acceptance and use of mobile phone in their studies. The study employed the extended UTAUT2 model (Venkatesh et al. 2012) which was adapted to the Greek context. The participants were 540 students of different Universities across Greece, who completed an online questionnaire. The most important predictors for students’ Behavioral Intention to use mobile phones in their studies were Habit (the strongest one), Performance Expectancy and Hedonic Motivation. The most important predictor for actual mobile phone use was Behavioral Intention. Gender, age and experience did not have any moderating effect. The findings of this study enhance the evidence on mobile phone acceptance among University students, and have implications for students’ training.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ahmed, M. S., & Kabir, A. (2018). The acceptance of smartphone as a mobile learning tool: Students of business studies in Bangladesh. Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Technology, 6(2), 38–47.
Ahmed, M. S., Everett, J., & Turnbull, W. F. (2017). Extracting best set of factors that affect students’ adoption of smartphone for university education: Empirical evidence from UTAUT-2 model. Journal of Management, Economics, and Industrial Organization, 1(1), 51–64.
Al-Adwan, A. S., Al-Adwan, A., & Berger, H. (2018a). Solving the mystery of mobile learning adoption in higher education. International Journal of Mobile Communications, 16(1), 24–49.
Al-Adwan, A. S., Al-Madadha, A., & Zvirzdinaite, Z. (2018b). Modeling students’ readiness to adopt Mobile learning in higher education: An empirical study. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 19(1), 221–241.
Al-Shihi, H., Sharma, S. K., & Sarrab, M. (2018). Neural network approach to predict mobile learning acceptance. Education and Information Technologies, 23(5), 1805–1824.
Ameen, N., & Willis, R. (2018). An analysis of the moderating effect of age on smartphone adoption and use in the United Arab Emirates. Retrieved from https://www.ukais.org/resources/Documents/ukais%202018%20proceedings%20papers/paper_1.pdf
Ameri, A., Khajouei, R., Ameri, A., & Jahani, Y. (2020). Acceptance of a mobile-based educational application (LabSafety) by pharmacy students: An application of the UTAUT2 model. Education and Information Technologies, 25, 419–435.
Anshari, M., Almunawar, M. N., Shahrill, M., Wicaksono, D. K., & Huda, M. (2017). Smartphone usage in the classrooms: Learning aid or interference? Education and Information Technology, 22, 3063–3079.
Arain, A. A., Hussain, Z., Vighio, M. S., & Rizvi, W. H. (2018). Factors influencing acceptance of Mobile learning by higher education students in Pakistan. Sindh University Research Journal (Science Series.), 50(1), 141–146.
Arain, A. A, Hussain, Z., Rizvi, W. H., &·Vighio, M. S. (2019). Extending UTAUT2 toward acceptance of mobile learning in the context of higher education. Universal Access in the Information Society, 18(3), 659–673.
Baydas, O., & Yilmaz, R. (2018). Pre-service teachers’ intention to adopt mobile learning: A motivational model. British Journal of Educational Technology, 49(1), 137–152.
Cheng, Y., Sharma, S., Sharma, P., & Kulathunga, K. (2020). Role of personalization in continuous use intention of Mobile news apps in India: Extending the UTAUT2 model. Information, 11(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11010033.
Cohen, J. (1977). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. (Revised Edition). New York, Academic Press.
Crompton, H., & Burke, D. (2018). The use of mobile learning in higher education: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 123, 53–64.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika., 16(3), 297–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02310555.
El-Masri, M., & Tarhini, A. (2017). Factors affecting the adoption of e-learning systems in Qatar and USA: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology 2 (UTAUT2). Educational Technology Research and Development, 65, 743–763.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/3151312.
García Botero, G., Questier, F., Cincinnato, S., He, T., & Zhu, C. (2018). Acceptance and usage of mobile assisted language learning by higher education students. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 30(3), 426–451.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2017). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hao, S., Dennen, V. P., & Mei, L. (2017). Influential factors for mobile learning acceptance among Chinese users. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65, 101–123.
Huang, C. Y., & Kao, Y. S. (2015). UTAUT2 based predictions of factors influencing the technology acceptance of phablets by DNP. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/603747.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU) (2018). Measuring the information society report 2018. ITU, Geneva. Retrieved from https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Statistics/Documents/publications/misr2018/MISR-2018-Vol-1-E.pdf.
Jakkaew, P., & Hemrungrote, S. (2017). The use of UTAUT2 model for understanding student perceptions using Google classroom: A case study of introduction to information technology course. In 2017 international conference on digital arts, media and technology (ICDAMT) (pp. 205–209).
Jung, I., & Lee, J. (2020). A cross-cultural approach to the adoption of open educational resources in higher education. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51(1), 263–280.
Kalogiannakis, M., & Paradakis, S. (2019). Evaluating pre-service kindergarten teachers' intention to adopt and use tablets into teaching practice for natural sciences. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 13(1), 113–127.
Kumar, J. A., & Bervell, B. (2019). Google classroom for mobile learning in higher education: Modelling the initial perceptions of students. Education and Information Technologies, issue 2/2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-09858-z.
Kumar, B. A., & Chand, S. S. (2019). Mobile learning adoption: A systematic review. Education and Information Technologies, 24(1), 471–487.
Lavidas, K., & Gialamas, V. (2019). Adaption and psychometric properties of the short forms marlowe-crowne social desirability scale with a sample of Greek university students. European Journal of Education Studies, 6(8), 230–239. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3552531
Lavidas, K., Athanassopoulos, S., Priovolou, K., Lappa, A., & Voutsina, L. (2019). Investigating practices and perceptions of higher education students concerning the utilization of mobile devices in their studies. Open Education - The Journal for Open and Distance Education and Educational Technology, 15(2), 114–123. https://doi.org/10.12681/jode.21990.
Lebzar, B., & Jahidi, R. (2017). Factors influencing the acceptance of m-learning by students of higher education in Morocco. International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology, 6(6), 1–7.
Moorthy, K., Tzu Yee, T., Chun T'ing, L., & Vija Kumaran, V. (2019). Habit and hedonic motivation are the strongest influences in mobile learning behaviours among higher education students in Malaysia. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 35(4).
Nikolopoulou, K. (2020). Secondary education teachers’ perceptions of mobile phone and tablet use in classrooms: benefits, constraints and concerns. Journal of Computers in Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-020-00156-7
Onaolapo, S., & Oyewole, O. (2018). Performance expectancy, effort expectancy, and facilitating conditions as factors influencing smart phones use for mobile learning by postgraduate students of the University of Ibadan, Nigeria. Interdisciplinary Journal of e-Skills and Lifelong Learning, 14, 95–115.
Papadakis, S. (2018). Evaluating pre-service teachers' acceptance of mobile devices with regards to their age and gender: A case study in Greece. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 12(4), 336–352.
R Core Team (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Retrieved from https://www.R-project.org/.
Raykov, T. (1997). Estimation of composite reliability for congeneric measures. Applied Psychological Measurement, 21(2), 173–184.
Sanchez, G. (2013). PLS Path Modeling with R. Berkeley: Trowchez editions. Retrieved from http://www.gastonsanchez.com/PLS Path Modeling with R.pdf.
Sanchez, G., Trinchera, L., & Russolillo, G. (2017). Plspm: Tools for partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM). R package version, (04), 9 Retrieved from https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=plspm.
Sánchez-Prieto, C. J., Huang, F., Olmos-Migueláñez, S., García-Peñalvo, F. J., & Teo, T. (2019). Exploring the unknown: The effect of resistance to change and attachment on mobile adoption among secondary pre-service teachers. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(5), 2433–2449.
Venkataraman, J. B., & Ramasamy, S. (2018). Factors influencing mobile learning: A literature review of selected journal papers. International Journal of Mobile learning and Organization, 12(2), 99–112.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davies, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478.
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Quarterly, 36(1), 157–178.
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2016). Unified theory of acceptance and use of technology: A synthesis and the road ahead. Journal of Association for Information Systems, 17(5), 328–376.
Vrana, R. (2018). Acceptance of mobile technologies and m-learning in higher education learning: An explorative study at the Faculty of Humanities and Social Science at the University of Zagreb. 2018 41st international convention on information and communication technology, Electronics and Microelectronics.
Wang, H., & Wang, S. (2010). User acceptance of mobile internet based on the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology: Investigating the determinants and gender differences. Social Behavior and Personality, 38, 415–426.
Wang, Y., Wu, M., & Wang, H. (2009). Investigating the determinants and age and gender differences in the acceptance of mobile learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 40(1), 92–118.
Funding
This research did not receive any grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the Department of Early Childhood Education, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Availability of data and material
(by the 2nd and 3rd author, if needed)
Code availability
(n.a)
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolopoulou, K., Gialamas, V. & Lavidas, K. Acceptance of mobile phone by university students for their studies: an investigation applying UTAUT2 model. Educ Inf Technol 25, 4139–4155 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10157-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10157-9