Abstract
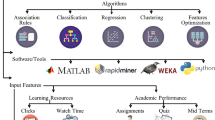
In the current educational landscape, where large amounts of data are being produced by institutions, Educational Data Mining (EDM) emerges as a critical discipline that plays a crucial role in extracting knowledge from this data to help academic policymakers make decisions. EDM has a primary focus on predicting students’ academic performance. Numerous studies have been conducted for this purpose, but they are plagued by challenges including limited dataset size, disparities in grade distributions, and feature selection issues. This paper introduces a Machine Learning (ML) based method for the early prediction of bachelor students’ final academic grade as well as drop-out cases. It focuses on identifying, from the first semester of study, the students requiring specific attention because of their academic weaknesses. The research employs nine classification models on students’ data from a Saudi university, subsequently implementing a majority voting algorithm. The experimental outcomes are noteworthy, with the Extra Trees (ET) algorithm achieving a promising accuracy of 82.8% and the Majority Voting (MV) model outperforming all existing models by an accuracy reaching 92.7%. Moreover, the study identifies the factors exerting the greatest impact on students’ academic performance, which belong to the three considered feature types: demographic, pre-admission, and academic.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and materials
The dataset analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to institutional policies but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The code is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
TP is the true positive, FP is the false positive, TN is the true negative and FN is the false negative.
References
Adekitan, A. I., & Salau, O. (2019). The impact of engineering students’ performance in the first three years on their graduation result using educational data mining. Heliyon, 5(2), e01250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01250
Alghamdi, A. S., & Rahman, A. (2023). Data mining approach to predict success of secondary school students: A saudi arabian case study. Education Sciences, 13(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13030293
Alturki, S., & Alturki, N. (2021). Using educational data mining to predict students’ academic performance for applying early interventions. Journal of Information Technology Education: Innovations in Practice, 20, 121–137. https://doi.org/10.28945/4835
Alyahyan, E., & Düştegör, D. (2020). Predicting academic success in higher education: Literature review and best practices. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-0177-7
Batista, G. E. A. P. A., Prati, R. C., & Monard, M. C. (2004). A study of the behavior of several methods for balancing machine learning training data. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 6(1), 20–29. https://doi.org/10.1145/1007730.1007735
Batool, S., Rashid, J., Nisar, M. W., Kim, J., Kwon, H.-Y., & Hussain, A. (2022). Educational data mining to predict students’ academic performance: A survey study. Education and Information Technologies, 28(1), 905–971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11152-y
Beaulac, C., & Rosenthal, J. S. (2019). Predicting university students’ academic success and major using random forests. Research in Higher Education, 60(7), 1048–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-019-09546-y
Bishop, C. M. (1995). Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press.
Brdesee, H. S., Alsaggaf, W., Aljohani, N., & Hassan, S.-U. (2022). Predictive model using a machine learning approach for enhancing the retention rate of students at-risk. International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems, 18(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijswis.299859
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine learning, 45(1), 5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010933404324
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., & Stone, C. J. (1984). Classication and regression trees. CRC Press.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., & Kegelmeyer, W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16, 321–357. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953
Chen, Y., & Zhai, L. (2023). A comparative study on student performance prediction using machine learning. Education and Information Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11672-1
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. Machine learning, 20(3), 273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00994018
Cover, T., & Hart, P. (1967). Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13(1), 21–27. https://doi.org/10.1109/tit.1967.1053964
Duda, R. O., Hart, P. E., & Stork, D. G. (2001). Pattern classification. Wiley.
Friedman, J. H. (2001). Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics, 1189–1232. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1013203451
Geurts, P., Ernst, D., & Wehenkel, L. (2006). Extremely randomized trees. Machine Learning, 63(1), 3–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-006-6226-1
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. (2009). The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference, and prediction. Springer.
He, H., & Garcia, E. (2009). Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 21(9), 1263–1284. https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2008.239
Hussain, A., Khan, M., & Ullah, K. (2022). Student’s performance prediction model and affecting factors using classifcation techniques. Education and Information Technologies, 27(6), 8841–8858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-10988-8
Ioannis, B., & Maria, K. (2018). Gender and student course preferences and course performance in computer science departments: A case study. Education and Information Technologies, 24(2), 1269–1291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9828-x
Khan, A., & Ghosh, S. K. (2020). Student performance analysis and prediction in classroom learning: A review of educational data mining studies. Education and Information Technologies, 26(1), 205–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10230-3
Kumar, B., & Pal, S. (2011). Mining educational data to analyze students performance. textitInternational Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, textit2(6). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2011.020609
Kuzilek, J., Hlosta, M., & Zdrahal, Z. (2017). Open university learning analytics dataset. Scientific Data, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.171
Mueen, A., Zafar, B., & Manzoor, U. (2016). Modeling and predicting students academic performance using data mining techniques. International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science, 8(11), 36–42. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijmecs.2016.11.05
Olabanjo, O. A., Wusu, A. S., & Manuel, M. (2022). A machine learning prediction of academic performance of secondary school students using radial basis function neural network. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 29, 100190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tine.2022.100190
Parajuli, M., & Thapa, A. (2017). Gender differences in the academic performance of students. Journal of Development and Social Engineering, 3(1), 39–47. https://doi.org/10.3126/jdse.v3i1.27958
Peña-Ayala, A. (2014). Educational data mining: A survey and a data mining-based analysis of recent works. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(4), 1432–1462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.08.042
Poudyal, S., Mohammadi-Aragh, M. J., & Ball, J. E. (2022). Prediction of student academic performance using a hybrid 2d CNN model. Electronics, 11(7), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11071005
Refaeilzadeh, P., Tang, L., & Liu, H. (2009). Cross-validation. In Encyclopedia of database systems (pp. 532–538). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-39940-9_565
Romero, C., & Ventura, S. (2020). Educational data mining and learning analytics: An updated survey. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1355
Romero, C. & Ventura, S. (2010). Educational data mining: A review of the state of the art. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), textit40 (6), 601–618. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmcc.2010.2053532
Shafiq, D. A., Marjani, M., Habeeb, R. A. A., & Asirvatham, D. (2022). Student retention using educational data mining and predictive analytics: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access, 10, 72480–72503. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3188767
Smith, J., & Johnson, M. (2022). Majority voting in ensemble classifiers. Journal of Machine Learning, 10(3), 123–145. https://doi.org/10.1234/jml.2022.12345
Suthaharan, S. (2016). Machine learning models and algorithms for big data classification.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-7641-3
Tatar, A. E., & Düştegör, D. (2020). Prediction of academic performance at undergraduate graduation: Course grades or grade point average? Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4967. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144967
Uliyan, D., Aljaloud, A. S., Alkhalil, A., Amer, H. S. A., Mohamed, M. A. E. A., & Alogali, A. F. M. (2021). Deep learning model to predict students retention using BLSTM and CRF. IEEE Access, 9, 135550–135558. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3117117
Wang, X., Zhao, Y., Li, C., & Ren, P. (2023). ProbSAP: A comprehensive and high-performance system for student academic performance prediction. Pattern Recognition, 137, 109309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109309
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through large group Research Project under grant number (R.G.P.2/549/44).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University under research grant number (R.G.P.2/549/44).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
None
Ethics approval
None
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent for publication.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Said, M., Hadj Kacem, Y., Algarni, A. et al. Early prediction of Student academic performance based on Machine Learning algorithms: A case study of bachelor’s degree students in KSA. Educ Inf Technol 29, 13247–13270 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12370-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12370-8