Abstract
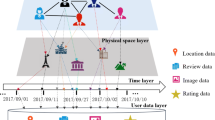
Location-based social networks (LBSNs) have become popular platforms that allow users to share their check-in activities with friends. Annotating semantic tags of locations, as one of the hottest research topics in LBSNs, has attracted considerable attention. Semantic annotation requires sufficient location features to train classifiers. Based on the analysis of LBSN data, we find that users’ check-in activities have similarities that can promote the extraction of location features and improve the accuracy of semantic annotation. However, the existing studies ignored the use of the similarities of users’ check-in activities for extracting suitable location features. Therefore, in this paper, a new location feature, called the similar user pattern (SUP), is first extracted by capturing the similarities among the different users’ check-in activities. Second, annotating semantic tags of locations is treated as a multi-label classification problem. Thus, multi-label semantic annotation with an extreme learning machine (ELM) is proposed, called MSA-ELM. The MSA-ELM algorithm trains a binary ELM classifier for each tag in the tag space to support multi-label classification. Finally, a series of experiments are conducted to demonstrate both the accuracy and efficiency of annotating semantic tags of locations. The experimental results show that the SUP is a proper location feature, and the MSA-ELM algorithm has a good performance for multi-label semantic annotation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adomavicius G, Tuzhilin A (2005) Toward the next generation of recommender systems: a survey of the state-of-the-art and possible extensions. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(6):734–749
Bao J, Zheng Y, Wilkie D, Mokbel MF (2015) Recommendations in location-based social networks: a survey. GeoInformatica 19(3):525–565
Boutell MR, Luo J, Shen X, Brown CM (2004) Learning multi-label scene classification. Pattern Recogn 37(9):1757–1771
Cao X, Chen L, Cong G, Guan J, Phan N, Xiao X (2013) KORS: keyword-aware optimal route search system. In: 29th IEEE International conference on data engineering, ICDE 2013, Brisbane, Australia, April 8-12, 2013, pp 1340–1343
Cao X, Chen L, Cong G, Xiao X (2012) Keyword-aware optimal route search. PVLDB 5(11):1136–1147
Chen L, Cong G (2015) Diversity-aware top-k publish/subscribe for text stream. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, May 31 - June 4, 2015, pp 347–362
Chen L, Cong G, Cao X (2013) An efficient query indexing mechanism for filtering geo-textual data. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, SIGMOD 2013, New York, NY, USA, June 22-27, 2013, pp 749–760
Chen L, Shang S, Zhang Z, Cao X, Jensen CS, Kalnis P (2018) Location-aware top-k term publish/subscribe. In: 34th IEEE international conference on data engineering, ICDE 2018, Paris, France, April 16-19, 2018, pp 749–760
Chen Z, Cong G, Zhang Z, Fu TZJ, Chen L (2017) Distributed publish/subscribe query processing on the spatio-textual data stream. In: 33rd IEEE International conference on data engineering, ICDE 2017, San Diego, CA, USA, April 19-22, 2017, pp 1095–1106
Chon Y, Lane ND, Li F, Cha H, Zhao F (2012) Automatically characterizing places with opportunistic crowdsensing using smartphones. In: Proceedings of the 2012 ACM conference on ubiquitous computing. ACM, pp 481–490
Chowdhury G (2010) Introduction to modern information retrieval, 3rd edn. Facet Publishing
Clare A, King RD (2001) Knowledge discovery in multi-label phenotype data. In: Principles of data mining and knowledge discovery, 5th European Conference, PKDD 2001, Freiburg, Germany, September 3-5, 2001, Proceedings, pp 42–53
Elisseeff A, Weston J (2001) A kernel method for multi-labelled classification. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 14 [neural information processing systems: natural and synthetic, NIPS 2001, December 3-8, 2001, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada], pp 681–687
Han J, Wen J (2013) Mining frequent neighborhood patterns in a large labeled graph. In: 22nd ACM International conference on information and knowledge management, CIKM’13, San Francisco, CA, USA, October 27 - November 1, 2013, pp 259–268
Han J, Wen J, Pei J (2014) Within-network classification using radius-constrained neighborhood patterns. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM international conference on conference on information and knowledge management, CIKM 2014, Shanghai, China, November 3-7, 2014, pp 1539–1548
Han J, Zheng K, Sun A, Shang S, Wen J (2016) Discovering neighborhood pattern queries by sample answers in knowledge base. In: 32nd IEEE International conference on data engineering, ICDE 2016, Helsinki, Finland, May 16-20, 2016, pp 1014–1025
Hegde V, Parreira JX, Hauswirth M (2013) Semantic tagging of places based on user interest profiles from online social networks. In: Advances in information retrieval. Springer, pp 218– 229
Huang GB, Siew CK (2004) Extreme learning machine: Rbf network case. In: Control, automation, robotics and vision conference, 2004. ICARCV 2004 8th, vol 2. IEEE, pp 1029–1036
Huang Z, Qian Y, Mamoulis N (2018) Location-aware query reformulation for search engines. GeoInformatica 22(4):869–893
Jensen CS, Kligys A, Pedersen TB, Timko I (2004) Multidimensional data modeling for location-based services. VLDB J 13(1):1–21
Li M, Chen L, Cong G, Gu Y, Yu G (2016) Efficient processing of location-aware group preference queries. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, CIKM 2016, Indianapolis, IN, USA, October 24-28, 2016, pp 559– 568
Li X, Cheng Y, Cong G, Chen L (2017) Discovering pollution sources and propagation patterns in urban area. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, Halifax, NS, Canada, August 13 - 17, 2017, pp 1863–1872
Liao L, Patterson DJ, Fox D, Kautz H (2007) Learning and inferring transportation routines. Artif Intell 171(5):311–331
Liu A, Wang W, Shang S, Li Q, Zhang X (2018) Efficient task assignment in spatial crowdsourcing with worker and task privacy protection. GeoInformatica 22 (2):335–362
Liu Y, Pham T, Cong G, Yuan Q (2017) An experimental evaluation of point-of-interest recommendation in location-based social networks. PVLDB 10 (10):1010–1021
Ou W (2014) Extracting user interests from graph connections for machine learning in location-based social networks. In: Proceedings of the MLSDA 2014 2nd workshop on machine learning for sensory data analysis. ACM, p 41
Pelekis N, Theodoridis Y, Vosinakis S, Panayiotopoulos T (2006) Hermes - a framework for location-based data management. In: 10th International conference on extending database technology on advances in database technology - EDBT 2006, Munich, Germany, March 26-31, 2006, Proceedings, pp 1130–1134
Saleem MA, Kumar R, Calders T, Xie X, Pedersen TB (2017) Imaxer: a unified system for evaluating influence maximization in location-based social networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on conference on information and knowledge management, CIKM 2017, Singapore, November 06 - 10, 2017, pp 2523–2526
Schapire RE, Singer Y (2000) Boostexter: a boosting-based system for text categorization. Mach Learn 39(2):135–168
Schapire RE, Singer Y (2000) Boostexter: a boosting-based system for text categorization. Mach Learn 39(2/3):135–168
Shang S, Chen L, Jensen CS, Wen J, Kalnis P (2017) Searching trajectories by regions of interest. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(7):1549–1562
Shang S, Chen L, Kai Z, Jensen CS, Kalnis P (2018) Parallel trajectory to location join. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng PP(99):1–1
Shang S, Chen L, Wei Z, Jensen CS, Wen J, Kalnis P (2016) Collective travel planning in spatial networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28(5):1132–1146
Shang S, Chen L, Wei Z, Jensen CS, Zheng K, Kalnis P (2017) Trajectory similarity join in spatial networks. PVLDB 10(11):1178–1189
Shang S, Chen L, Wei Z, Jensen CS, Zheng K, Kalnis P (2018) Parallel trajectory similarity joins in spatial networks. VLDB J 27(3):395–420
Shang S, Ding R, Yuan B, Xie K, Zheng K, Kalnis P (2012) User oriented trajectory search for trip recommendation. In: 15th International conference on extending database technology, EDBT ’12, Berlin, Germany, March 27-30, 2012, Proceedings, pp 156–167
Shang S, Ding R, Zheng K, Jensen CS, Kalnis P, Zhou X (2014) Personalized trajectory matching in spatial networks. VLDB J 23(3):449–468
Shang S, Zheng K, Jensen CS, Yang B, Kalnis P, Li G, Wen J (2015) Discovery of path nearby clusters in spatial networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(6):1505–1518
She J, Tong Y, Chen L (2015) Utility-aware social event-participant planning. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, May 31 - June 4, 2015, pp 1629–1643
She J, Tong Y, Chen L, Cao CC (2015) Conflict-aware event-participant arrangement. In: 31st IEEE international conference on data engineering, ICDE 2015, Seoul, South Korea, April 13-17, 2015, pp 735–746
She J, Tong Y, Chen L, Cao CC (2016) Conflict-aware event-participant arrangement and its variant for online setting. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28 (9):2281–2295
She J, Tong Y, Chen L, Song T (2017) Feedback-aware social event-participant arrangement. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM international conference on management of data, SIGMOD Conference 2017, Chicago, IL, USA, May 14-19, 2017, pp 851–865
Tong Y, Chen L, Zhou Z, Jagadish HV, Shou L, Lv W (2018) SLADE: a smart large-scale task decomposer in crowdsourcing. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 30(8):1588–1601
Tong Y, She J, Ding B, Wang L, Chen L (2016) Online mobile micro-task allocation in spatial crowdsourcing. In: 32nd IEEE international conference on data engineering, ICDE 2016, Helsinki, Finland, May 16-20, 2016, pp 49–60
Tong Y, She J, Meng R (2016) Bottleneck-aware arrangement over event-based social networks: the max-min approach. World Wide Web 19(6):1151–1177
Wu S, Wu K (2003) Dynamic data management for location based services in mobile environments. In: 7th International database engineering and applications symposium (IDEAS 2003), 16-18 July 2003, Hong Kong, China, pp 180–191
Ye M, Shou D, Lee WC, Yin P, Janowicz K (2011) On the semantic annotation of places in location-based social networks. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, pp 520–528
Yue X, Xi M, Chen B, Gao M, He Y, Xu J A revocable group signatures scheme to provide privacy-preserving authentications. Mobile Networks and Applications, pp 1–30, online first
Zhang M, Zhou Z (2006) Multi-label neural networks with applications to functional genomics and text categorization. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 18(10):1338–1351
Zhang M, Zhou Z (2007) ML-KNN: a lazy learning approach to multi-label learning. Pattern Recogn 40(7):2038–2048
Zhao K, Chen L, Cong G (2016) Topic exploration in spatio-temporal document collections. In: Proceedings of the 2016 international conference on management of data, SIGMOD conference 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, June 26 - July 01, 2016, pp 985–998
Acknowledgements
This research is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61672145, 61572121, 61702086, 61572119 and 61622202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants and/or animals by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhao, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Annotating semantic tags of locations in location-based social networks. Geoinformatica 24, 133–152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10707-019-00367-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10707-019-00367-w