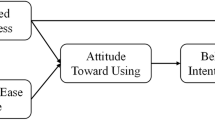
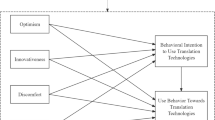
Abstract
This study investigated the motivation of Taiwanese undergraduate EFL students in learning English-to-Chinese translation and the intention to use a digital game-based learning app called CHEN-slate. The app, consisting of a learning zone, practice zone, and competition zone and including translation skills needed for actual translation practice, was developed as a supportive learning tool to equip students with the necessary translation skills and to enhance their translation experiences. This study was conducted in spring semester in 2020. The responses to a questionnaire, designed based on theories including Dörnyei’s L2 motivational self-system and the technology acceptance model, were analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively to identify the most prevalent type of motivation among students to learn English-to-Chinese translation (one-way repeated-measures ANOVA), students’ perception toward the use of CHEN-slate, and the relationship between students’ intention to use CHEN-slate and their learning motivation (linear regression analysis). Moreover, the pre-test and post-test variables were compared by using a paired-sample t test. The results of the study indicated that achieving the ideal self-image and translation learning experience are the most prevalent motivation types that encourage Taiwanese students to learn translation. The findings of this study also indicate that students have positive attitudes toward the adoption of CHEN-slate and have high intention to use the app facilitate their learning process. Finally, a significant positive relationship was found between students’ intention to use the app and their translation learning experience. This study offers pedagogical implications for instructors in translation courses to enhance students’ learning motivation and effectively use game-based learning apps in translation courses.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Aburagaga, I., Agoyi, M., & Elgedawy, I. (2020). Assessing Faculty’s Use of Social Network Tools in Libyan Higher Education via a Technology Acceptance Model. IEEE Access, 8, 116415–116430.
Ameri, S., & Ghahari, S. (2018). Developing a motivational framework in translation training programs: A mixed methods study following self-determination and social capital theories. The Interpreter and Translator Trainer, 12(2), 227–243. https://doi.org/10.1080/1750399x.2018.1465678
Açıkgül, K., & Şad, S. N. (2021). High school students’ acceptance and use of mobile technology in learning mathematics. Education and Information Technologies, 26(4), 4181–4201.
Azizinezhad, M. (2006). Is translation teachable?” dalam. Translation Journal, 10(2).
Bahremand, A. (2015). The concept of translation in different teaching approaches and methods. Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Research, 3(01), 6–10.
Barreto, A. M. R. (2018). Motivating English language use by using the benefits of technology. GIST Education and Learning Research Journal, 16, 117–140. Retrieved June 19, 2022, from: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1184917.pdf
Becker, K. (2007). Digital game-based learning once removed: Teaching teachers. British Journal of Educational Technology, 38, 478–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2007.00711.x
Blumberg, F. C., Deater-Deckard, K., Calvert, S. L., Flynn, R. M., Green, C. S., Arnold, D., & Brooks, P. J. (2019). Digital Games as a Context for Children’s Cognitive Development: Research Recommendations and Policy Considerations. Social Policy Report, 32, 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/sop2.3
Bruner, J. S. (1961). The act of discovery. Harvard Educational Review, 31(1), 21–32.
Cam, L., & Tran, T. T. M. (2017). An evaluation of using games in teaching English grammar for first year English-majored students at Dong Nai Technology University. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 16(7), 55–71.
Chang, P. C., Yu, Y. K., Li, T. C., & Peng, M. Y. (1998). Practical translation: An introductory coursebook. Bookman Books.
Chen, C. H., Law, V., & Huang, K. (2019). The roles of engagement and competition on learner’s performance and motivation in game-based science learning. Educational Technology Research and Development, 67, 1003–1024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09670-7
Darejeh, A., & Salim, S. S. (2016). Gamification Solutions to Enhance Software User Engagement—A Systematic Review. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 32(8), 613–642. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2016.1183330
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–340. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35(8), 982–1003.
De-Marcos, L., Garcia-Lopez, E., & Garcia-Cabot, A. (2016). On the effectiveness of game-like and social approaches in learning: Comparing educational gaming, gamification & social networking. Computers & Education, 95, 99–113.
Doiz, A., & Lasagabaster, D. (2018). Teachers’ and students’ second language motivational self system in English-Medium Instruction: A qualitative approach. TESOL Quarterly, 52(3), 657–679.
Dörnyei, Z. (2001). Teaching and researching motivation. Pearson Education.
Dörnyei, Z. (2005). The Psychology of the Language Learner: Individual Differences in Second Language Acquisition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0272263105370288
Dörnyei, Z. (2009). The L2 motivational self-system. In Z. Dörnyei & E. Ushioda (Eds.), Motivation, language identity and the L2 self (pp. 9–42). Multilingual Matters.
Dimitrijević, S., & Devedžić, V. (2021). Utilitarian and experiential aspects in acceptance models for learning technology. Educational Technology Research and Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-09970-x
Dutton, W. H., & Loader, B. D. (2004). Digital academe: new media in higher education and learning. Routledge.
Eltahir, M., Alsalhi, N. R., Al-Qatawneh, S., AlQudah, H. A., & Jaradat, M. (2021). The impact of game-based learning (GBL) on students’ motivation, engagement and academic performance on an Arabic language grammar course in higher education. Education and Information Technologies, 26(3), 3251–3278.
Fadarka, D. (2014). Investigating students’ motivations and purposes of learning translation at BA levels (Unpublished MA thesis). Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran.
Gardner, R. C. (1985). Social psychology in second language learning: The role of attitudes and motivation. London: Edward Arnold.
Ghazala, H. S. (2018). The cognitive stylistic translator. AWEJ for Translation & Literary Studies, 2(1), 4–25.
Higgins, E. T. (1998). Promotion and prevention: Regulatory focus as a motivational principle. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 30, 1–46.
Hu, X., & McGeown, S. (2020). Exploring the relationship between foreign language motivation and achievement among primary school students learning English in China. System, 89, 102199.
Iosup, A., & Epema, D. (2014). An Experience Report on Using Gamification in Technical Higher Education. SIGCSE ‘14 Proceedings of the 45th ACM technical symposium on Computer science education, 27–32. https://doi.org/10.1145/2538862.2538899
Johnson, L., Levine, A., Smith, R., & Stone, S. (2010). The 2010 Horizon Report. New Media Consortium. 6101 West Courtyard Drive Building One Suite 100, Austin, TX 78730.
Kabooha, R. H. (2016). Using movies in EFL classrooms: A study conducted at the English language institute (ELI), King Abdul-Aziz University. English Language Teaching, 9(3), 248–267. Retrieved June 19, 2022 from: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1095569
Kelly, D. (2005). A handbook for translator trainers. St Jerome.
Kelly, D., & Martin, A. (2009). Training and Education. In M. Baker & G. Saldahna (Eds.), Routledge Encyclopedia of Translation Studies (pp. 294–300). Routledge.
Kormos, J., Csizér, K., & Iwaniec, J. (2014). A mixed-method study of language-learning motivation and intercultural contact of international students. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 35(2), 151–166.
Larsen-Freeman, D., & Anderson, M. (2013). Techniques and principles in language teaching 3rd edition-Oxford handbooks for language teachers. Oxford University Press.
Lin, W. (2013). Why do students learn interpreting at the graduate level?-a survey on the interpreting learning motives of Chinese graduate students in BFSU. T&I Review, 3, 145–168. Retrieved June 19, 2022 from: http://www.papersearch.net/thesis/article.asp?key=3369008
Lin, C. P., & Liu, M. T. (2002). SPSS10.0 & The statistical model building. Kings Information.
Lister, M. C. (2015). Gamification: The effect on student motivation and performance at the post-secondary level. Issues and Trends in Educational Technology, 3(2), 1–22.
Liu, C., & Yu, C. (2019). Understanding students’ motivation in translation learning: A case study from the self-concept perspective. Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education, 4(1), 4.
Liu, Y. C., Wang, W. T., & Lee, T. L. (2021). An integrated view of information feedback, game quality, and autonomous motivation for evaluating game-based learning effectiveness. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(1), 3–40.
Malmkjaer, K. (Ed.). (1998). Translation and Language Teaching: Language Teaching and Translation. St. Jerome Publishing.
Markus, H., & Nurius, P. (1986). Possible Selves. American Psychologist, 41(9), 954–969.
Melnichuk, M. V., & Osipova, V. M. (2017). Cooperative learning as a valuable approach to teaching translation. Xlinguae Journal, 10(1), 25–34.
Munday, J. (2016). Introducing translation studies: Theories and applications. Routledge.
Presas, M. (2000). Bilingual competence and translation competence. In C. Schäffner & B. Adab (Eds.), Developing translation competence (pp.19–31). John Benjamins.
Riccardi, A. (Ed.). (2002). Translation studies: Perspectives on an emerging discipline. Cambridge University Press.
Starks, K. (2014). Cognitive behavioral game design: A unified model for designing serious games. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 28.
Tang, J., Zhao, Y (Chris)., Wang, T., & Zeng, Z. (2021). Examining the Effects of Feedback-giving as a Gamification Mechanic in Crowd Rating Systems. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 37(20), 1916–1930. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2021.1917866
Teo, T., Doleck, T., Bazelais, P., et al. (2019). Exploring the drivers of technology acceptance: A study of Nepali school students. Educational Technology Research and Development, 67, 495–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09654-7
Ushioda, E. (2011). Language learning motivation, self and identity: Current theoretical perspectives. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 24(3), 199–210.
Wichadee, S., & Pattanapichet, F. (2018). Enhancement of performance and motivation through application of digital games in an English language class. Teaching English with Technology, 18(1), 77–92.
Yen, L., Chen, C. M., & Huang, H. B. (2016, June). Effects of mobile game-based English vocabulary learning APP on learners' perceptions and learning performance: A case study of Taiwanese EFL learners. In International Conference on e-Learning (p. 255). Academic Conferences International Limited.
York, J., & deHaan, J. W. (2018). A constructivist approach to game-based language learning: Student perceptions in a beginner-level EFL context. International Journal of Game-Based Learning (IJGBL), 8(1), 19–40.
Yong, M. Y., & Yu, J. J. (2000). Using Games in an EFL class for Children. Dalam Dasjin University ELT Research Paper.
Yukselturk, E., Altıok, S., & Başer, Z. (2018). Using Game-Based Learning with Kinect Technology in Foreign Language Education Course. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 21(3), 159–173.
Zainuddin, Z. (2018). Students’ learning performance and perceived motivation in gamified flipped-class. Computers & Education, 126, 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.07.003
Zainuddin, Z., Chu, S. K. W., Shujahat, M., & Perera, C. J. (2020). The impact of gamification on learning and instruction: A systematic review of empirical evidence. Educational Research Review, 30, 100326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
All participants Informed consent was obtained from all participants who were well informed about the research objectives and contents and were assured about the privacy.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y. The effect of using a game-based translation learning app on enhancing college EFL learners’ motivation and learning experience. Educ Inf Technol 28, 255–282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11174-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11174-6