Abstract
Many studies have explored the effect of grouping and task distribution strategies in collaborative learning in the conventional condition, for example, grouping based on student’s learning style, gender diversity, and motivation, but few studies have investigated the impact of heterogeneous grouping with mixed gender and ability factors and the distribution of roles and tasks on members’ engagement and collaboration in the IVE environment. This study proposed external scripts that were composed of grouping strategies and distribution strategies. The former includes Mixed Gender and Ability Grouping (MGAG) and Mixed Gender Grouping (MGG), while the latter contains Role-based Task Distribution (RTD) and Freely Distribution (FD). The scripts serve as a heterogeneous grouping and distribution procedural guide for collaborative learning in an Immersive Virtual Environment (IVE), which has the potential to address issues such as homogeneous competencies, collaboration confusion, and conflict among group members to meet the needs of IVE-based collaborative learning. This study used a quasi-experimental research method to explore the effects of IVE-based collaborative learning on students. The results of the experiment which contained 77 junior high school participants from 2 classes showed that: (1) MGAG can stimulate students’ motivation(d = 1.55); (2) RTD can improve students’ engagement(d = 0.66) and reduce their cognitive load(d=-0.92); (3) There is no significant interaction between MGAG and RTD in motivation, engagement, and cognitive load. Therefore, the study recommends MGAG combined with RTD to be stressed in IVE-based collaborative learning.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Almasri, F. (2022). The impact of e-learning, gender-groupings and learning pedagogies in biology undergraduate female and male students’ attitudes and achievement. Education and Information Technologies, 27(6), 8329–8380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-10967-z
Baker, M. J. (2015). Collaboration in collaborative learning. Interaction Studies Social Behaviour and Communication in Biological and Artificial Systems, 16(3), 451–473. https://doi.org/10.1075/is.16.3.05bak
Barsom, E. Z., Duijm, R. D., Dusseljee-Peute, L. W. P., Landman‐van der Boom, E. B., Lieshout, E. J., Jaspers, M. W., & Schijven, M. P. (2020). Cardiopulmonary resuscitation training for high school students using an immersive 360‐degree virtual reality environment. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51(6), 2050–2062. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13025
Bear, J. B., & Woolley, A. W. (2011). The role of gender in team collaboration and performance. Interdisciplinary Science Reviews, 36(2), 146–153. https://doi.org/10.1179/030801811X13013181961473
Belbin, M. R. (2010). Team roles at work (2nd ed.). Taylor & Francis.
Buhrmester, D., Furman, W., Wittenberg, M. T., & Reis, H. T. (1988). Five domains of interpersonal competence in peer relationships. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55(6), 991–1008. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.55.6.991
Cen, L., Ruta, D., Powell, L., Hirsch, B., & Ng, J. (2016). Quantitative approach to collaborative learning: performance prediction, individual assessment, and group composition. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 11(2), 187–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-016-9234-6
Cesareni, D., Cacciamani, S., & Fujita, N. (2016). Role taking and knowledge building in a blended university course. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 11(1), 9–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-015-9224-0
Chen, J., Wang, M., Kirschner, P. A., & Tsai, C. C. (2018a). The role of collaboration, computer use, learning environments, and supporting strategies in cscl: a meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 88(6), 799–843. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654318791584
Chen, Y. T., Liou, S., & Chen, L. F. (2018b). The relationships among gender, cognitive styles, learning strategies, and learning performance in the flipped classroom. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 35(4–5), 395–403. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2018.1543082
Cheng, K. H., & Tsai, C. C. (2019). A case study of immersive virtual field trips in an elementary classroom: students’ learning experience and teacher-student interaction behaviors. Computers & Education, 140, 103600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103600
Dowell, N. M. M., Nixon, T. M., & Graesser, A. C. (2019). Group communication analysis: a computational linguistics approach for detecting sociocognitive roles in multiparty interactions. Behavior Research Methods, 51(3), 1007–1041. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-018-1102-z
Ellison, S. F., & Mullin, W. P. (2014). Diversity, social goods provision, and performance in the firm. Journal of Economics & Management Strategy, 23(2), 465–481. https://doi.org/10.1111/jems.12051
Frederiksen, J. G., Sørensen, S. M. D., Konge, L., Svendsen, M. B. S., Nobel-Jørgensen, M., Bjerrum, F., & Andersen, S. A. W. (2020). Cognitive load and performance in immersive virtual reality versus conventional virtual reality simulation training of laparoscopic surgery: a randomized trial. Surgical Endoscopy, 34(3), 1244–1252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06887-8
Fu, Q. K., & Hwang, G. J. (2018). Trends in mobile technology-supported collaborative learning: a systematic review of journal publications from 2007 to 2016. Computers & Education, 119, 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.01.004
Gagne, M., Forest, J., Vansteenkiste, M., Crevier-Braud, L., Van den Broeck, A., Aspeli, A. K., & Westbye, C. (2015). The multidimensional work motivation scale: validation evidence in seven languages and nine countries. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 24(2), 178–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/1359432X.2013.877892
Halpern, D. F. (2011). Sex differences in cognitive abilities (4th ed.). Psychology Press.
Hwang, G. J., Yang, L. H., & Wang, S. Y. (2013). A concept map-embedded educational computer game for improving students’ learning performance in natural science courses. Computers & Education, 69, 121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.07.008
Jeong, H., & Hmelo-Silver, C. E. (2016). Seven affordances of computer-supported collaborative learning: how to support collaborative learning? How can technologies help? Educational Psychologist, 51(2), 247–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2016.1158654
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2018). Cooperative learning: the foundation for active learning. In B. Sílvio Manuel (Ed.), Active Learning: Beyond the Future (pp. Ch. 5). Intechopen.
Kirschner, P. A., Sweller, J., Kirschner, F., & Zambrano, R. (2018). From cognitive load theory to collaborative cognitive load theory. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 13(2), 213–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-018-9277-y
Kobbe, L., Weinberger, A., Dillenbourg, P., Harrer, A., Hämäläinen, R., Häkkinen, P., & Fischer, F. (2007). Specifying computer-supported collaboration scripts. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 2(2), 211–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-007-9014-4
Korlat, S., Kollmayer, M., Holzer, J., Lüftenegger, M., Pelikan, E. R., Schober, B., & Spiel, C. (2021). Gender differences in digital learning during COVID-19: competence beliefs, intrinsic value, learning engagement, and perceived teacher support. Frontiers in psychology, 12, 637776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.637776
Kumar, A., Mantri, A., Singh, G., & Kaur, D. P. (2022). Impact of AR-based collaborative learning approach on knowledge gain of engineering students in embedded system course. Education and Information Technologies, 27(5), 6015–6036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10858-9
Kuo, Y. C., Chu, H. C., & Huang, C. H. (2015). A learning style-based grouping collaborative learning approach to improve EFL students’ performance in English courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 18(2), 284–298.
Laal, M., & Ghodsi, S. M. (2012). Benefits of collaborative learning. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 31, 486–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.12.091
Liao, C. W., Chen, C. H., & Shih, S. J. (2019). The interactivity of video and collaboration for learning achievement, intrinsic motivation, cognitive load, and behavior patterns in a digital game-based learning environment. Computers & Education, 133, 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.01.013
Liu, S., Liu, S., Liu, Z., Peng, X., & Yang, Z. (2022). Automated detection of emotional and cognitive engagement in MOOC discussions to predict learning achievement. Computers & Education, 181, 104461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104461
Liu, Z., Yang, C., Rüdian, S., Liu, S., Zhao, L., & Wang, T. (2019). Temporal emotion-aspect modeling for discovering what students are concerned about in online course forums. Interactive Learning Environments, 27(5–6), 598–627. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1610449
Liu, Z., Kong, W., Peng, X., Yang, Z., Liu, S., Liu, S., & Wen, C. (2023). Dual-feature-embeddings-based semi-supervised learning for cognitive engagement classification in online course discussions. Knowledge-Based Systems, 259, 110053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.110053
Makransky, G., & Lilleholt, L. (2018). A structural equation modeling investigation of the emotional value of immersive virtual reality in education. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1141–1164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9581-2
Meijer, H., Brouwer, J., Hoekstra, R., & Strijbos, J. W. (2022). Exploring construct and consequential validity of collaborative learning assessment in higher education. Small Group Research, 53(6), 891–925. https://doi.org/10.1177/10464964221095545
Neumann, D. L., Sturm, A. C., Boyle, G. J., & Furedy, J. J. (2010). Effects of nicotine administration via a sublingual tablet on arousal and verbal ability in non-smokers. Australian Journal of Psychology, 62(2), 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/00049530902795458
Oluwajana, D., & Adeshola, I. (2021). Does the student’s perspective on multimodal literacy influence their behavioural intention to use collaborative computer-based learning? Education and Information Technologies, 26(5), 5613–5635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10526-y
Pandolfelli, L., Meinzen-Dick, R., & Dohrn, S. (2008). Gender and collective action: motivations, effectiveness and impact. Journal of International Development, 20(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/jid.1424
Radkowitsch, A., Vogel, F., & Fischer, F. (2020). Good for learning, bad for motivation? A meta-analysis on the effects of computer-supported collaboration scripts. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 15(1), 5–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-020-09316-4
Reeve, J., & Tseng, C. M. (2011). Agency as a fourth aspect of students’ engagement during learning activities. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 36(4), 257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2011.05.002
Reilly, D., & Neumann, D. L. (2013). Gender-role differences in spatial ability: a meta-analytic review. Sex Roles, 68(9), 521–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-013-0269-0
Saeed, S., & Zyngier, D. (2012). How motivation influences student engagement: a qualitative case study. Journal of Education and Learning, 1(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.5539/jel.v1n2p252
Saleh, M., Lazonder, A. W., & de Jong, T. (2007). Structuring collaboration in mixed-ability groups to promote verbal interaction, learning, and motivation of average-ability students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 32(3), 314–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2006.05.001
Sinha, S., Rogat, T. K., Adams-Wiggins, K. R., & Hmelo-Silver, C. E. (2015). Collaborative group engagement in a computer-supported inquiry learning environment. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 10(3), 273–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-015-9218-y
Tchounikine, P. (2019). Learners’ agency and CSCL technologies: towards an emancipatory perspective. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 14(2), 237–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-019-09302-5
Talbi, O., & Ouared, A. (2022). Goal-oriented student motivation in learning analytics: how can a requirements-driven approach help? Education and Information Technologies, 27(9), 12083–12121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11091-8
Vogel, F., Weinberger, A., & Fischer, F. (2021). Collaboration Scripts: Guiding, Internalizing, and Adapting. In U. Cress, C. Rosé, A. F. Wise, & J. Oshima (Eds.), International Handbook of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning (pp. 335–352). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65291-3_18
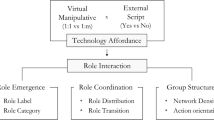
Wang, C., & Li, S. (2021). The trade-off between individuals and groups: role interactions under different technology affordance conditions. International Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, 16(4), 525–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-021-09355-5
Wu, S. Y., & Wang, S. M. (2020). Exploring the effects of gender grouping and the cognitive processing patterns of a Facebook-based online collaborative learning activity. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1799026
Yoon, S. Y. (2011). Psychometric properties of the revised purdue spatial visualization tests: visualization of rotations (the revised PSVT: R). Purdue University.
Zeid, A., & El-Bahey, R. (2011). Impact of introducing single-gender classrooms in higher education on student achievement levels: A case study in software engineering courses in the GCC region. 2011 Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), T2H-1-T2H-6. https://doi.org/10.1109/FIE.2011.6142921
Zhan, Z., Fong, P. S. W., Mei, H., & Liang, T. (2015). Effects of gender grouping on students’ group performance, individual achievements and attitudes in computer-supported collaborative learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 48, 587–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.02.038
Zhong, Z., Zhang, G., Jin, S., Wang, J., Ma, N., & Feng, S. (2022). Investigating the effect of peer instruction on learners with different cognitive styles in VR-based learning environment. Education and Information Technologies, 27(8), 11875–11899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11115-3
Zhu, Y., Xu, S., Wang, W., Zhang, L., Liu, D., Liu, Z., & Xu, Y. (2022). The impact of Online and Offline Learning motivation on learning performance: the mediating role of positive academic emotion. Education and Information Technologies, 27(7), 8921–8938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-10961-5
Funding
This work was supported by [National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 62277024)] and [The Central China Normal University of Research Projects of National Teachers’ Development Cooperation Innovation Experimental Base Construction (Grant numbers: CCNUTEIII 2021-05)]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Ability test scale


Appendix 2
Collaborative learning scale
Variable | Item | Source and Cronbach’s alpha reliability |
|---|---|---|
Motivation | Adapted by Gagné et al. (2015) | |
Mot_1 | In group learning, I am very interested in the new learning material. | Cronbach’s alpha = 0.752 |
Mot_2 | In my opinion, cooperation and communication with peers are more conducive to acquire knowledge from learning materials. | |
Mot_3 | Intra-members and I can complete the collaborative learning tasks. | |
Mot_4 | I can use what I have learned before in group learning. | |
Mot_5 | I get along well with peers in group learning. | |
Mot_6 | The help of my peers can make up for my deficiency in collaborative learning. | |
Participation | Adapted by Reeve and Tseng (2011) | |
Part_1 | In group work, I tried to collaborate with peers, to complete the task. | Cronbach’s alpha = 0.892 |
Part_2 | I can listen carefully to peers’ views and express my opinions during the group discussion. | |
Part_3 | I become more willing to participate in group learning due to the discussion and communication. | |
Part_4 | I try to understand different peers’ ideas so that I can help me to understand important concepts | |
Cognitive load | Adapted by Hwang et al. (2013) | |
CL_1 | I think it difficult to complete the collaborative learning tasks. | Cronbach’s alpha = 0.800 |
CL_2 | I need to make a lot of effort in group learning. | |
CL_3 | It took me a log time to think about the problems in group learning. | |
CL_4 | I think communicating with peers can help me understand some concepts more quickly. | |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Z., Wang, J., Deng, Y. et al. Effects of external scripts incorporating capabilities, roles and tasks on IVE’s collaborative learning. Educ Inf Technol 28, 11495–11516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11640-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11640-9