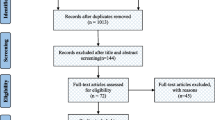
Abstract
The purpose of this meta-analysis was to examine the effects of Gamified-Assessment Tools (GAT) used in formal educational settings on student academic achievement. We used PRISMA systematic procedures to screen the articles across Web of Science, ERIC, Scopus, Pubmed, and PsycArticles databases. We identified 23 independent results from 17 primary studies with academic achievement outcomes using GAT in formal educational settings. These primary studies accounted for a total of N = 2836 (n = 1318 in GAT, n = 1518 in control) participants. We evaluated publication bias and quality assurance of selected studies for the validity and reliability of our meta-analysis results. Publication bias was not determined as a threat to overall Effect Size (ES). We employed Random-Effects Models (REM) to calculate the overall effect size. According to the REM, the overall effect of the GAT on academic achievement was calculated as g = .62 at the medium level. We also examined the learner stage, learning domain, sync type of assessment tools, research design, and assessment tool as moderators in which GAT may be effective. ESs of GAT significantly differed according to the learner stage. GAT had a larger ES on academic achievement in higher education than K12. There were no significant differences in the ESs of the GAT for other moderators. Quizizz, which is the most effective assessment tool according to our results, has a large ES on academic achievement. Especially in K-12, more experimental research is needed to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of GAT.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
All data calculated and analysed during this meta-analysis are included in this article (Appendix-A and Appendix-B).
References
References marked with an asterisk * indicate studies included in the meta-analysis
Affouneh, S., Salha, S., & Khlaif, Z. N. (2020). Designing quality e-learning environments for emergency remote teaching in coronavirus crisis. Interdisciplinary Journal of Virtual Learning in Medical Sciences, 11(2), 135–137.
Aguiar-Castillo, L., Hernández-López, L., De Saá-Pérez, P., & Pérez-Jiménez, R. (2020). Gamification as a motivation strategy for higher education students in tourism face-to-face learning. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 27, 100267.
*Al Sunni, A., & Latif, R. (2020). Determining the effectiveness of a cell phone-based student response system. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences, 15(1), 59–65.
Al-Azawi, R., Al-Faliti, F., & Al-Blushi, M. (2016). Educational gamification vs. game-based learning: Comparative study. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, 7(4), 132–136.
Bai, S., Hew, K. F., & Huang, B. (2020). Does gamification improve student learning outcome? Evidence from a meta-analysis and synthesis of qualitative data in educational contexts. Educational Research Review, 30, 100322.
Baptista, G., & Oliveira, T. (2019). Gamification and serious games: A literature meta-analysis and integrative model. Computers in Human Behavior, 92, 306–315.
Barata, G., Gama, S., Jorge, J., & Gonçalves, D. (2013). Improving participation and learning with gamification. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on gameful design, research, and applications (pp. 10–17).
Barreto, D., Vasconcelos, L., & Orey, M. (2017). Motivation and learning engagement through playing math video games. Malaysian Journal of Learning and Instruction, 14(2), 1–21.
*Bawa, P. (2020). Game On!: Investigating digital game-based versus gamified learning in higher education. International Journal of Game-Based Learning (IJGBL), 10(3), 16–46.
Begg, C. B., & Mazumdar, M. (1994). Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics, 50(4), 1088–1101. https://doi.org/10.2307/2533446
Bencsik, A., Mezeiova, A., & Samu, B. O. (2021). Gamification in higher education (Case study on a management subject). International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 20(5).
Bernik, A., Radošević, D., & Bubaš, G. (2017). Introducing gamification into e-learning university courses. In 2017 40th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO) (pp. 711–716). IEEE.
Bhuiyan, T., & Mahmud, I. (2015). Digital game-based education: A meta analysis. In International Conference of Inclusive Innovation and Innovative Management (ICIIIM 2015), Thailand.
Bicen, H., & Kocakoyun, S. (2018). Perceptions of students for gamification approach: Kahoot as a case study. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 13(2).
Binti Yusof, N. (2019). The effect of gamified assessment on student’s achievement, motivation and engagement in database design course. Journal on Technical and Vocational Education, 4(3), 78–91.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis. John Wiley and Sons Publishing.
Boudadi, N. A., & Gutiérrez-Colón, M. (2020). Effect of Gamification on students’ motivation and learning achievement in Second Language Acquisition within higher education: A literature review 2011–2019. The EuroCALL Review, 28(1), 57–69.
Boulet, G. (2012). Gamification: The latest buzzword and the next fad. ELearn, 2012(12). https://doi.org/10.1145/2407138.2421596
Buckley, P., & Doyle, E. (2016). Gamification and student motivation. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1162–1175.
Çağılltay, N. E., Özcelik, E., & Özcelik, N. S. (2015). The effect of competition on learning in games. Computers & Education, 87, 35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.04.001
Card, N. A. (2012). Applied meta-analysis for social science research. The Guilford Press.
Castillo-Manzano, J. I., Castro-Nuño, M., López-Valpuesta, L., Sanz-Díaz, M. T., & Yñiguez, R. (2016). Measuring the effect of ARS on academic performance: A global meta-analysis. Computers & Education, 96, 109–121.
*Chou, P. N., Chang, C. C., & Lin, C. H. (2017). BYOD or not: A comparison of two assessment strategies for student learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 74, 63–71.
Christakis, D. A., Ebel, B. E., Rivara, F. P., & Zimmerman, F. J. (2004). Television, video, and computer game usage in children under 11 years of age. The Journal of Pediatrics, 145(5), 652–656.
*Cutumisu, M., Chin, D. B., & Schwartz, D. L. (2019). A digital game-based assessment of middle-school and college students’ choices to seek critical feedback and to revise. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(6), 2977–3003.
Dağyar, M., & Demirel, M. (2015). Probleme dayalı öğrenmenin akademik başarıya etkisi: Bir meta-analiz çalışması. Eğitim Ve Bilim, 40(181), 139–174.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2014). The importance of universal psychological needs for understanding motivation in the workplace.
De-Marcos, L., Domínguez, A., Saenz-de-Navarrete, J., & Pagés, C. (2014). An empirical study comparing gamification and social networking on e-learning. Computers & Education, 75, 82–91.
Denny, P. (2013). The effect of virtual achievements on student engagement. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 763–772).
Deterding, S., Dixon, D., Khaled, R., & Nacke, L. (2011). From game design elements to gamefulness: defining" gamification". In Proceedings of the 15th international academic MindTrek conference: Envisioning future media environments (pp. 9–15).
Dichev, C., & Dicheva, D. (2017). Gamifying education: What is known, what is believed and what remains uncertain: A critical review. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 14(1), 1–36.
Ding, L. (2019). Applying gamifications to asynchronous online discussions: A mixed methods study. Computers in Human Behavior, 91, 1–11.
Downes, S. (2005). E-learning 2.0. ELearn, 2005(10), 1.
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). A nonparametric “Trim and Fill” method of accounting for publicationbias in meta-analysis. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 95(449), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2000.10473905
Ebner, M., & Holzinger, A. (2007). Successful implementation of user-centered game based learning in higher education: An example from civil engineering. Computers & Education, 49(3), 873–890.
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. British Medical Journal, 315(7109), 629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
*Eltahir, M., Alsalhi, N. R., Al-Qatawneh, S., AlQudah, H. A., & Jaradat, M. (2021). The impact of game-based learning (GBL) on students’ motivation, engagement and academic performance on an Arabic language grammar course in higher education. Education and Information Technologies, 26(3), 3251–3278.
Fadhli, M., Brick, B., Setyosari, P., Ulfa, S., & Kuswandi, D. (2020). A meta-analysis of selected studies on the effectiveness of gamification method for children. International Journal of Instruction, 13(1).
Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 63(3), 665–694. https://doi.org/10.1348/000711010X502733
*Filella, G., Ros-Morente, A., Oriol, X., & March-Llanes, J. (2018). The assertive resolution of conflicts in school with a gamified emotion education program. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 2353.
Fisher, R. A. (1932). Statistical methods for research workers (4th ed.). Oliver & Boyd.
Garcia-Iruela, M., Fonseca, M. J., Hijon-Neira, R., & Chambel, T. (2020). Gamification and computer science students’ activity. IEEE Access, 8, 96829–96836.
Garland, C. M. (2015). Gamification and implications for second language education: A meta analysis. 2015 (Doctoral dissertation, Dissertação (Mestrado em Teaching English as a Second Language)—St. Cloud State University, St. Cloud).
Gåsland, M. M. (2011). Game mechanic based e-learning: A case study (Master's thesis, Institutt for datateknikk og informasjonsvitenskap).
*Gümüş, H., & Gençoglu, C. (2020). The usage of" Quizizz"™ App by sport sciences students in the bachelor’s degree anatomy lecture and its effects on attitude and course success. International Education Studies, 13(11), 66–73.
Huang, R., Ritzhaupt, A. D., Sommer, M., Zhu, J., Stephen, A., Valle, N., … & Li, J. (2020). The impact of gamification in educational settings on student learning outcomes: A meta-analysis. Educational Technology Research and Development, 68(4), 1875–1901.
*Hursen, C. (2021). The effect of problem-based learning method supported by web 2.0 tools on academic achievement and critical thinking skills in teacher education. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 26(3), 515–533.
*Iskrenović-Momčilović, O. (2020). Quiz-enhanced learning in elementary school. Croatian Journal of Education: Hrvatski Časopis Za Odgoj i Obrazovanje, 22(3), 913–933.
Ismail, M. I., Abu Bakar, N. A., & Mohamed, M. (2020). Ludological application in the gamification of tertiary level education. Voice of Academia (VOA), 16(2), 89–100.
*Iwamoto, D. H., Hargis, J., Taitano, E. J., & Vuong, K. (2017). Analyzing the efficacy of the testing effect using KahootTM on student performance. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 18(2), 80–93.
Kapp, K. M. (2012). The gamification of learning and instruction: Game-based methods and strategies for training and education. John Wiley & Sons.
Karakoç, B., Eryılmaz, K., Özpolat, E. T., & Yıldırım, İ. (2020). The effect of game-based learning on student achievement: A meta-analysis study. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 1–16.
Khaleel, F. L., Ashaari, N. S., Wook, T. S. M. T., & Ismail, A. (2017). Gamification-based learning framework for a programming course. In 2017 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Kim, Y. H. (2020). Analysis of the educational effects of gamification social studies lesson in elementary school using game for education. Journal of Korea Game Society, 20(5), 21–30.
Kim, J., & Castelli, D. M. (2021). Effects of gamification on behavioral change in education: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3550.
*Kinder, F. D., & Kurz, J. M. (2018). Gaming strategies in nursing education. Teaching and Learning in Nursing, 13(4), 212–214.
Kocak, O. (2021). A systematic literature review of web-based student response systems: Advantages and challenges. Education and Information Technologies, 1–35.
Koh, C. (2020). A qualitative meta-analysis on the use of serious games to support learners with intellectual and developmental disabilities: What we know, what we need to know and what we can do. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education, 1–32.
Lee, J. J., & Hammer, J. (2011). Gamification in education: What, how, why bother? Academic Exchange Quarterly, 15(2), 146.
*Lee, C. C., Hao, Y., Lee, K. S., Sim, S. C., & Huang, C. C. (2019). Investigation of the effects of an online instant response system on students in a middle school of a rural area. Computers in Human Behavior, 95, 217–223.
Li, X., Long, R., & Pan, H. (2021). Gamification design on popular science education for children with hemopathy based on serious game theory. In International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (pp. 216–225). Springer.
Lin, D. T. A., Ganapathy, M., & Kaur, M. (2018). Kahoot! It: Gamification in higher education. Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 26(1), 565–582.
*Lin, J. W., Tsai, C. W., & Hsu, C. C. (2020). A comparison of computer-based and game-based formative assessments: a long-term experiment. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–17.
Linehan, C., Kirman, B., Lawson, S., & Chan, G. (2011). Practical, appropriate, empirically-validated guidelines for designing educational games. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 1979–1988).
Mamekova, A. T., Toxanbayeva, N. K., Naubaeva, K. T., Ongarbayeva, S. S., & Akhmediyeva, K. N. (2021). A meta-analysis on the impact of gamification over students’ motivation. Journal of Intellectual Disability-Diagnosis and Treatment, 9(4), 417–422.
Manzano-León, A., Camacho-Lazarraga, P., Guerrero, M. A., Guerrero-Puerta, L., Aguilar-Parra, J. M., Trigueros, R., & Alias, A. (2021). Between level up and game over: A systematic literature review of gamification in education. Sustainability, 13(4), 2247.
*Mavridis, A., & Tsiatsos, T. (2017). Game-based assessment: Investigating the impact on test anxiety and exam performance. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 33(2), 137–150.
Mayer, R. E. (2019). Computer games in education. Annual Review of Psychology, 70, 531–549.
Menezes, C. C. N., & Bortoli, R. D. (2016). Potential of gamification as assessment tool.
Michael, D., & Chen, S. (2006). Serious games: Games that educate, train, and inform. Thomson Course Technology.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med, 6(7), e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Nicol, D. J., & Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education, 31(2), 199–218.
O’Brien, D., Lawless, K. A., & Schrader, P. G. (2010). A taxonomy of educational games. In Gaming for classroom-based learning: Digital role playing as a motivator of study (pp. 1–23). IGI Global.
*Paul, M. W., Torgerson, C., Tracz, S., Coy, K., & Wahleithner, J. (2020). Engaging the control-value theory: a new era of student response systems and formative assessment to improve student achievement. Research in Learning Technology, 28. https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v28.2454
Pelling, N. (2011). The (short) prehistory of gamification, Funding Startups (& other impossibilities). Journal of Nano Dome. Retrieved from https://nanodome.wordpress.com/2011/08/09/the-short-prehistory-of-gamification/.
Peterson, M., White, J., Mirzaei, M. S., & Wang, Q. (2020). A review of research on the application of digital games in foreign language education. New technological applications for foreign and second language learning and teaching (pp. 69–92).
Pigott, T. D., & Polanin, J. R. (2020). Methodological guidance paper: High-quality meta-analysis in a systematic review. Review of Educational Research, 90(1), 24–46. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654319877153
Prensky, M. (2003). Digital game-based learning. Computers in Entertainment (CIE), 1(1), 21–21.
Rahayu, I. S. D., & Purnawarman, P. (2019). The use of Quizizz in improving students’ grammar understanding through self-assessment. In Eleventh Conference on Applied Linguistics (CONAPLIN 2018) (pp. 102–106). Atlantis Press.
Riopel, M., Nenciovici, L., Potvin, P., Chastenay, P., Charland, P., Sarrasin, J. B., & Masson, S. (2019). Impact of serious games on science learning achievement compared with more conventional instruction: An overview and a meta-analysis. Studies in Science Education, 55(2), 169–214.
Ritzhaupt, A. D., Huang, R., Sommer, M., Zhu, J., Stephen, A., Valle, N., … & Li, J. (2021). A meta-analysis on the influence of gamification in formal educational settings on affective and behavioral outcomes. Educational Technology Research and Development, 1–30.
Rogaway, P., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Simplifying game-based definitions. In Annual International Cryptology Conference (pp. 3–32). Springer.
Rosenthal, R. (1979). The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychological Bulletin, 86(3), 638–64. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.86.3.638
Sailer, M., & Homner, L. (2020). The gamification of learning: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 32, 77–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09498-w
Sawilowsky, S. S. (2009). New effect size rules of thumb. Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods, 8(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.22237/jmasm/1257035100
Sitzmann, T. (2011). A meta-analytic examination of the instructional effectiveness of computer-based simulation games. Personnel Psychology, 64(2), 489–528.
Squire, K., & Jenkins, H. (2003). Harnessing the power of games in education. Insight, 3(1), 5–33.
Strmecki, D., Bernik, A., & Radosevic, D. (2015). Gamification in E-Learning: Introducing gamified design elements into E-Learning systems. Journal of Computer Science, 11(12), 1108–1117.
Suurmond, R., van Rhee, H., & Hak, T. (2017). Introduction, comparison, and validation of Meta-Essentials: A free and simple tool for meta-analysis. Research Synthesis Methods, 8(4), 537–553. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1260
Tokac, U., Novak, E., & Thompson, C. G. (2019). Effects of game-based learning on students’ mathematics achievement: A meta-analysis. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 35(3), 407–420.
Trinidad, M., Ruiz, M., & Calderón, A. (2021). A bibliometric analysis of gamification research. IEEE Access, 9, 46505–46544.
Van Roy, R., & Zaman, B. (2018). Need-supporting gamification in education: An assessment of motivational effects over time. Computers & Education, 127, 283–297.
Wang, Y. J., Shang, H. F., & Briody, P. (2011). Investigating the impact of using games in teaching children English. International Journal of Learning and Development, 1(1), 127–141.
Wang, A. I., & Lieberoth, A. (2016). The effect of points and audio on concentration, engagement, enjoyment, learning, motivation, and classroom dynamics using Kahoot. In European conference on games based learning (Vol. 20). Academic Conferences International Limited.
Wichadee, S., & Pattanapichet, F. (2018). Enhancement of performance and motivation through application of digital games in an English language class. Teaching English with Technology, 18(1), 77–92.
Williams, A. (2017). History of digital games: Developments in art, design, and interaction. CRC Press.
Wouters, P., Van Nimwegen, C., Van Oostendorp, H., & Van Der Spek, E. D. (2013). A meta-analysis of the cognitive and motivational effects of serious games. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(2), 249.
*Yarahmadzehi, N., & Goodarzi, M. (2020). Investigating the role of formative mobile based assessment in vocabulary learning of pre-intermediate EFL learners in comparison with paper based assessment. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 21(1), 181–196.
Yıldırım, İ., & Şen, S. (2019). The effects of gamification on students’ academic achievement: A meta-analysis study. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–18.
*Yürük, N. (2020). Using Kahoot as a skill improvement technique in pronunciation. Journal of Language and Linguistic Studies, 16(1), 137–153.
Zainuddin, Z., Shujahat, M., Haruna, H., & Chu, S. K. W. (2020). The role of gamified e-quizzes on student learning and engagement: An interactive gamification solution for a formative assessment system. Computers & Education, 145, 103729.
Zemliansky, P., & Wilcox, D. (Eds.). (2010). Design and implementation of educational games: Theoretical and practical perspectives: Theoretical and practical perspectives. IGI Global.
Zhao, F. (2019). Using quizizz to integrate fun multiplayer activity in the accounting classroom. International Journal of Higher Education, 8(1), 37–43.
Zhu, H., & Lee, H. (2021). Analysis of the possible effects of computer games on young children. In 2021 5th International Seminar on Education, Management and Social Sciences (ISEMSS 2021) (pp. 645–651). Atlantis Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bolat, Y.I., Taş, N. A meta-analysis on the effect of gamified-assessment tools’ on academic achievement in formal educational settings. Educ Inf Technol 28, 5011–5039 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11411-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11411-y