Abstract
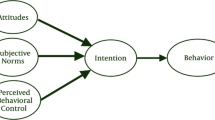
A key factor in the success of a technology is its use by target users. Therefore, the effectiveness of mobile learning depends on student acceptance. In this regard, the purpose of this study is to analyze the factors that influence university students’ acceptance of mobile learning. This study is based on Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB). Thus, the study covered attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control as the major antecedents of students’ behavioral intention to use mobile learning. The study was conducted during the 2020–2021 fall term at two different universities, which are a state university in Turkey, and a state university in Kyrgyzstan. There were a total of 400 participants, including 200 students from each country. Structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis was employed to investigate the effects of factors on participant students’ behavioral intention to use mobile learning. Turkish and Kyrgyz students showed both similarities and differences in the effects of factors on mobile learning use. The results demonstrated that subjective norm and perceived behavioral control have a significant impact on the use of mobile learning by both Turkish and Kyrgyz students. While attitude has a significant effect on Kyrgyz students’ acceptance of mobile learning, it has no significant effect on Turkish students’ acceptance.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211.
Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1972). Attitudes and normative beliefs as factors influencing behavioral intentions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 21(1), 1–9.
Akour, H. (2010). Determinants of mobile learning acceptance: an empirical investigation in higher education (UMI No. AAT 3408682.) [Doctoral dissertation]. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses database.
Al-Arabiat, D., Ahmad, W. F. W., & Sarlan, A. (2015). Review on critical factors of adopting cloud mobile learning. In 2015 International Symposium on Technology Management and Emerging Technologies (ISTMET) (pp. 69–73). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISTMET.2015.7359003.
Alasmari, T., & Zhang, K. (2019). Mobile learning technology acceptance in Saudi Arabian higher education: An extended framework and a mixed-method study. Education and Information Technologies, 24(3), 2127–2144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09865-8.
Al-Emran, M., Mezhuyev, V., & Kamaludin, A. (2018). Technology acceptance model in M-learning context: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 125, 389–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.06.008.
Alkış, N., & Coşkunçay, D. F. (2018). Mobil learning acceptance: A systematic literature review. Erzincan Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, 20(2), 571–589. https://doi.org/10.17556/erziefd.440974.
Almaiah, M. A., & Alismaiel, O. A. (2019). Examination of factors influencing the use of mobile learning system: An empirical study. Education and Information Technologies, 24(1), 885–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9810-7.
Almaiah, M. A., Alamri, M. M., & Al-Rahmi, W. (2019). Applying the UTAUT model to explain the students’ acceptance of mobile learning system in higher education. IEEE Access, 7, 174673–174686. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2957206.
Alrasheedi, M., Capretz, L. F., & Raza, A. (2015). A systematic review of the critical factors for success of mobile learning in higher education (university students' perspective). Journal of Educational Computing Research, 52(2), 257–276. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633115571928.
Al-Somali, S. A., Gholami, R., & Clegg, B. (2009). An investigation into the acceptance of online banking in Saudi Arabia. Technovation, 29, 130–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2008.07.004.
Arpaci, I. (2015). A comparative study of the effects of cultural differences on the adoption of mobile learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 46(4), 699–712. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12160.
Azizi, S. M., & Khatony, A. (2019). Investigating factors affecting on medical sciences students’ intention to adopt mobile learning. BMC Medical Education, 19(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1831-4.
Bakhsh, M., Mahmood, A., & Sangi, N. A. (2017). Examination of factors influencing students and faculty behavior towards m-learning acceptance. The International Journal of Information and Learning Technology, 34(3), 166–188. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-08-2016-0028.
Bardakcı, S. (2019). Exploring high school students’ educational use of YouTube. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 20(2). https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v20i2.4074.
Buabeng-Andoh, C. (2021). Exploring university students’ intention to use mobile learning: A research model approach. Education and Information Technologies, 26(1), 241–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10267-4.
Cheon, J., Lee, S., Crooks, S. M., & Song, J. (2012). An investigation of mobile learning readiness in higher education based on the theory of planned behavior. Computers & Education, 59(3), 1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.04.015.
Clarke, I., Flaherty, T., & Madison, J. (2003). Mobile portals: The development of M-commerce, in Mobile commerce: Technology, theory and applications. IRM Press.
Corbeil, J. R., & Valdes-Corbeil, M. E. (2007). Are you ready for mobile learning? Educause Quarterly, 30, 51–58.
Criollo-C, S., Luján-Mora, S., & Jaramillo-Alcázar, A. (2018). Advantages and disadvantages of M-learning in current education. In 2018 IEEE World Engineering Education Conference (EDUNINE) (pp. 1-6). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/EDUNINE.2018.8450979.
Crompton, H. (2013). A historical overview of mobile learning: Toward learner-centered education. In Z. L. Berge & L. Y. Muilenburg (Eds.), Handbook of mobile learning (pp. 3–14). Routledge.
Crompton, H., & Burke, D. (2018). The use of mobile learning in higher education: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 123, 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.04.007.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use and use acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–339.
Dias, L., & Victor, A. (2017). Teaching and learning with mobile devices in the 21st century digital world: Benefits and challenges. European Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 2(5), 339–344. https://doi.org/10.26417/ejms.v5i1.p339-344.
Dye, A., (2003). Mobile education – A glance at the future. Dye’s web site. http://www.dye.no/articles/a_glance_at_the_future/index.html.
Fagan, M. H. (2019). Factors influencing student acceptance of mobile learning in higher education. Computers in the Schools, 36(2), 105–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/07380569.2019.1603051.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Addison-Wesley.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50.
Gómez-Ramirez, I., Valencia-Arias, A., & Duque, L. (2019). Approach to m-learning acceptance among university students: An integrated model of TPB and TAM. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 20(3). https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v20i4.406.
Goodhue, D. L. (1995). Understanding user evaluations of information systems. Management Science, 41(12), 1827–1844.
Goodhue, D. L., & Thompson, R. L. (1995). Task-technology fit and individual performance. MIS Quarterly, 213–236.
Hao, S., Dennen, V. P., & Mei, L. (2017). Influential factors for mobile learning acceptance among Chinese users. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65(1), 101–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-016-9465-2.
Hu, L., & Xu, H. (2013, July). Collaborative m-learning based on multi-agent system. In Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics (pp. 59–62). https://doi.org/10.1109/SOLI.2013.6611382.
Isaacs, S. (2012). Turning on mobile learning in Africa and the Middle East – illustrative initiatives and policy implications. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
Kaliisa, R., Palmer, E., & Miller, J. (2019). Mobile learning in higher education: A comparative analysis of developed and developing country contexts. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(2), 546–561. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12583.
Krotov, V. (2015). Critical success factors in m-learning: A socio-technical perspective. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 36(1), 106–126. https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.03606.
Kucuk, S., Baydas Onlu, O., & Kapakin, S. (2020). A model for medical students’ behavioral intention to use mobile learning. Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development, 7, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/2382120520973222.
Kumar, B. A., & Chand, S. S. (2019). Mobile learning adoption: A systematic review. Education and Information Technologies, 24(1), 471–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9783-6.
Lin, S. H., Lee, H. C., Chang, C. T., & Fu, C. J. (2020). Behavioral intention towards mobile learning in Taiwan, China, Indonesia, and Vietnam. Technology in Society, 63, 101387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101387.
Lomax, R. G. (2010). A Beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling (third ed.). Routledge.
Mehta, R. (2016). Mobile learning for education-benefits and challenges. RJMSH, 7(1), 75-81. https://doi.org/10.32804/IRJMSH.
Naveed, Q. N., Alam, M. M., & Tairan, N. (2020). Structural equation modeling for mobile learning acceptance by university students: An empirical study. Sustainability, 12(20), 8618. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208618.
Nikolopoulou, K., Gialamas, V., Lavidas, K., & Komis, V. (2021). Teachers’ readiness to adopt mobile learning in classrooms: A study in Greece. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 26(1), 53–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-020-09453-7.
Nunnaly, J. (1978). Psychometric theory. McGraw-Hill.
Park, S. Y., Nam, M. W., & Cha, S. B. (2012). University students' behavioral intention to use mobile learning: Evaluating the technology acceptance model. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(4), 592–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2011.01229.x.
Pramana, E. (2018). Determinants of the adoption of mobile learning systems among university students in Indonesia. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 17, 365–398.
Pratama, A. R. (2021). Fun first, useful later: Mobile learning acceptance among secondary school students in Indonesia. Education and Information Technologies, 26, 1737–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10334-w.
Qashou, A. (2021). Influencing factors in m-learning adoption in higher education. Education and Information Technologies, 26(2), 1755–1785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10323-z.
Sanjebad, N. N., Shrestha, A., & Shahid, P. (2020). The Impact of Personality Traits Towards the Intention to Adopt Mobile Learning. In International Working Conference on Transfer and Diffusion of IT (pp. 182–193). Springer.
Statistica (2020a). Forecast number of mobile devices worldwide from 2020 to 2024 (in billions). Statistica. https://www.statista.com/statistics/245501/multiple-mobile-device-ownership-worldwide/.
Statistica (2020b). Percentage of consumers who use a mobile device for product research while shopping in-store worldwide as of January 2019, by country. Statistica. https://www.statista.com/statistics/348398/mobile-device-usage-product-research-in-store-shopping-worldwide/.
Tan, G. W. H., Ooi, K. B., Sim, J. J., & Phusavat, K. (2012). Determinants of mobile learning adoption: An empirical analysis. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 52(3), 82–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/08874417.2012.11645561.
Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management Science, 46(2), 186–204.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afacan Adanır, G., Muhametjanova, G. University students’ acceptance of mobile learning: A comparative study in Turkey and Kyrgyzstan. Educ Inf Technol 26, 6163–6181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10620-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10620-1