Abstract
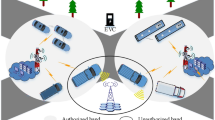
In view of the serious problems of increasing delay energy consumption and decreasing service quality caused by complex network state and massive computing data in Internet of vehicles (IOT), a high reliable computing offloading strategy based on edge computing is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the architecture of the Internet of vehicles is designed. The real-time business of terminal vehicles is directly unloaded to the mobile edge computing (MEC) equipment for processing, which reduces the high transmission delay of data on the core network. The combination of software defined network (SDN) and MEC is used to provide flexible network control and centralized resource management for the Internet of vehicles. Then, according to the computing model, communication model and privacy protection model, a joint computing offload and resource allocation strategy is proposed. Finally, taking the shortest time delay and minimum computing cost as the optimization objectives, Q-learning is used to solve the problem to achieve the optimization of unloading strategy, that is, the optimal allocation of communication and computing resources, and the system security is the best. Based on the Matlab simulation platform, the system model is built to carry out the experimental test. The results show that compared with other strategies, the unloading strategy can achieve fast convergence and reduce the system overhead effectively, and the computation complexity, data size and the number of computation nodes have the least impact on the delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai, Y., Xu, D., Maharjan, S., Qiao, G., Zhang, Y.: Artificial intelligence empowered edge computing and caching for internet of vehicles. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 26(3), 12–18 (2019)
Oliveira, D., Brinkmann, A., Rosa, N., Maciel, P.: Performability evaluation and optimization of workflow applications in cloud environments. J. Grid. Comput. 17, 749–770 (2019)
Xu, X., Xue, Y., Qi, L., Yuan, Y., Zhang, X., Umer, T., Wan, S.: An edge computing-enabled computation offloading method with privacy preservation for internet of connected vehicles. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 96(07), 89–100 (2019)
Inaltekin, H., Gorlatova, M., Chiang, M.: Virtualized control over fog: interplay between reliability and latency. IEEE Internet Things J. 5(6), 5030–5045 (2018)
Wu, C., Chen, X., Yoshinaga, T., Ji, Y., Zhang, Y.: Integrating licensed and unlicensed Spectrum in the internet of vehicles with Mobile edge computing. IEEE Netw. 33(4), 48–53 (2019)
Feng, J., Liu, Z., Wu, C., et al.: Mobile edge computing for the internet of vehicles: offloading framework and job scheduling. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 14(1), 28–36 (2019)
Cai, Z., Lee, I., Chu, S.C., et al.: SimSim: a service discovery method preserving content similarity and spatial similarity in P2P Mobile cloud. J. Grid. Comput. 17(1), 749–770 (2019)
Nogueira, B., Tavares, F.W., Matar, P.: Performability evaluation of a cloud-based disaster recovery solution for IT environments. J. Grid. Comput. 17(3), 603–621 (2019)
Hammoud, A., Sami, H., Mourad, A.: AI, Blockchain, and vehicular edge computing for smart and secure IoV: challenges and directions. IEEE Intern. Things Magazine. 3(2), 68–73 (2020)
Zhuang, W., Ye, Q., Lyu, F., Cheng, N., Ren, J.: SDN/NFV-empowered future IoV with enhanced communication, computing, and caching. Proc. IEEE. 108(2), 274–291 (2020)
Qiao, G., Leng, S., Zhang, K., He, Y.: Collaborative task offloading in vehicular edge multi-access networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 56(8), 48–54 (2018)
Aazam, M., Zeadally, S., Harras, K.A.: Offloading in fog computing for IoT: review, enabling technologies, and research opportunities. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 87, 278–289 (2018)
Sharmin, Z., Malik, A.W., Rahman, A.U., et al.: Toward sustainable micro-level fog-federated load sharing in internet of vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(4), 3614–3622 (2020)
Wang, X., Wei, X., Wang, L.: A deep learning based energy-efficient computational offloading method in internet of vehicles. China Commun. 16(003), 81–91 (2019)
He, X., Jin, R., Dai, H.: Peace: privacy-preserving and cost-efficient task offloading for Mobile-edge computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 19(3), 1814–1824 (2020)
He, Y., Ma, L., Zhou, R., Huang, C., Li, Z.: Online task allocation in Mobile cloud computing with budget constraints. Comput. Netw. 151(03), 42–51 (2019)
Nguyen, V.D., Khanh, T.T., Tran, N.H., et al.: Joint offloading and IEEE 802.11p-based contention control in vehicular edge computing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 9(7), 1014–1018 (2020)
Chen, W., Wang, D., Li, K.: Multi-user multi-task computation offloading in green Mobile edge cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 12(5), 726–738 (2019)
Zhang, Q., Gui, L., Hou, F., Chen, J., Zhu, S., Tian, F.: Dynamic task offloading and resource allocation for Mobile edge computing in dense cloud RAN. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(4), 3282–3299 (2020)
Wen, Z., Yang, K., Liu, X., Li, S., Zou, J.: Joint offloading and computing Design in Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Systems with full-duplex relaying. IEEE Access. 6(99), 72786–72795 (2018)
Li, C., Chen, W., Tang, J., Luo, Y.: Radio and computing resource allocation with energy harvesting devices in mobile edge computing environment. Comput. Commun. 145(09), 193–202 (2019)
Wang, Y., Lang, P., Tian, D., Zhou, J., Duan, X., Cao, Y., Zhao, D.: A game-based computation offloading method in vehicular multi-access edge computing networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(6), 4987–4996 (2020)
Dinh, T.Q., La, Q.D., Quek, T.Q.S., et al.: Learning for computation offloading in Mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Commun. 66(12), 6353–6367 (2018)
Shu, C., Zhao, Z., Han, Y., Min, G., Duan, H.: Multi-user offloading for edge computing networks: a dependency-aware and latency-optimal approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(3), 1678–1689 (2020)
Cao, X., Wang, F., Xu, J., et al.: Joint computation and communication cooperation for energy-efficient Mobile edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4188–4200 (2019)
Zhang, T., Xu, Y., Loo, J., Yang, D., Xiao, L.: Joint computation and communication design for UAV-assisted Mobile edge computing in IoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 16(8), 5505–5516 (2020)
Pham, Q.V., Le, L.B., Chung, S.H., et al.: Mobile edge computing with wireless backhaul: joint task offloading and resource allocation. IEEE Access. 7(99), 16444–16459 (2019)
Chen, Y., Zhang, N., Zhang, Y., Chen, X.: Dynamic computation offloading in edge computing for internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4242–4251 (2019)
Wang, J., Hu, J., Min, G., Zhan, W., Ni, Q., Georgalas, N.: Computation offloading in multi-access edge computing using a deep sequential model based on reinforcement learning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 57(5), 64–69 (2019)
Liu, Y., Wu, J., Li, J., Yang, W., Chen, H., Li, G.: ISRF: interest semantic reasoning based fog firewall for information-centric internet of vehicles. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 13(6), 975–982 (2019)
Huang, L., Feng, X., Zhang, C., et al.: Deep reinforcement learning-based joint task offloading and bandwidth allocation for multi-user mobile edge computing. Digit. Commun. Netw. 1, 10–17 (2019)
Guo, H., Liu, J.: UAV-enhanced intelligent offloading for internet of things at the edge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 16(4), 2737–2746 (2020)
Kang, J., Yu, R., Huang, X., Wu, M., Maharjan, S., Xie, S., Zhang, Y.: Blockchain for secure and efficient data sharing in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4660–4670 (2019)
Dai, Y., Xu, D., Maharjan, S., Zhang, Y.: Joint load balancing and offloading in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4377–4387 (2019)
Shao, Y., Li, C., Fu, Z., Jia, L., Luo, Y.: Cost-effective replication management and scheduling in edge computing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 129(03), 46–61 (2019)
Zhou, F., Wu, Y., Hu, R.Q., et al.: Computation rate maximization in UAV-enabled wireless powered Mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 36(9), 1927–1941 (2018)
Kanwal, M., Malik, A.W., Rahman, A.U., Mahmood, I., Shahzad, M.: Sustainable vehicle-assisted edge computing for big data migration in smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(3), 1857–1871 (2020)
Zhou, L., Yu, L., Du, S., et al.: Achieving differentially private location privacy in edge-assistant connected vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4472–4481 (2019)
Wang, Q., Dai, H.N., Wang, Q., et al.: On connectivity of UAV-assisted data Acquisition for Underwater Internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(6), 5371–5385 (2020)
Saleem, U., Liu, Y., Jangsher, S., Tao, X., Li, Y.: Latency minimization for D2D-enabled partial computation offloading in Mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(99), 4472–4486 (2020)
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (STIP, No. 201802004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The main idea of this paper is proposed by Kun Wang. The algorithm design and experimental environment construction are jointly completed by Kun Wang and Xiaofeng Wang. The experimental verification was completed by all the three authors. The writing of the article is jointly completed by Kun Wang and Xiaofeng Wang. And the writing guidance, English polish and funding project are completed by Xuan Liu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Wang, X. & Liu, X. A High Reliable Computing Offloading Strategy Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for IoVs in Edge Computing. J Grid Computing 19, 15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-021-09542-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-021-09542-6