Abstract
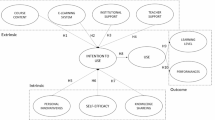
Performance expectancy is the expected impact of a technology’s functional advantage even in uncertain conditions. This study suggests that the learning collaboration quality, information quality, and course content support impact the actual use of e-learning and satisfaction perceived by the user, resulting in performance expectancy that meets stakeholder expectations. This study outlines the theoretical model for defining student success in e-learning systems through a theory of online collaborative learning. The research examines the empirical data gathered from 109 postgraduate doctoral students’ participated in the postgraduate universities in Indonesia. The research attempts to focus specifically on how the actual use of e-learning and satisfaction perceived by users mediates the influence of learning collaboration quality, information quality, and course content support on performance expectancy to enhance the sustainability and performance of e-learning in Indonesian universities. The study shows that the learning collaboration quality, information quality, and course content support have no impact on performance expectancy, while each of the constructs indirectly impacts the performance expectancy through the actual use of e-learning. Conversely, the learning collaboration quality and course content support have not indirectly influenced toward performance expectancy by satisfaction perceived by the user as mediator except the information quality.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Abu-Al-Aish, A., & Love, S. (2013). Factors influencing students’ acceptance of m-learning: An investigation in higher education. International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 14(5), 82–107. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v14i5.1631(14) (PDF) Predicting mobile learning acceptance: An integrated model and empirical study based on higher education students' perceptions. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349927523_Predicting_mobile_learning_acceptance_An_integrated_model_and_empirical_study_based_on_higher_education_students'_perceptions [accessed May 13 2021]
Ahmad, N., Quadri, N. N., Qureshi, M. R. N., & Alam, M. M. (2018). Relationship modeling of critical success factors for enhancing sustainability and performance in E-learning. Sustainability, 10(12), 4776.
Akbar, F. (2013). What affects students’ acceptance and use of technology? https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/1ab8/0a44a26e2d09ae0dc3729be409730a782910.pdf. Accessed 1 July 2020.
Al-Araibi, A. A. M., Naz’ri Bin Mahrin, M., & Yusoff, R. C. M. (2019). Technological aspect factors of E- learning readiness in higher education institutions: Delphi technique. Education and Information Technologies, 24(1), 567–590.
Aldowah, H., Al-Samarraie, H., & Ghazal, S. (2019). How course, contextual, and technological challenges are associated with instructors’ individual challenges to successfully implement E-learning: A developing country perspective. IEEE Access, 7, 48792–48806.
Al-Fraihat, D., Joy, M., & Sinclair, J. (2018). A comprehensive model for evaluating e-learning systems success. Distance Learning, 15(3), 57–88.
Almaiah, M. A., & Almulhem, A. (2018). A conceptual framework for determining the success factors of e- learning system implementation using Delphi technique. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 96, 1–15.
Almaiah, M. A., & Alyoussef, I. Y. (2019). Analysis of the effect of course design, course content support, course assessment and instructor characteristics on the actual use of E-learning system. IEEE Access, 7, 171907–171922.
Almaiah, M. A., Al-Khasawneh, A., & Althunibat, A. (2020). Exploring the critical challenges and factors influencing the E-learning system usage during COVID-19 pandemic. Education and Information Technologies, 25, 5261 5280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10219-y
Anderson, & Elloumi. (2004). Theory and practice of online learning. Athabasca University.
Ani, O. E. (2013). Accessibility and utilization of electronic information resources for research and its effect on productivity of academic staff in selected Nigerian universities between 2005 and 2012. A Thesis submitted in accordance with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Literature and Philosophy in the subject Information Science at.
Aparicio, M., Bacao, F., & Oliveira, T. (2014). Trends in the e-learning ecosystem: A bibliometric study. In proceedings of 20th American conference on information system. Retrieved from http://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2014/Posters/ISEducation/7
Aparicio, M., Bacao, F., & Oliveira, T. (2016). Cultural impacts on e-learning systems' success. The Internet and Higher Education, 31, 58–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.06.003
Aparicio, M., Bacao, F., & Oliveira, T. (2017). Grit in the path to e-learning success. Computers in Human Behavior, 66, 388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.10.009
Bailey, J. E., & Pearson, S. W. (1983). Development of a tool for measuring and analyzing computer user satisfaction. Management Science, 29, 530–545.
Bao, W. (2020). COVID -19 and online teaching in higher education: A case study of Peking University. Human Behaviour and Emerging Technologies, 2(2), 113–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbe2.191
Beam, P. (1997). Breaking The Sprinter’s Wrist: Achieving cost-effectiveness online learning. The International Symposium on Distance Education and Open Learning. MONE Indonesia, IDLN, SEAMOLEC, ICDE, UNDP dan UNESCO, Bali.
Bentler, PM, Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness-of-fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88, 588–600.
Brahmasrene, T, Lee, J. W. (2012). Determinants of intent to continue using online learning: A tale of two universities. Interdisciplinary Journal of Information, Knowledge, and Management, 7, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.28945/1548
Bullen, M. (2001). E-learning and the Internationalizat Education. Malaysian Journal of Education Technologi., 1(1), 37–46.
Cheng, Y. M. (2011). Antecedents and consequences of e-learning acceptance. Information Systems Journal, 21(3), 269–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2575.2010.00356.x
Chua, H. F., Boland, J. E., & Nisbett, R. E. (2005). Cultural variation in eye movements during scene perception. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(35), 12629–12633.
Cidral, W. A., Oliveira, T., Di Felice, M., & Aparicio, M. (2018). E-learning success determinants: Brazilian empirical study. Computers & Education, 122, 273–290.
Daniel, S. J. (2020). Education and the COVID-19 pandemic. Prospects, 49, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-020-09464-3
Davis, F. D. (1989). “Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology". MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–339.
Dede, R. (2004). Education paradigm (p. 276). Kencana.
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (1992). Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Information Systems Research, 3(1), 60–95. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.3.1.60
DeLone, W. H., McLean, E. R. (2002). Information systems success revisited. In Proceedings of the 35th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (p. 1–11).
Dewiyanti, S., Brand-Gruwel, S., Jochems, W., & Broers, N. J. (2007). Students’ experiences with collaborative learning in asynchronous computer-supported collaborative learning environments. Computers in Human Behavior, 23(1), 496–514.
Dikti, (2019) Directorate of higher education Indonesia. https://dikti.kemdikbud.go.id/. Accessed 17 July 2020.
Eltahir, M. E. (2019). E-learning in developing countries: Is it a panacea? A case study ofSudan. IEEEAccess, 7, 97784–97792.
Engotoit, B., Kituyi, G. M., & Moya, M. B. (2016). Influence of performance expectancy on commercial farmers’ intention to use mobile-based communication technologies for agricultural market information dissemination in Uganda. Journal of Systems and Information Technology, 18(4), 346–363.
Garrison, D. R. (2006a). Online collaboration principles. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 10(1), 25–34.
Garrison, D. R. (2006b). Online collaboration principles. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 10(1), 25–34. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v10i1.1768
Garrison, D. R., & Anderson, T. (2003). E-learning in the 21st century: Aframework for research and practice. Routledge Falmer.
Garrison, D. R., & Cleveland-Innes, M. (2005). Facilitating cognitive presence in online learning: Interaction is not enough. The American Journal of Distance Education, 19(3), 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15389286ajde1903_2
Garrison dan Innes. (2005). Facilitating Cognitive Presence in Online Learning: Interaction is Not Enough. The American Journal of Distance Education, 19(3).
Gillborn, D., & Mirza, H. S. (2000). Educational inequality: Mapping race, class and gender—A synthesis of research evidence. Report #HMI 232. Office for Standards in Education.
Gold, A. H., Malhotra, A., & Segars, A. H. (2001). Knowledge management: An organizational capabilities perspective. Journal of Management Information Systems, 18(1), 185–214.
Haghshenas, M. (2019). A model for utilizing social Softwares in learning management system of E-learning. Quarterly Journal of Iranian Distance Education, 1(4), 25–38.
Hammer, M., & Champy, J. (1993). Reengineering the corporation, A Manifesto for Business Revolution. Nicholas Brealey.
Harasim, L. M. (2017). Learning theory and online technologies. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/ulaval/detail.action?docID=4865772.
Hattie, J. A. C. (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modelling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115–135.
Hu, L.-T., & Bentler, P. M. (1998). Fit indices in covariance structure modeling: Sensitivity to Underparameterized model misspecification. Psychological Methods, 3(4), 424–453.
Idris, F. A. A., & Osman, Y. B. (2015). Challenges facing the implementation of e-learning at University of Gezira According to view of staff members. 2015 Fifth International Conference on e- Learning (econf) (pp. 336–348). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECONF.2015.51.
Jambulingam, M. (2013). Behavioral intention to adopt mobile technology among tertiary students. World Applied Sciences Journal, 22(9), 1262–1271.
Jung, I., Choi, S., Lim, C., & Leem, J. (2002). Effects of different types of interaction on learning achievement, satisfaction, and participation in web-based instruction. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 39(2), 153e162.
Marchewka, J. T., & Kostiwa, K. (2007). An application of the UTAUT model for understanding student perceptions usingcourse management software. Communications of the IIMA, 7(2), 10.
Min, Q., Ji, S., Qu, G. (2008). Mobile commerce user acceptance study in china: A revised utaut model. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 13(3), 257–264
Moore, M., & Kearsley, G. (2011). Distance Education: A systems view of online learning (3rd ed.). Cengage Learning.
Nwone, S. A., & Mutula, S. (2019). Determinants of use of electronic information resources by the professoriate in Nigerian universities: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and utilization of technology model. South African Journal of Information Management, 21(1), 1–8.
Ozudogru, F., & Hismanoglu, M. (2016). Views of freshmen students on foreign language courses delivered via E-learning. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 17(1), 31–47.
Paton, A., Fooks, G., Maestri, G., & Lowe, P. (2020). Submission of evidence on the disproportionate impact of COVID 19, and the UK government response, on ethnic minorities and women in the UK. Aston University Publication. https://publicationsaston.ac.uk/id/eprint/41460/. Accessed 29 Sep 2020.
Royle, K., & Nikolic, J. (2013). Agile Digital Age Pedagogy for Teachers: ADAPT. http://legacy.naace.co.uk/2299. Accessed 30 July 2020.
Sahu, P. (2020). Closure of universities due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Impact on education and mental health of students and academic staff. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7541
Salloum, S. A. S., & Shaalan, K. (2018). Investigating students’ acceptance of E-learning system in higher educational environments in the UAE: Applying the extended technology acceptance model (TAM). The British University in Dubai.
Selim, H. M. (2003). An empirical investigation of student acceptance of course websites. Computers & Education, 40(4), 343–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1315(02)00142-2
Shahzad, A., Hassan, R., Aremu, A. Y., Hussain, A., & Lodhi, R. N. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 in E-learning on higher education institution students: The group comparison between male and female. Quality & Quantity, 1–22.
Sun, PC, Tsai, RJ, Finger, G, Chen, YY, & Yeh, D (2008). What drives a successful e-learning? An empirical investigation of the critical factors influencing learner satisfaction. Computers & Education, 50(4), 1183–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2006.11.007.
Tai, D. B. G., Shah, A., Doubeni, C. A., Sia, I. G., & Wieland, M. L. (2020). The disproportionate impact of COVID-19 on racial and ethnic minorities in the United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 72(4), 703–706.
Tam, C., & Oliveira, T. (2016). Understanding the impact of m-banking on individual performance: DeLone & McLean and TTF perspective. Computers in Human Behavior, 61, 233–244.
Tan, P. J. B. (2013). Applying the UTAUT to understand factors affecting the use of English e-learning websites in Taiwan. SAGE Open. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244013503837
Tchoubar, T. (2014). Effective use of multimedia explanations in open e-learning environment fosters student success. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 4(1), 63.
Tu, C. H., & McIsaac, M. (2002). The relationship of social presence and interaction in online classes. The American Journal of Distance Education, 16(3), 131–150.
Ülker, D., & Yılmaz, Y. (2016). Learning management systems and comparison of open-source learning management systems and proprietary learning management systems. Journal of Systems Integration, 7(2), 18–24.
UNESCO. (2020). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. Retrieved from https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse
Urbach, N., Smolnik, S., & Riempp, G. (2010). An empirical investigation of employee portal success. Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 19(3), 184–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2010.06.002
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 425–478.
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Quarterly, 157–178.
Vershitskaya, E. R., Mikhaylova, A. V., Gilmanshina, S. I., Dorozhkin, E. M., & Epaneshnikov, V. V. (2020). Present-day management of universities in Russia: Prospects and challenges of e-learning. Education and Information Technologies, 25(1), 611–621.
Voogt, J., Erstad, O., Dede, C., & Mishra, P. (2013). Challenges to learning and schooling in the digital networked world of the 21st century. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 29(5), 403–413.
Wahana Visi Indonesia (2020). Teacher Response Survey Results during the Covid-19 pandemic. https://wahanavisi.org/id/media-materi/media. Accessed 5 Aug 2020.
Wahyuni, D. S., Agustini, K., Sindu, I. G. P., & Sugihartini, N. (2020a). Analysis on vocational high school teacher competency gaps: Implication for VHS teacher training needs. In Journal of physics: Conference series (Vol. 1516, no. 1, p. 012051). IOP publishing.
Wahyuni, D., Sudira, P., Agustini, K., & Gede, A. (2020b). The effect of external learning on vocational high school performance with mediating role of instructional agility and product innovation efficacy in Indonesia. Management Science Letters, 10(16), 3931–3940.
Walters, K. , Shaw, M., De Gagne, J. C. (2010). Want to teach online? Things you should know. Journal of eLearning and Online Teaching.
Wang, Y., Wu, M., & Wang, H. (2009). Investigating the determinants and age and gender differences in the acceptance of mobile learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 40(1), 92–118 (14) (PDF) factors influencing Students' acceptance of M-learning: An investigation in higher Education. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284339985_Factors_Influencing_Students%27_Acceptance_of_M-Learning_An_Investigation_in_Higher_Education [accessed May 13 2021]
Wright, C. R. (2003). Criteria for evaluating the quality of online courses. Edmonton, Alberta: Alberta Distance and Training Association, 16(2), 185–200. https://elearning.typepad.com/thelearnedman/ID/evaluatingcourses.pdf
Yahaya, Z. N., Yahaya, N. M., & Zain, N. N. B. M. (2017). Factors influencing mobile learning among higher education students in Malaysia. International Journal of Advanced Scientific Research and Management, 2(8), 86–91. http://www.ijasrm.com. Accessed 15 Aug 2020.
Yulius, R. (2016). Voluntary moderation effect on online learning at the Suhid University, Surakarta. Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 10. 10.22216/jit.2016.v10i4.534
Zhu, C. (2012). Student satisfaction, performance, and knowledge construction in online collaborative learning. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 15(1), 127–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
UNIVERSITAS BRAWIJAYA has achieved an accreditation by The Alliance on Business Education and Scholarship for Tomorrow, a twenty-first century organization (ABEST21) for Accounting, Economics, and Management study programmes from Faculty of Economics and Business. UNIVERSITAS BRAWIJAYA is Indonesian State University.
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sewandono, R.E., Thoyib, A., Hadiwidjojo, D. et al. Performance expectancy of E-learning on higher institutions of education under uncertain conditions: Indonesia context. Educ Inf Technol 28, 4041–4068 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11074-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11074-9