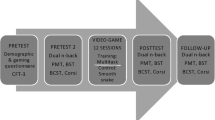
Abstract
Evaluation is crucial in the treatment of autistic children. The Psychoeducational Profile -Third Edition (PEP-3) is a standardized scale used to evaluate the development of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). However, as a traditional scale, the PEP-3 relies highly on the experience of the evaluator, and the evaluation process is complicated and time-consuming. Therefore, based on the PEP-3, this study aimed to use touchscreen and speech recognition technology to develop a set of human–computer interaction (HCI) games for the evaluation of the cognitive and language abilities of children with ASD. The study consisted of three parts: construct evaluation of the items and games, calibration and validation of the games, and cross-validation of the games. A total of 45 ASD children were recruited. They were divided into two groups: the calibration/validation group and the cross-validation group. The calibration/validation group was used to test the feasibility of the evaluation games. The cross-validation group was used to validate the effectiveness of the evaluation games. The results showed (1) the HCI evaluation games were a supportive tool to evaluate the cognitive and language ability of children with ASD; (2) there was a high agreement between the HCI evaluation games and the PEP-3, and the evaluation based on the HCI evaluation games reflected the evaluation results of the PEP-3; and (3) compared to the PEP-3, the HCI evaluation games saved time and were objective and attractive. Overall, our findings demonstrated that the HCI evaluation games were an effective means for evaluation and encourage future work in exploring technology-based methods for evaluating children with ASD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, H., Garberson, F., Liu-Mayo, S., Glover, E., & Wall, D. P. (2020). Multi-modular AI approach to streamline autism diagnosis in young children. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61213-w
Amaral, C., Mouga, S., Simoes, M., Pereira, H. C., Bernardino, I., et al. (2018). A feasibility clinical trial to improve social attention in autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) using a brain computer interface. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00477
American Psychiatric Association. (2015). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Association.
Anzulewicz, A., Sobota, K., & Delafield-Butt, J. T. (2016). Toward the Autism Motor Signature: Gesture patterns during smart tablet gameplay identify children with autism. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 31107. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31107
Baio, J., Wiggins, L., Christensen, D. L., Maenner, M. J., Daniels, J., et al. (2018). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years — autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, united states, 2014. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 67(6), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1
Baker, F. (2001). The basics of item response theory. ERIC Clearinghouse.
Billeci, L., Narzisi, A., Tonacci, A., Sbriscia-Fioretti, B., Serasini, L., Fulceri, F., et al. (2017). An integrated EEG and eye-tracking approach for the study of responding and initiating joint attention in autism spectrum disorders. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 13560. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13053-4
Bovery, M., Dawson, G., Hashemi, J., & Sapiro, G. (2021). A scalable off-the-shelf framework for measuring patterns of attention in young children and its application in autism spectrum disorder. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 12(3), 722–731. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2018.2890610
Bradshaw, J., Steiner, A. M., Gengoux, G., & Koegel, L. K. (2015). Feasibility and effectiveness of very early intervention for infants at-risk for autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(3), 778–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2235-2
Caron, V., Berube, A., & Paquet, A. (2017). Implementation evaluation of early intensive behavioral intervention programs for children with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review of studies in the last decade. Evaluation and Program Planning, 62, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2017.01.004
Castro, S., Trentini, C., & Riboldi, J. (2010). Item response theory applied to the beck depression inventory. Revista Brasileira De Epidemiologia, 13(3), 487–501. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-790X2010000300012
Chen, J., Wang, G., Zhang, K., Wang, G., & Liu, L. (2019). A pilot study on evaluating children with autism spectrum disorder using computer games. Computers in Human Behavior, 90, 204–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.057
Clark, M., Vinen, Z., Barbaro, J., & Dissanayake, C. (2018). School age outcomes of children diagnosed early and later with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders, 48(1), 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3279-x
Dahiya, A. V., DeLucia, E., McDonnell, C. G., & Scarpa, A. (2021). A systematic review of technological approaches for autism spectrum disorder assessment in children: Implications for the COVID-19 pandemic. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 109, 103852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2021.103852
De Ayala, R. J. (2009). The Theory and Practice of Item Response Theory. Guilford Press.
DeVon, H., Block, M., Moyle-Wright, P., Ernst, D., et al. (2007). A psychometric toolbox for testing validity and reliability. Nursing. Scholarship, 39(2), 155–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2007.00161.x
Drumm, S., Bradley, C., & Moriarty, F. (2022). ‘More of an art than a science’? The development, design and mechanics of the Delphi Technique. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 18(1), 2230–2236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.06.027
Embretson, S. E., & Reise, S. P. (2000). Item response theory for psychologists. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Fakhoury, M. (2015). Autistic spectrum disorders: A review of clinical features, theories and diagnosis. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 43, 70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2015.04.003
Ferketich, S. (1991). Focus on psychometrics. Aspects of item analysis. Research in Nursing and Health, 14(2), 165–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.4770140211
Fu, C., Hsieh, C., Tseng, M., Chen, Y., Huang, W., Wu, P., et al. (2010). Inter-rater reliability and smallest real difference of the Chinese Psychoeducational Profile-third edition for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4(1), 89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2009.09.002
Fu, C. P., Chen, K. L., Tseng, M. H., Chiang, F. M., & Hsieh, C. L. (2012). Reliability and validity of the psychoeducational profile-third edition caregiver report in children with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(1), 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2011.03.011
Fulton, M. L., & D’Entremont, B. (2013). Utility of the Psychoeducational Profile-3 for assessing cognitive and language skills of children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 43(10), 2460–2471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1794-y
Fusaroli, R., Weed, E., Fein, D., & Naigles, L. (2019). Hearing me hearing you: Reciprocal effects between child and parent language in autism and typical development. Cognition, 183, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2018.10.022
Giacomo, A. D., Craig, F., Cristella, A., Terenzio, V., & Margari, L. (2016). Can PEP-3 provide a cognitive profile in children with ASD? A comparison between the developmental ages of PEP-3 and IQ of Leiter-R. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 29(6), 566–573. https://doi.org/10.1111/jar.12216
Goulart, C., Valadão, C., Caldeira, E., et al. (2019). Brain signal evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorder in the interaction with a social robot. Biotechnology Research and Innovation, 3(1), 60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biori.2018.11.003
Harrison, A. J., Slane, M. M., Hoang, L., & Campbell, J. M. (2017). An international review of autism knowledge assessment measures. Autism, 21(3), 262–275. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361316638786
He, H., Zhou, T., Zeng, D., & Ma, Y. (2021). Development of the competency evaluation scale for clinical nursing teachers: Results of a Delphi study and validation. Nurse Education Today, 101, 104876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104876
Hoofs, V., Princen, M. M., Poljac, E., Stolk, A., & Poljac, E. (2018). Task switching in autism: An EEG study on intentions and actions. Neuropsychologia, 117, 398–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.07.008
Jyoti, V., & Lahiri, U. (2020). Human-Computer Interaction based Joint Attention cues: Implications on functional and physiological measures for children with autism spectrum disorder. Computers in Human Behavior, 104, 106163–106163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.106163
Kwon, M. K., Moore, A., Barnes, C. C., et al. (2019). Typical levels of eye-region fixation in toddlers with ASD across multiple contexts. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 58(10), 1004–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2018.12.011
Lee, J. W., Jones, P. S., Mineyama, Y., & Zhang, X. E. (2002). Cultural differences in responses to a Likert scale. Research in Nursing & Health, 25(4), 295–306. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.10041
Lee, C., Su, C., Chiang, F., Chen, Y., Hsieh, C., & Fu, C. (2016). Developing a short form of the Psychoeducational Profile-Third Edition for children with autism spectrum disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 21, 37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2015.09.008
Lee, S., Lin, S., Ko, H., & Liu, Y. (2020). Construct validity and reliability of the Chinese version personal adjustment and role skills scale iii for adolescents with chronic disease. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, 53, e136–e141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2020.03.008
Lord, F. M. (1980). Applications of item response theory to practical testing problems. Erlbaum.
Malaia, E., Cockerham, D., & Rublein, K. (2017). Visual integration of fear and anger emotional cues by children on the autism spectrum and neurotypical peers: An EEG study. Neuropsychologia, 126, 138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.06.014
Marchi, E., Schuller, B., Baird, A., Baron-Cohen, S., Lassalle, A., et al. (2019). The ASC-inclusion perceptual serious gaming platform for autistic children. IEEE Transactions on Games, 11(4), 328–339. https://doi.org/10.1109/TG.2018.2864640
McConachie, H., Parr, J. R., Glod, M., Hanratty, J., Livingstone, N., Oono, I. P., et al. (2015). Systematic review of tools to measure outcomes for young children with autism spectrum disorder. Health Technology Evaluation, 19(41), 1–506. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta19410
Memari, A. H., Mirfazeli, F. S., Kordi, R., et al. (2017). Cognitive and social functioning are connected to physical activity behavior in children with autism spectrum disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 33, 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2016.10.001
Mo, S., Liang, L., Bardikoff, N., & Sabbagh, M. A. (2019). Shifting visual attention to social and non-social stimuli in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 65, 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2019.05.006
Mohammadi, F., Rakhshan, M., Molazem, Z., Zareh, N., & Gillespie, M. (2020). Development of parental competence scale in parents of children with autism. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, 50, e77–e84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2019.04.006
Moon, S. J., Hwang, J., Kana, R., Torous, J., & Kim, J. W. (2019). Accuracy of machine learning algorithms for the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis of brain magnetic resonance imaging studies. JMIR Mental Health, 6(12), e14108. https://doi.org/10.2196/14108
Morimoto, C., Nakazono, S., Kobori, S., Kaneko, F., Muratake, S., & Okamura, H. (2020). Easy assessment of individuals with various severities of autism spectrum disorder, focusing on motor timing control. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 79, 101682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2020.101682
Pallant, J. F., & Tennant, A. (2007). An introduction to the Rasch measurement model: An example using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). British Journal of Clinical Psychology., 46(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466506X96931
Pérez-Espinosa, H., Gutiérrez-Serafín, B., Martínez-Miranda, J., & Espinosa-Curiel, I. E. (2022). Automatic children’s personality assessment from emotional speech. Expert Systems with Applications, 187, 115885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115885
Portney, L. G., & Watkins, M. P. (2009). Foundations of clinical research: Applications to practice (3rd ed.). Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Richman, J., Makrides, L., & Prince, B. (1980). Research methodology and applied statistics. Part 3: Measurement procedures in research. Physiotherapy Canada, 32, 253–257.
Samejima, F. (1969). Estimation of latent ability using a response pattern of graded scores. Psychometrika Monograph Supplement, 34(4), 1–97.
Sandin, S., Lichtenstein, P., Kuja-Halkola, R., Larsson, H., Hultman, C. M., & Reichenberg, A. (2014). The familial risk of autism. Journal of the American Medical Association, 311(17), 1770–1777. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.4144
Schopler, E., Lansing, M. D., Reichler, R. J., & Marcus, L. M. (2005). Examiner’s manual of psychoeducational profile (3rd ed.). Pro-ed Incorporation.
Shek, D. T., Tsang, S. K., Lam, L. L., Tang, F. L., & Cheung, P. M. (2005). Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Psycho-educational Profile-Revised (CPEP-R). Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35(1), 37–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-004-1029-3
Solari, E. J., Henry, A. R., Mcintyre, N. S., Grimm, R. P., & Zajic, M. (2020). Testing the effects of a pilot listening comprehension and vocabulary intervention for individuals with autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 71, 101501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2019.101501
Tasca, G. A., Cabrera, C., Kristjansson, E., et al. (2016). The therapeutic factor inventory-8: Using item response theory to create a brief scale for continuous process monitoring for group psychotherapy. Psychotherapy Research, 26(2), 131–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503307.2014.963729
Thabtah, F., Kamalov, F., & Rajab, K. (2018). A new computational intelligence approach to detect autistic features for autism screening. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 117, 112–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2018.06.009
Tian, Y. A., Zhang, H. A., Xiao, X. B., Wei, G. A., & Cao, X. A. (2021). Measuring perceived risk in sharing economy: a classical test theory and item response theory approach. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 96, 102980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102980
Torrado, J. C., Javier, G., & Germán, M. (2017). Emotional self-regulation of individuals with autism spectrum disorders: Smartwatches for monitoring and interaction. Sensors (basel, Switzerland), 17(6), 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061359
Vabalas, A., Gowen, E., Poliakoff, E., & Casson, A. J. (2020). Applying machine learning to kinematic and eye movement features of a movement imitation task to predict autism diagnosis. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65384-4
Vettori, S., Dzhelyova, M., Donck, S., et al. (2020). Combined frequency-tagging EEG and eye tracking reveal reduced social bias in boys with autism spectrum disorder. Cortex, 125, 135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2019.12.013
Zhou, H., Zhang, L., Wu, L., Zou, X., Luo, X., et al. (2015). Validity and reliability analysis of the Chinese parent version of the Autism Spectrum Rating Scale (6–18 years). Psychiatry Research, 230(2), 255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2015.09.003
Ziemer, C. J., Wyss, S., & Rhinehart, K. (2021). The origins of touchscreen competence: Examining infants’ exploration of touchscreens. Infant Behavior and Development, 64, 101609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2021.101609
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under (grant number 61977027), in part by the Hubei Province Technological Innovation Major Project under (grant number 2019AAA044), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number 2021M692472) and Science &Technology Major Project of Hubei Province (Next-Generation AI Technologies) (grant number 2021BEA159).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [Xiaodi Liu], [Jingying Chen], [Kun Zhang], [Xuan Wang], [Guangshuai Wang] and [Rujing Zhang]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [Xiaodi Liu] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Chen, J., Zhang, K. et al. The evaluation of the cognitive and language abilities of autistic children with interactive game technology based on the PEP-3 scale. Educ Inf Technol 27, 12027–12047 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11114-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11114-4