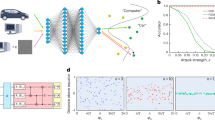
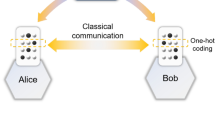
Abstract
Machine learning (ML) is the core of Artificial Intelligence (AI), and it is the fundamental way to make computer have intelligence. ML is a technology that uses algorithms to parse data, constantly learn, and make judgements and predictions about what happens. With the continuous development of ML technology, using ML algorithms to analyze the security of physical hardware has gradually become one of the hot spots in the research field. In the field of hardware security, post quantum cryptography is one of the research hotspots, e.g., multivariate cryptography. However, analyzing post-quantum signatures based on ML is still in the early stage. As substitutions of current used signatures, post-quantum signatures should fully consider side channel attack based on ML techniques so that they can be used in reality. In order to address such challenges, we present ML techniques to exploit the measurement of side channel attacks to post-quantum signatures. We propose a ML model for the measurement of side channel attacks. The efficiency of the proposed model is measured and it can be extended to analyze other similar signatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Yang, T., Zhang, Y., Xiao, S., Zhao, Y.: Digital signature based on ISRSAC. China Commun. 18(1), 161–168 (2021)
Xiao, Y., Zhang, P., Liu, Y.: Secure and efficient multi-signature schemes for fabric: An enterprise blockchain platform. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensic. Secur. 16, 1782–1794 (2020)
Meshram, C., Obaidat, M.S., Tembhurne, J.V., Shende, S.W., Kalare, K.W., Meshram, S.G.: A lightweight provably secure digital short-signature technique using extended chaotic maps for human-centered IoT systems. IEEE Syst. J. 15(4), 5507–5515 (2020)
Esiner, E., et al.: LoMoS: Less-online/more-offline signatures for extremely time-critical systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 13(4), 3214–3226 (2022)
Verma, G.K., Kumar, N., Gope, P., Singh, B.B., Singh, H.: SCBS: A short certificate-based signature scheme with efficient aggregation for industrial-Internet-of-Things Environment. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(11), 9305–9316 (2021)
Bisheh-Niasar, M., Azarderakhsh, R., Mozaffari-Kermani, M.: Cryptographic accelerators for digital signature based on Ed25519. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 29 (7), 1297–1305 (2021)
Shim, K.-A.: A survey on post-quantum public-key signature schemes for secure vehicular communications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(9), 14025–14042 (2021)
Culqui-Culqui, G., Sanchez-Gordon, S., Hernández-Álvarez, M.: An algorithm for classifying handwritten signatures using convolutional networks. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 20(3), 465–473 (2021)
Yavuz, A.A., Ozmen, M.O.: Ultra lightweight multiple-time digital signature for the Internet of Things devices. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 15(1), 215–227 (2019)
Li, H., Wei, P., Hu, P.: AVN: An adversarial variation network model for handwritten signature verification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 24, 594–608 (2022)
Suhail, S., Hussain, R., Khan, A., Hong, C.S.: On the role of hash-based signatures in quantum-safe Internet of Things: Current solutions and future directions. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(1), 1–17 (2020)
Huang, H., Wu, Y., Xiao, F., Malekian, R.: An efficient signature scheme based on mobile edge computing in the NDN-IoT environment. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 8(5), 1108–1120 (2021)
Hou, Y., Xiong, H., Huang, X., Kumari, S.: Certificate-based parallel key-insulated aggregate signature against fully chosen key attacks for industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(11), 8935–8948 (2021)
Liu, J., Yu, Y., Li, K., Gao, L.: Post-quantum secure ring signatures for security and privacy in the Cybertwin-Driven 6G. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(22), 16290–16300 (2021)
Akleylek, S., Soysaldı, M., Lee, W.-K., Hwang, S.O., Wong, D.C.-K.: Novel postquantum MQ-based signature scheme for Internet of Things with parallel implementation. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(8), 6983–6994 (2020)
Impedovo, D., Pirlo, G.: Automatic signature verification in the mobile cloud scenario: Survey and way ahead. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 9(1), 554–568 (2018)
Li, Q., Luo, M., Hsu, C., Wang, L., He, D.: A quantum secure and noninteractive identity-based aggregate signature protocol from lattices. IEEE Syst. J. 16(3), 4816–4826 (2021)
Yang, W., Wang, S., Mu, Y.: An enhanced certificateless aggregate signature without pairings for E-Healthcare system. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(6), 5000–5008 (2020)
Fouladi, S., Safaei, A.A., Mammone, N., et al.: Efficient deep neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment from scalp EEG recordings. Cogn. Comput. 14, 1247–1268 (2022)
Sma, B., Ar, C., Ym, D., et al.: Reliability-driven distribution power network dynamic reconfiguration in presence of distributed generation by the deep reinforcement learning method (2021)
Nejatishahidin, N., Fayyazsanavi, P., Kosecka, J.: Object pose estimation using mid-level visual representations (2022)
Malekshah, S., Alhelou, H.H., Siano, P.: An optimal probabilistic spinning reserve quantification scheme considering frequency dynamic response in smart power environment. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 31(11) (2021)
Umana, V.G., Knudsen, L.R., Leander, G.: Post-quantum cryptography. Nature 549(7671), 188 (2017)
Guneysu, T., Lyubashevsky, V., Poppelmann, T.: Lattice-based signatures: Optimization and implementation on reconfigurable hardware. IEEE Trans. Comput. 64(7), 1954–1967 (2015)
Zhu, H., Tan, Y.A., Yu, X., et al.: An identity-based proxy signature on NTRU lattice. Chin. J. Electron. 27(2), 297–303 (2018)
Tao, S., Hengli, P., Jianwei, L.: Secure network coding based on lattice signature. China Commun. 11(1), 138–151 (2014)
Yi, H., Tang, S.: Very small FPGA processor for multivariate signatures. Comput. J. 59(7), 1091–1101 (2018)
Yu, Y., Chen, J., Tan, Y., et al.: Building a new secure variant of Rainbow signature scheme. IET Inf. Secur. 10(2), 53–59 (2016)
Wang, H., Shen, C., Xu, Z.: Multivariate public-key encryption scheme based on error correcting codes. China Commun. 8(4), 23–31 (2011)
Butin, D.: Hash-based signatures: State of play. IEEE Secur. Priv. 15(4), 37–43 (2017)
Aysu, A., Schaumont, P.: Precomputation methods for hash-based signatures on energy-harvesting platforms. IEEE Trans. Comput. 65(9), 2925–2931 (2016)
Gauravaram, P., Knudsen, L.R.: Security analysis of randomize-hash-then-sign digital signatures. J. Cryptol. 25(4), 748–779 (2012)
Sendrier, N.: Code-based cryptography: State of the art and perspectives. IEEE Secur. Priv. 15(4), 44–50 (2017)
Niebuhr, R., Meziani, M., Bulygin, S., et al.: Selecting parameters for secure McEliece-based cryptosystems. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 11(3), 137–147 (2012)
Aguilar, C., Blazy, O., Deneuville, J.-C., et al.: Efficient encryption from random quasi-cyclic codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory PP(99), 1–1 (2016)
Yang, L., Tang, S., Ran, L., et al.: Secure and robust digital image watermarking scheme using logistic and RSA encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 97, 95–105 (2018)
Vollala, S., Varadhan, V.V., Geetha, K., et al.: Design of RSA processor for concurrent cryptographic transformations. Microelectron. J. 63(C), 112–122 (2017)
He, H., Li, R., Xu, Z., et al.: An efficient ECC-based mechanism for securing network coding-based P2P content distribution. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 7(4), 572–589 (2014)
Dou, Y., Weng, J., Ma, C., et al.: Secure and efficient ECC speeding up algorithms for wireless sensor networks. Soft. Comput. 21(19), 1–9 (2016)
Proos, J., Zalka, C.: Shor’s discrete logarithm quantum algorithm for elliptic curves. Quantum Inf. Comput. 3(4), 317–344 (2003)
Pavlidis, A., Gizopoulos, D.: Fast quantum modular exponentiation architecture for Shor’s factorization algorithm. Quantum Inf. Comput. 14(7&8), 0649–0682 (2013)
Yusuf, K., Dincer, B., Yilmaz, C., et al.: SpyDetector: An approach for detecting side-channel attacks at runtime. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2018(3), 1–30 (2018)
Ducharme, G.R., Maurine, P.: Estimating the Signal-to-Noise ratio under repeated sampling of the same centered signal: Applications to side-channel attacks on a cryptoprocessor. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory PP(99), 1–1 (2018)
Sayakkara, A., Le-Khac, N.-A., Scanlon, M.: A survey of electromagnetic side-channel attacks and discussion on their case-progressing potential for digital forensics. Digit. Investig. 29, 43–54 (2019)
Roy, D.B., Bhasin, S., Guilley, S., et al.: CC meets FIPS: A hybrid test methodology for first order side channel analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput. PP(99), 1–1 (2018)
Yang, Q., Gasti, P., Balagani, K., et al.: USB side-channel attack on Tor. Comput. Netw. 141, 57–66 (2018)
Bisi, E., Melzani, F., Zaccaria, V.: Symbolic analysis of higher-order side channel countermeasures. IEEE Trans. Comput. 66(6), 1099–1105 (2017)
Tajik, S., Dietz, E., Frohmann, S., et al.: Photonic side-channel analysis of arbiter PUFs. J. Cryptol. 30(2), 550–571 (2017)
Kim, H.: Thwarting side-channel analysis against RSA cryptosystems with additive blinding. Inform. Sci. 412-413, 36–49 (2017)
Xiao, M., Liu, G.: Fault-tolerant controlled quantum dialogue using logical qubit. Chin. J. Electron. 27(2), 263–269 (2018)
Huang, J., Huang, Q., Pan, C.: A black-box construction of strongly unforgeable signature scheme in the leakage setting. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 28(6), 761–780 (2018)
Kong, Y., Saeedi, E.: The investigation of neural networks performance in side-channel attacks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2018(4), 1–17 (2019)
Almeida, J.B., Barbosa, M., Pinto, J.S., et al.: Formal verification of side-channel countermeasures using self-composition. Sci. Comput. Program. 78(7), 796–812 (2013)
Zaccaria, V., Melzani, F., Bertoni, G.: Spectral features of higher-order side-channel countermeasures. IEEE Trans. Comput. PP(99), 1–1 (2018)
Tromer, E., Osvik, D.A., Shamir, A.: Efficient cache attacks on AES, and countermeasures. J. Cryptol. 23(1), 37–71 (2010)
Bayrak, A.G., Regazzoni, F., Novo, D., et al.: Automatic application of power analysis countermeasures. IEEE Trans. Comput. 64(2), 329–341 (2015)
Sidiropoulos, N., De Lathauwer, L., Fu, X., et al.: Tensor decomposition for signal processing and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Sig. Process. 65(13), 3551–3582 (2017)
Cao, X., Xie, W., Ahmed, S.M., Li, C.R.: Defect detection method for rail surface based on line-structured light. Measurement 159, 1–17 (2020)
Zhang, H., Zhang, C., Wang, C., Xie, F.: A survey of non-destructive techniques used for inspection of bearing steel balls. Measurement 159, 1–20 (2020)
Chen, J., Huang, Y., Guo, X., Zhou, S., Jia, L.: Parameter identification and adaptive compliant control of rehabilitation exoskeleton based on multiple sensors. Measurement 159, 1–13 (2020)
Wu, Z., Ramsundar, B., Feinberg, E.N., et al.: MoleculeNet: A benchmark for molecular machine learning. Chem. Sci. 9(2), 513–530 (2017)
Miltiadis, A., Barr Earl, T., Premkumar, Devanbu, et al.: A survey of machine learning for big code and naturalness. ACM Comput. Surv. 51(4), 1–37 (2017)
Arganda-Carreras, I., Kaynig, V., Rueden, C., et al.: Trainable Weka Segmentation: a machine learning tool for microscopy pixel classification. Bioinformatics 33(15), 2424 (2017)
Mohr, D.C., Zhang, M., Schueller, S.M.: Personal sensing: Understanding mental health using ubiquitous sensors and machine learning. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 13(1), 23 (2017)
Butler, K.T., Davies, D.W., Cartwright, H., et al.: Machine learning for molecular and materials science. Nature 559(7715), 547–555 (2018)
Carifio, J., Halverson, J., Krioukov, D., et al.: Machine learning in the string landscape. J. High Energy Phys. 2017(9), 157 (2017)
Rouet-Leduc, B., Hulbert, C., Lubbers, N., et al.: Machine learning predicts laboratory earthquakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44(18), 9276–9282 (2017)
Maxwell, A.E., Warner, T.A., Fang, F.: Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: an applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 39(9), 2784–2817 (2018)
Jiang, J., Yu, L., Jiang, J., et al.: Angel: A new large-scale machine learning system. Natl. Sci. Rev. 5(2), 102–122 (2018)
Nazari, K., Ebadi, M.J., Berahmand, K.: Diagnosis of Alternaria disease and leafminer pest on tomato leaves using image processing techniques. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102(15), 6907–6920 (2022)
Kokaeva, L.Y., Belosokhov, A.F., Doeva, L.Y., et al.: Distribution of Alternaria species on blighted potato and tomato leaves in Russia. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 125, 205–212 (2018)
Azadifar, S., Rostami, M., Berahmand, K., Moradi, P., Oussalah, M.: Graph-based relevancy-redundancy gene selection method for cancer diagnosis. Comput. Biol. Med. 147, 1–14 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Scientific Research Startup Fund for Shenzhen High-Caliber Personnel of Shenzhen Polytechnic (No.6021310026K).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, H. Machine Learning Method with Applications in Hardware Security of Post-Quantum Cryptography. J Grid Computing 21, 19 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-023-09643-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-023-09643-4