Abstract
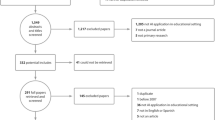
As online learning has been widely adopted in higher education in recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has brought new ways for improving instruction and learning in online higher education. However, there is a lack of literature reviews that focuses on the functions, effects, and implications of applying AI in the online higher education context. In addition, what AI algorithms are commonly used and how they influence online higher education remain unclear. To fill these gaps, this systematic review provides an overview of empirical research on the applications of AI in online higher education. Specifically, this literature review examines the functions of AI in empirical researches, the algorithms used in empirical researches and the effects and implications generated by empirical research. According to the screening criteria, out of the 434 initially identified articles for the period between 2011 and 2020, 32 articles are included for the final synthesis. Results find that: (1) the functions of AI applications in online higher education include prediction of learning status, performance or satisfaction, resource recommendation, automatic assessment, and improvement of learning experience; (2) traditional AI technologies are commonly adopted while more advanced techniques (e.g., genetic algorithm, deep learning) are rarely used yet; and (3) effects generated by AI applications include a high quality of AI-enabled prediction with multiple input variables, a high quality of AI-enabled recommendations based on student characteristics, an improvement of students’ academic performance, and an improvement of online engagement and participation. This systematic review proposes the following theoretical, technological, and practical implications: (1) the integration of educational and learning theories into AI-enabled online learning; (2) the adoption of advanced AI technologies to collect and analyze real-time process data; and (3) the implementation of more empirical research to test actual effects of AI applications in online higher education.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
* Reviewed articles (n = 32)
* Aguiar, E., Chawla, N. V., Brockman, J., Ambrose, G. A., & Goodrich, V. (2014). Engagement vs performance: using electronic portfolios to predict first semester engineering student retention. Journal of Learning Analytics, 1(3), 7–33. https://doi.org/10.18608/jla.2014.13.3
* Almeda, M. V., Zuech, J., Utz, C., Higgins, G., Reynolds, R., & Baker, R. S. (2018). Comparing the factors that predict completion and grades among for-credit and open/MOOC students in online learning. Online Learning, 22(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v22i1.1060
* Aluthman, E. S. (2016). The effect of using automated essay evaluation on esl undergraduate students’ writing skill. International Journal of English Linguistics, 6(5), 54. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijel.v6n5p54
Alyahyan, E., & Düştegör, D. (2020). Predicting academic success in higher education: literature review and best practices. In International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education (Vol. 17, Issue 1). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-0177-7
Arsovic, B., & Stefanovic, N. (2020). E-learning based on the adaptive learning model:case study in Serbia. Sadhana-Academy Proceedings in Engineering Sciences, 45(1), 266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-01499-8.
* Baneres, D., Rodriguez-Gonzalez, E., M., & Serra, M. (2019). An early feedback prediction system for learners at-risk within a first-year higher education course. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 12(2), 249–263. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2019.2912167
* Benhamdi, S., Babouri, A., & Chiky, R. (2017). Personalized recommender system for e-Learning environment. Education and Information Technologies, 22(4), 1455–1477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-016-9504-y
* Bousbahi, F., & Chorfi, H. (2015). MOOC-Rec: A case based recommender system for MOOCs. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, 1813–1822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.06.395
Breslow, L., Pritchard, D. E., DeBoer, J., Stump, G. S., Ho, A. D., & Seaton, D. T. (2013). Studying learning in the worldwide classroom: Research into edX’s first MOOC. Research & Practice in Assessment, 8, 13–25. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1062850.pdf
* Burgos, C., Campanario, M. L., de la Peña, D., Lara, J. A., Lizcano, D., & Martínez, M. A. (2018). Data mining for modeling students’ performance: A tutoring action plan to prevent academic dropout. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 66, 541–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.03.005
* Cárdenas-Cobo, J., Puris, A., Novoa-Hernández, P., Galindo, J. A., & Benavides, D. (2020). Recommender systems and scratch: An integrated approach for enhancing computer programming learning. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 13(2), 387–403. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2019.2901457
Castañeda, L., & Selwyn, N. (2018). More than tools? Making sense of the ongoing digitizations of higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 15(22), https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-018-0109-y
Chassignol, M., Khoroshavin, A., Klimova, A., & Bilyatdinova, A. (2018). Artificial intelligence trends in education: A narrative overview. 7th International Young Scientist Conference on Computational Science. Procedia Computer Science, 136, 16-24
Chang, T. Y., & Ke, Y. R. (2013). A personalized e-course composition based on a genetic algorithm with forcing legality in an adaptive learning system. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 36(1), 533–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2012.04.002
Chen, C. M. (2008). Intelligent web-based learning system with personalized learning path guidance. Computers & Education, 51(2), 787–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2007.08.004
* Chen, W., Niu, Z., Zhao, X., & Li, Y. (2014). A hybrid recommendation algorithm adapted in e-learning environments. World Wide Web, 17(2), 271–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-012-0187-z
Chen, X., Xie, H., & Hwang, G. J. (2020a). A multi-perspective study on artificial intelligence in education: grants, conferences, journals, software tools, institutions, and researchers. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 1, 100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2020.100005
Chen, X., Xie, H., Zou, D., & Hwang, G. J. (2020b). Application and theory gaps during the rise of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 1(July), 100002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2020.100002
* Christudas, B. C. L., Kirubakaran, E., & Thangaiah, P. R. J. (2018). An evolutionary approach for personalization of content delivery in e-learning systems based on learner behavior forcing compatibility of learning materials. Telematics and Informatics, 35(3), 520–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.02.004
* Costa, E. B., Fonseca, B., Santana, M. A., de Araújo, F. F., & Rego, J. (2017). Evaluating the effectiveness of educational data mining techniques for early prediction of students’ academic failure in introductory programming courses. Computers in Human Behavior, 73, 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.047
Deeva, G., Bogdanova, D., Serral, E., Snoeck, M., & De Weerdt, J. (2021). A review of automated feedback systems for learners: Classification framework, challenges and opportunities. Computers & Education, 162, 104094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.104094
Du Boulay, B. (2000). Can we learn from ITSs? In International conference on intelligent tutoring systems (pp. 9–17). Springer. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-45108-0_3
* Dwivedi, P., & Bharadwaj, K. K. (2015). E-Learning recommender system for a group of learners based on the unified learner profile approach. Expert Systems, 32(2), 264–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12061
Gardner, L., Sheridan, D., & White, D. (2002). A web-based learning and assessment system to support flexible education. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 18, 125e136. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0266-4909.2001.00220.x
Gartner (2019). Hype cycle for emerging technologies, 2019. Gartner. Retrieved on 2021/1/1 https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/3956015/hype-cycle-for-emerging-technologies-2019
George, G., & Lal, A. M. (2019). Review of ontology-based recommender systems in e-learning. Computers & Education, 142(July), 103642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103642
Giannakos, M. N., Sharma, K., Pappas, I. O., Kostakos, V., & Velloso, E. (2019). Multimodal data as a means to understand the learning experience. International Journal of Information Management, 48, 108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.02.003
Godwin, A., & Kirn, A. (2020). Identity‐based motivation: Connections between first‐year students' engineering role identities and future‐time perspectives. Journal of Engineering Education, 109(3), 362–383. https://doi.org/10.1002/jee.20324
Graneheim, U. H., & Lundman, B. (2004). Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Education Today, 24(2), 105e112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2003.10.001
Guan, C., Mou, J., & Jiang, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence innovation in education: A twenty-year data-driven historical analysis. International Journal of Innovation Studies, 4(4), 134–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijis.2020.09.001
Harasim, L. (2000). Shift happens: Online education as a new paradigm in learning. The Internet and higher education, 3(1–2), 41–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1096-7516(00)00032-4
* Helal, S., Li, J., Liu, L., Ebrahimie, E., Dawson, S., Murray, D. J., & Long, Q. (2018). Predicting academic performance by considering student heterogeneity. Knowledge-Based Systems, 161(July), 134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.07.042
Henly, D. C. (2003). Use of web-based formative assessment to support student learning in a metabolism/nutrition unit. European Journal of Dental Education, 7(3), 116e122. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0579.2003.00310.x
* Hew, K. F., Hu, X., Qiao, C., & Tang, Y. (2020). What predicts student satisfaction with MOOCs: A gradient boosting trees supervised machine learning and sentiment analysis approach. Computers & Education, 145, 103724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103724
Hinojo-Lucena, F. J., Aznar-Díaz, I., Cáceres-Reche, M. P., & Romero-Rodríguez, J. M. (2019). Artificial intelligence in higher education: A bibliometric study on its impact in the scientific literature. Education Sciences, 9(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci9010051
Hollan, J., Hutchins, E., & Kirsh, D. (2000). Distributed cognition: Toward a new foundation for human-computer interaction research. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction (TOCHI), 7(2). https://doi.org/10.1145/353485.353487
Holmberg, B. (2005). Theory and practice of distance education. Routledge
Holmes, W., Bialik, M., & Fadel, C. (2019). Artifificial intelligence in education: Promises and implications for teaching and learning. Center for Curriculum Redesign
* Hooshyar, D., Ahmad, R. B., Yousefi, M., Fathi, M., Horng, S. J., & Lim, H. (2016). Applying an online game-based formative assessment in a flowchart-based intelligent tutoring system for improving problem-solving skills. Computers & Education, 94, 18–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.10.013
* Howard, E., Meehan, M., & Parnell, A. (2018). Contrasting prediction methods for early warning systems at undergraduate level. The Internet and Higher Education, 37, 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2018.02.001
Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15(9), 1277–1288. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732305276687
Hu, Y. H. (2021). Effects and acceptance of precision education in an AI-supported smart learning environment. Education and Information Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10664-3
* Hu, Y., Lo, C., & Shih, S. (2014). Developing early warning systems to predict students’ online learning performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 36, 469–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.04.002
* Huang, A. Y. Q., Lu, O. H. T., Huang, J. C. H., Yin, C. J., & Yang, S. J. H. (2020). Predicting students’ academic performance by using educational big data and learning analytics: evaluation of classification methods and learning logs. Interactive Learning Environments, 28(2), 206–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1636086
Hwang, G. J., & Tu, Y. F. (2021). Roles and research trends of artificial intelligence in mathematics education: A bibliometric mapping analysis and systematic review. Mathematics. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9060584
Hwang, G. J., Xie, H., Wah, B. W., & Gašević, D. (2020). Vision, challenges, roles and research issues of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 1, 100001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2020.100001
* Ijaz, K., Bogdanovych, A., & Trescak, T. (2017). Virtual worlds vs books and videos in history education. Interactive Learning Environments, 25(7), 904–929. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2016.1225099
* Jayaprakash, S. M., Moody, E. W., Eitel, J. M., Regan, J. R., & Baron, J. D. (2014). Early alert of academically at-risk students: An open source analytics initiative. Journal of Learning Analytics, 1, 6–47. https://doi.org/10.18608/jla.2014.11.3
Kabudi, T., Pappas, I., & Olsen, D. H. (2021). AI-enabled adaptive learning systems: A systematic mapping of the literature. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 2, 100017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2021.100017
Kim, J. N., & Grunig, J. E. (2011). Problem solving and communicative action: A situational theory of problem solving. Journal of Communication, 61(1), 120–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.2010.01529.x
* Koć-Januchta, M. M., Schönborn, K. J., Tibell, L. A. E., Chaudhri, V. K., & Heller, H. C. (2020). Engaging with biology by asking questions: Investigating students’ interaction and learning with an artificial intelligence-enriched textbook. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 58(6), 1190–1224. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120921581
Law, N. W. Y. (2019). Human development and augmented intelligence. In The 20th international conference on artificial intelligence in education (AIED 2019). Springer. Retrieved on 2021/1/1 from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/refhub/S2666-920X(21)00014-undefined/sref31
* Li, J., Chang, Y., Chu, C., & Tsai, C. (2012). Expert systems with applications a self-adjusting e-course generation process for personalized learning. Expert Systems With Applications, 39(3), 3223–3232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.09.009
Liu, M., Kang, J., Zou, W., Lee, H., Pan, Z., & Corliss, S. (2017). Using data to understand how to better design adaptive learning. Technology Knowledge and Learning, 22(3), 271–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-017-9326-z
Liu, S., Guo, D., Sun, J., Yu, J., & Zhou, D. (2020). MapOnLearn: The use of maps in online learning systems for education sustainability. Sustainability, 12(17), 7018. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177018
Liz-Domínguez, M., Caeiro-Rodríguez, M., Llamas-Nistal, M., & Mikic-Fonte, F. A. (2019). Systematic literature review of predictive analysis tools in higher education. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 9(24). MDPI AG. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245569
Lykourentzou, I., Giannoukos, I., Nikolopoulos, V., Mpardis, G., & Loumos, V. (2009). Dropout prediction in e-learning courses through the combination of machine learning techniques. Computers & Education, 53(3), 950–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.05.010
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., Prisma Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS medicine, 6(7), e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.t001
Moreno-Marcos, P. M., Muñoz-Merino, P. J., Alario-Hoyos, C., Estévez-Ayres, I., & Delgado Kloos, C. (2018). Analysing the predictive power for anticipating assignment grades in a massive open online course. Behaviour & Information Technology, 37(10–11), 1021–1036. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2018.1458904
Moreno-Marcos, P. M., Alario-Hoyos, C., Munoz-Merino, P. J., & Kloos, C. D. (2019). Prediction in MOOCs: A Review and Future Research Directions. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 12(3), 384–401. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2018.2856808
Moseley, L. G., & Mead, D. M. (2008). Predicting who will drop out of nursing courses: a machine learning exercise. Nurse Education Today, 28(4), 469–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2007.07.012
* Mubarak, A. A., Cao, H., & Zhang, W. (2020). Prediction of students’ early dropout based on their interaction logs in online learning environment. Interactive Learning Environments. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1727529
Neuendorf, K. A., & Kumar, A. (2015). Content analysis. The international Encyclopedia of Political Communication, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118541555.wbiepc065
Ouyang, F. & Jiao, P. (2021). Artificial Intelligence in Education: The Three Paradigms. Computers & Education: Artificial Intelligence, 100020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2021.100020
Rico-Juan, J. R., Gallego, A. J., & Calvo-Zaragoza, J. (2019). Automatic detection of inconsistencies between numerical scores and textual feedback in peer-assessment processes with machine learning. Computers & Education, 140, 103609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103609
Riedl, M. O. (2019). Human-centered artificial intelligence and machine learning. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, 1(1), 33–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbe2.117
Rowe, M. (2019). Shaping our algorithms before they shape us. Artificial Intelligence and Inclusive Education (pp. 151–163). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8161-4_9
Romero, C., Espejo, P. G., Zafra, A., Romero, J. R., & Ventura, S. (2013). Web usage mining for predicting final marks of students that use Moodle courses. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 21(1), 135–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/cae.20456
* Romero, C., López, M. I., Luna, J. M., & Ventura, S. (2013). Predicting students’ final performance from participation in on-line discussion forums. Computers & Education, 68, 458–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.06.009
Selwyn, N. (2016). Is technology good for education? Polity Press. Retrieved on 2021/1/10 from http://au.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0745696465.html
Shahiri, A. M., Husain, W., & Rashid, N. A. (2015). A review on predicting student’s performance using data mining techniques. Procedia Computer Science, 72, 414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.12.157
Simpson, O. (2018). Supporting students in online, open and distance learning (1st ed.). Routledge
* Sukhbaatar, O., Usagawa, T., & Choimaa, L. (2019). An artificial neural network based early prediction of failure-prone students in blended learning course. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 14(19), 77–92. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v14i19.10366
Tang, K. Y., Chang, C. Y., & Hwang, G. J. (2021). Trends in artificial intelligence supported e-learning: A systematic review and co-citation network analysis (1998-2019). Interactive Learning Environments. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1875001
Tegmark, M. (2017). Life 3.0: Being human in the age of artificial intelligence. (Knopf)
Tomasevic, N., Gvozdenovic, N., & Vranes, S. (2020). An overview and comparison of supervised data mining techniques for student exam performance prediction. Computers & Education, 143, 103676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103676
Tyler-Smith, K. (2006). Early attrition among first time eLearners: A review of factors that contribute to drop-out, withdrawal and non-completion rates of adult learners undertaking eLearning programmes. Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 2(2), 73–85. Retrieved on 2021/1/11 from https://jolt.merlot.org/documents/Vol2_No2_TylerSmith_000.pdf
Vygotsky, L. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Harvard University Press
* Wakelam, E., Jefferies, A., Davey, N., & Sun, Y. (2020). The potential for student performance prediction in small cohorts with minimal available attributes. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51(2), 347–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12836
Wohlin, C. (2014). Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering (pp. 1-10). https://doi.org/10.1145/2601248.2601268
Xie, H., Chu, H. C., Hwang, G. J., & Wang, C. C. (2019). Trends and development in technology-enhanced adaptive/personalized learning: A systematic review of journal publications from 2007 to 2017. Computers & Education, 140, 103599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103599
* Xing, W., Chen, X., Stein, J., & Marcinkowski, M. (2016). Computers in human behavior temporal predication of dropouts in MOOCs: Reaching the low hanging fruit through stacking generalization. Computers in Human Behavior, 58, 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.12.007
Xu, W. & Ouyang, F. (2021). A systematic review of AI role in the educational system based on a proposed conceptual framework. Education and Information Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10774-y
* Xu, X., Wang, J., Peng, H., & Wu, R. (2019). Prediction of academic performance associated with internet usage behaviors using machine learning algorithms. Computers in Human Behavior, 98(April), 166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.04.015
* Yang, T., Brinton, C. G., & Joe-wong, C. (2017). Behavior-based grade prediction for MOOCs via time series neural networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 11(5), 716–728. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2017.2700227
Yang, Y. T. C., Gamble, J. H., Hung, Y. W., & Lin, T. Y. (2014). An online adaptive learning environment for critical-thinking-infused English literacy instruction. British Journal of Educational Technology, 45(4), 723–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12080
Yang, C., Huan, S., & Yang, Y. (2020). A practical teaching mode for collegessupported by Artificial Intelligence. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 15(17), 195–206. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v15i17.16737
* Yoo, J., & Kim, J. (2014). Project performance? Investigating the roles of linguistic features and participation patterns. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 24, 8–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-013-0010-8
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education – where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0
Zhai, X., Chu, X., Chai, C. S., Siu, M., Jong, Y., Istenic, A. … Li, Y. (2021). A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education from 2010 to 2020. 2021. Complexity, 8812542. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8812542
* Zohair, L. M. (2019). Prediction of student’s performance by modelling small dataset size. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0160-3
Zupic, I., & Čater, T. (2015). Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organizational Research Methods, 18(3), 429–472. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428114562629
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 62177041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, F., Zheng, L. & Jiao, P. Artificial intelligence in online higher education: A systematic review of empirical research from 2011 to 2020. Educ Inf Technol 27, 7893–7925 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-10925-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-10925-9