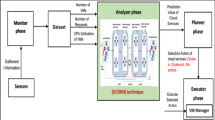
Abstract
Cloud service providers can operate several execution instances on a single physical server using virtualization technology, which improves resource utilization. In recent years, container-based virtualization has been developed as a remarkably lightweight alternative to virtual machines. Containers consume less memory than virtual machines, enabling faster setup and portability. Cloud-based applications require dynamic resource allocation in response to fluctuations in the number of incoming requests. Most articles on proactive autoscaling in cloud computing have shortcomings in two ways. 1) During feature extraction, the temporal patterns of the data are ignored, and the historical sequences are assigned equal weight. 2) Existing research omits cool down time (CDT) from the planning phase. 3) Scaling operations can be performed at any time depending only on the current input workload, resulting in a large number of contradicting scaling actions. In response to the above shortcomings, this paper presents a proactive autoscaling method for web applications in Kubernetes using an attention-based gated recurrent unit (GRU) encoder-decoder (K-AGRUED), which predicts the resource usage of several future steps based on CDT. The results demonstrate that the proposed method reduces prediction error by 2–25% compared to state of the art methods. Our approach significantly reduces scaling operations and under-provisioning compared to the standard horizontal pod autoscaler (HPA) of Kubernetes and two previous studies. The K-AGRUED increases the scaling speedup by a factor of up to five in a real environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during scenario1 and scenario2 of experiments in the current study are available at ftp://ftp.ita.ee.lbl.gov/html/contrib/NASA-HTTP.html and ftp://ftp.ita.ee.lbl.gov/html/contrib/WorldCup.html, respectively. The datasets analyzed during scenario3 in current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hosseinzadeh, M., Ghafour, M., Hama, H., Vo, B., Khoshnevis, A.: Multi-objective task and workflow scheduling approaches in cloud computing: a comprehensive review. J. Grid Comput. 18(3), 327–356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-020-09533-z
Shukur, H., Zeebaree, S., Zebari, R., Zeebaree, D., Ahmed, O., Salih, A.: Cloud computing virtualization of resources allocation for distributed systems. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 1(3), 98–105 (2020). https://doi.org/10.38094/jastt1331
Imdoukh, M., Ahmad, I., Alfailakawi, M.: Machine learning-based auto-scaling for containerized applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(13), 9745–9760 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04507-z
Borangiu, T., Trentesaux, D., Thomas, A., Leitão, P., Barata, J.: Digital transformation of manufacturing through cloud services and resource virtualization. Comput. Ind. 108, 150–162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2019.01.006
Guerrero, C., Lera, I., Juiz, C.: Genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization of container allocation in cloud architecture. J. Grid Comput. 16(1), 113–135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-017-9419-x
Goethals, T., DeTurck, F., Volckaert, B.: Extending kubernetes clusters to low-resource edge devices using virtual kubelets. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 1–1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcc.2020.3033807
Risco, S., Moltó, G., Naranjo, D., Blanquer, I.: Serverless workflows for containerised applications in the cloud continuum. J. Grid Comput. 19(3) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-021-09570-2
Zhu, C., Han, B., Zhao, Y.: A bi-metric autoscaling approach for n-tier web applications on kubernetes. Front. Comput. Sci. 16(3) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-021-0118-1
Ullah, A., Li, J., Shen, Y., Hussain, A.: A control theoretical view of cloud elasticity: taxonomy, survey and challenges. Clust. Comput. 21(4), 1735–1764 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2807-6
Barnawi, A., Sakr, S., Xiao, W., Al-Barakati, A.: The views, measurements and challenges of elasticity in the cloud: a review. Comput. Commun. 154, 111–117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.010
Liu, B., Guo, J., Li, C., Luo, Y.: Workload forecasting based elastic resource management in edge cloud. Comput. Ind. Eng. 139, 106136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.106136
Li, C., Tang, J., Luo, Y.: Elastic edge cloud resource management based on horizontal and vertical scaling. J. Supercomput. 76(10), 7707–7732 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03192-3
Kovács, J.: Supporting programmable autoscaling rules for containers and virtual machines on clouds. J. Grid Comput. 17(4), 813–829 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-019-09488-w
Aslanpour, M., Ghobaei-Arani, M., NadjaranToosi, A.: Auto-scaling web applications in clouds: a cost-aware approach. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 95, 26–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.07.012
Moghaddam, S., Buyya, R., Ramamohanarao, K.: ACAS: an anomaly-based cause aware auto-scaling framework for clouds. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 126, 107–120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2018.12.002
Rattihalli, G., Govindaraju, M., Lu, H., Tiwari, D.: Exploring potential for non-disruptive vertical auto scaling and resource estimation in Kubernetes. 2019 IEEE 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/cloud.2019.00018
Lorido-Botran, T., Miguel-Alonso, J., Lozano, J.A.: A review of auto-scaling techniques for elastic applications in cloud environments. J. Grid Comput. 12(4), 559–592 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-014-9314-7
Nadjaran Toosi, A., Son, J., Chi, Q., Buyya, R.: ELASTICSFC: Auto-scaling techniques for elastic service function chaining in network functions virtualization-based clouds. J. Syst. Softw. 152, 108–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2019.02.052
Sahni, J., Vidyarthi, D.P.: Heterogeneity-aware adaptive auto-scaling heuristic for improved QoS and resource usage in cloud environments. Computing 99(4), 351–381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-016-0530-9
Alaei, N., Safi-Esfahani, F.: Repro-active: a reactive–proactive scheduling method based on simulation in cloud computing. J. Supercomput. 74(2), 801–829 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-017-2161-0
Augustyn, D. R.: Improvements of the reactive auto scaling method for cloud platform. Computer Networks, pp. 422–431 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59767-6_33
Bento, A., Correia, J., Filipe, R., Araujo, F., Cardoso, J.: Automated analysis of distributed tracing: challenges and research directions. J. Grid Comput. 19(1) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-021-09551-5
Bauer, A., Herbst, N., Spinner, S., Ali-Eldin, A., Kounev, S.: Chameleon: a hybrid, proactive auto-scaling mechanism on a level-playing field. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 30(4), 800–813 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpds.2018.2870389
Masdari, M., Zangakani, M.: Green cloud computing using proactive virtual machine placement: challenges and issues. J. Grid Comput. 18(4), 727–759 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-019-09489-9
Iqbal, W., Erradi, A., Mahmood, A.: Dynamic workload patterns prediction for proactive auto-scaling of web applications. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 124, 94–107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.09.023
Kim, W.-Y., Lee, J.-S., Huh, E.-N.: Study on proactive auto scaling for instance through the prediction of network traffic on the container environment. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3022227.3022243
Saxena, D., Singh, A.K.: A proactive autoscaling and energy-efficient VM allocation framework using online multi-resource neural network for cloud data center. Neurocomputing 426, 248–264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.076
Singh, P., Kaur, A., Gupta, P., Gill, S.S., Jyoti, K.: RHAS: robust hybrid auto-scaling for web applications in cloud computing. Clust. Comput. 24(2), 717–737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03148-5
Al-Dulaimy, A., Taheri, J., Kassler, A., Hoseiny Farahabady, M.R., Deng, S., Zomaya, A.: MULTISCALER: a multi-loop auto-scaling approach for cloud-based applications. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 1–1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcc.2020.3031676
Guo, Y., Stolyar, A., Walid, A.: Online VM auto-scaling algorithms for application hosting in a cloud. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 1–1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcc.2018.2830793
Kan, C.: DoCloud: an elastic cloud platform for web applications based on Docker. 2016 18th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT) (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/icact.2016.7423440
Ciptaningtyas, H.T., Santoso, B.J., Razi, M.F.: Resource elasticity controller for docker-based web applications. 2017 11th International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and System (ICTS) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/icts.2017.8265669
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Cho, K., van Merrienboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder–decoder for statistical machine translation. Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (2014). https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/d14-1179
Dang-Quang, N.-M., Yoo, M.: Deep learning-based autoscaling using bidirectional long short-term memory for kubernetes. Appl. Sci. 11(9), 3835 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093835
Du, S., Li, T., Yang, Y., Horng, S.-J.: Multivariate time series forecasting via attention-based encoder–decoder framework. Neurocomputing 388, 269–279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.118
Casalicchio, E.: A study on performance measures for auto-scaling CPU-intensive containerized applications. Clust. Comput. 22(3), 995–1006 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-02890-1
Srirama, S.N., Adhikari, M., Paul, S.: Application deployment using containers with auto-scaling for microservices in cloud environment. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 160, 102629 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102629
Al-Dhuraibi, Y., Paraiso, F., Djarallah, N., Merle, P.: Autonomic vertical elasticity of Docker containers with ELASTICDOCKER. 2017 IEEE 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/cloud.2017.67
Tang, X., Zhang, F., Li, X., Khan, S.U., Li, Z.: Quantifying cloud elasticity with container-based autoscaling. 2017 IEEE 15th Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, 15th Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, 3rd Intl Conf on Big Data Intelligence and Computing and Cyber Science and Technology Congress(DASC/PiCom/DataCom/CyberSciTech) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/dasc-picom-datacom-cyberscitec.2017.143
Simic, V., Stojanovic, B., Ivanovic, M.: Optimizing the performance of optimization in the cloud environment–an intelligent auto-scaling approach. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 101, 909–920 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.07.042
Shahin, A.A.: Automatic cloud resource scaling algorithm based on long short-term memory recurrent neural network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 7(12). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2016.071236
Calheiros, R.N., Masoumi, E., Ranjan, R., Buyya, R.: Workload prediction using Arima model and its impact on cloud applications’ QoS. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 3(4), 449–458 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcc.2014.2350475
Prachitmutita, I., Aittinonmongkol, W., Pojjanasuksakul, N., Supattatham, M., Padungweang, P.: Auto-scaling microservices on iaas under SLA with cost-effective framework. 2018 Tenth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/icaci.2018.8377525
Fang, W., Lu, Z.H., Wu, J., Cao, Z.Y.: RPPS: a novel resource prediction and provisioning scheme in Cloud Data Center. 2012 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Services Computing (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/scc.2012.47
Tang, X., Liu, Q., Dong, Y., Han, J., Zhang, Z.: Fisher: an efficient container load prediction model with deep neural network in clouds. 2018 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Ubiquitous Computing & Communications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Social Computing & Networking, Sustainable Computing & Communications (ISPA/IUCC/BDCloud/SocialCom/SustainCom) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/bdcloud.2018.00041
Radhika, E.G., Sudha Sadasivam, G., Fenila Naomi, J.: An efficient predictive technique to autoscale the resources for web applications in private cloud. 2018 Fourth International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Information, Communication and Bio-Informatics (AEEICB) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/aeeicb.2018.8480899
Messias, V.R., Estrella, J.C., Ehlers, R., Santana, M.J., Santana, R.C., Reiff-Marganiec, S.: Combining time series prediction models using genetic algorithm to autoscaling web applications hosted in the Cloud Infrastructure. Neural Comput. Appl. 27(8), 2383–2406 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2133-3
Toka, L., Dobreff, G., Fodor, B., Sonkoly, B.: Adaptive AI-based auto-scaling for kubernetes. 2020 20th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGRID) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ccgrid49817.2020.00-33
Toka, L., Dobreff, G., Fodor, B., Sonkoly, B.: Machine learning-based scaling management for kubernetes edge clusters. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manage. 18(1), 958–972 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsm.2021.3052837
Wang, B., Kong, W., Guan, H.: Air quality forcasting based on gated recurrent long short-term memory model. Proceedings of the ACM Turing Celebration Conference – China (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3321408.3326656
Zhu, Q., Zhang, F., Liu, S., Wu, Y., Wang, L.: A hybrid VMD–BIGRU model for rubber futures time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 84, 105739 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105739
Luong, T., Pham, H., Manning, C.D.: Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2015). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/d15-1166
Yan, M., Liang, X.M., Lu, Z.H., Wu, J., Zhang, W.: Hansel: adaptive horizontal scaling of microservices using BiLSTM. Appl. Soft Comput. 105, 107216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107216
The Reliable, High Performance TCP/HTTP Load Balancer. Available online: http://www.haproxy.org/. Accessed on August 1 2020
Prometheus-Monitoring System & Time Series Database. Available online: https://prometheus.io/. Accessed on August 1 2020
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/
Girish, L., Rao, S.K.: Anomaly detection in cloud environment using artificial intelligence techniques. Computing (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-021-00941-x
Zulqarnain, M., Ghazali, R., Hassim, Y.M., Aamir, M.: An enhanced gated recurrent unit with auto-encoder for solving text classification problems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46(9), 8953–8967 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05691-8
Arlitt, M., Jin, T.: A workload characterization study of the 1998 World Cup Web Site. IEEE Network, 14(3), 30–37 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/65.844498. Online: ftp://ftp.ita.ee.lbl.gov/html/contrib/WorldCup.html
Two Month'sWorth of All HTTP Requests to the NASA Kennedy Space Center. Available online: ftp://ftp.ita.ee.lbl.gov/html/contrib/NASA-HTTP.html
Peng, C., Li, Y., Yu, Y., Zhou, Y., Du, S.: Multi-step-ahead host load prediction with GRU based encoder-decoder in cloud computing. 2018 10th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), (2018). Available online: https://doi.org/10.1109/kst.2018.8426104
Bauer, A., Grohmann, J., Herbst, N., Kounev, S.: On the value of service demand estimation for auto-scaling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 142–156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74947-1_10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Javad Dogani: Methodology, Software, Simulation, Writing—original draft.
Farshad Khunjush: Conceptualization, Validation, Methodology, Writing—review & editing.
Mehdi Seydali: Conceptualization, software, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dogani, J., Khunjush, F. & Seydali, M. K-AGRUED: A Container Autoscaling Technique for Cloud-based Web Applications in Kubernetes Using Attention-based GRU Encoder-Decoder. J Grid Computing 20, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-022-09634-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-022-09634-x