Abstract
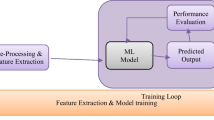
For a higher degree of penetration of renewable energy into the controls of the existing power system, an accurate solar energy prediction is necessary. Data-driven algorithms may be used to enhance solar generation forecasts as data has now become readily accessible in large quantities. To address these predicting issues in this research article three machine learning models: Support Vector Regressor (SVR), Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Random Forest Regressor (RFR) have been incorporated to forecast the Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI), Diffused Horizontal Irradiance (DHI), Diffused Normal Irradiance (DNI) based on the spatiotemporal factors. In order to improve the prediction accuracy, the parametric tuning of models has been carried out with the two met heuristic algorithms: Moth Flame Optimization (MFO) and Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) and also validated with the novel application of Evolve Class Topper Optimization (ECTO) method. Corresponding performance measures, including Mean Square Error (MSE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Max Error (ME), and Coefficient of Determination (R2), are employed to evaluate each model's performance. The results obtained through a comparative assessment of all machine learning models confirmed that the ECTO based models have outperformed others and the RFR-ECTO model is the best forecasting model having the highest R2 scores of 0.9441, 0.9107 and 0.8882 and the lowest RMSE value of 75.8613 W/m2, 40.8714 W/m2, 94.8916 W/m2 for GHI, DHI and DNI respectively which ensures that the designed predictive model can be implemented for prediction of solar energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
On request, the data utilised in this work may be made public.
Abbreviations
- IEA :
-
International Energy Agency
- IRENA :
-
International Renewable Energy Agency
- PV :
-
Photovoltaic
- GW :
-
Gigawatt
- LR :
-
Linear Regression
- ANN :
-
Artificial Neural Network
- XGB :
-
Extreme Gradient Boosting
- KNN :
-
K-Nearest Neighbours
- GPR :
-
Gaussian Process Regression
- DNN :
-
Deep Neural Network
- PSO :
-
Particle Swarm Optimization
- SVM :
-
Support Vector Machine
- LGBM :
-
Light Gradient Boosting Machine
- NREL :
-
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
- BMA :
-
Bayesian Model Averaging
- ANFIS :
-
Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interface System
- MVO :
-
Multiverse Optimization
- FFA :
-
Firefly Algorithm
- IGWO :
-
Improved Grey Wolf Optimization
- SSA :
-
Salp Swarm Algorithm
- WOA :
-
Whale Optimization Algorithm
References
Guo, Z., Zhou, K., Zhang, C., Lu, X., Chen, W., Yang, S.: Residential electricity consumption behavior: Influencing factors, related theories and intervention strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 399–412 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.07.046
Zhang, Y., He, C.Q., Tang, B.J., Wei, Y.M.: China’s energy consumption in the building sector: A life cycle approach. Energy Build. 94, 240–251 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENBUILD.2015.03.011
IEA: Global Energy Review: CO2 Emissions in 2021.: Global Emission rebound sharply to highest ever level. (2021). https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-co2-emissions-in-2021-2. Accessed 22 Sept 2022
Samadhiya, A., Namrata, K., Kumar, N.: An Experimental Performance Evaluation and Management of a Dual Energy Storage System in a Solar Based Hybrid Microgrid. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–24 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13369-022-07023-W
Nourani, V., Elkiran, G., Abdullahi, J., Tahsin, A.: Multi-region Modeling of Daily Global Solar Radiation with Artificial Intelligence Ensemble. Nat. Resour. Res. 28, 1217–1238 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11053-018-09450-9
Ahmad, T., Zhang, D., Huang, C.: Methodological framework for short-and medium-term energy, solar and wind power forecasting with stochastic-based machine learning approach to monetary and energy policy applications. Energy 231, 120911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2021.120911
Kumar, N., Namrata, K., Samadhiya, A.: Bi-level decision making in techno-economic planning and probabilistic analysis of community based sector-coupled energy system. Appl. Intell. 2022, 1–25 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10489-022-03794-9
Badescu, V.: A new kind of cloudy sky model to compute instantaneous values of diffuse and global solar irradiance. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 72, 127–136 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007040200017
Yadav, A.K., Chandel, S.S.: Solar radiation prediction using Artificial Neural Network techniques: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 33, 772–781 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2013.08.055
Chen, J.L., Li, G.S., Xiao, B.B., Wen, Z.F., Lv, M.Q., Chen, C.D., Jiang, Y., Wang, X.X., Wu, S.J.: Assessing the transferability of support vector machine model for estimation of global solar radiation from air temperature. Energy Convers. Manag. 89, 318–329 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2014.10.004
Mayer, M.J.: Benefits of physical and machine learning hybridization for photovoltaic power forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 168, 112772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2022.112772
Jebli, I., Belouadha, F.Z., Kabbaj, M.I., Tilioua, A.: Prediction of solar energy guided by pearson correlation using machine learning. Energy 224, 120109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2021.120109
Benlebna, S., Kumar, N.M., Tahri, A.: Realtime monitoring on the HIT photovoltaic module characteristic parameters at STC, high and low irradiance conditions in Algeria. Procedia Comput. Sci. 132, 1238–1242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCS.2018.05.039
Nazir, M.S., Almasoudi, F.M., Abdalla, A.N., Zhu, C., Alatawi, K.S.S.: Multi-objective optimal dispatching of combined cooling, heating and power using hybrid gravitational search algorithm and random forest regression: Towards the microgrid orientation. Energy Rep. 9, 1926–1936 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EGYR.2023.01.012
Tu, J., Hu, L., Mohammed, K.J., Le, B.N., Chen, P., Ali, E., Ali, H.E., Sun, L.: Application of logistic regression, support vector machine and random forest on the effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using macroalgae in treatment of certain risk factors associated with kidney injuries. Environ. Res. 220, 115167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2022.115167
Moosa, A., Shabir, H., Ali, H., Darwade, R., Gite, B.: Predicting solar radiation using machine learning techniques. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems, ICICCS 2018, pp. 1693–1699. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (2019)
Husain, S., Khan, U.A.: Machine learning models to predict diffuse solar radiation based on diffuse fraction and diffusion coefficient models for humid-subtropical climatic zone of India. Clean. Eng. Technol. 5, 100262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLET.2021.100262
Manoj Kumar, N., Subathra, M.S.P.: Three years ahead solar irradiance forecasting to quantify degradation influenced energy potentials from thin film (a-Si) photovoltaic system. Results Phys. 12, 701–703 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RINP.2018.12.027
Lee, J., Wang, W., Harrou, F., Sun, Y.: Reliable solar irradiance prediction using ensemble learning-based models: A comparative study. Energy Convers. Manag. 208, 112582 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2020.112582
Azimi, Y., Talaeian, M., Sarkheil, H., Hashemi, R., Shirdam, R.: Developing an evolving multi-layer perceptron network by genetic algorithm to predict full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10, 108398 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2022.108398
Massaoudi, M., Refaat, S.S., Chihi, I., Trabelsi, M., Oueslati, F.S., Abu-Rub, H.: A novel stacked generalization ensemble-based hybrid LGBM-XGB-MLP model for Short-Term Load Forecasting. Energy 214, 118874 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2020.118874
Kumar, P., Nair, G.G.: An efficient classification framework for breast cancer using hyper parameter tuned Random Decision Forest Classifier and Bayesian Optimization. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 68, 102682 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BSPC.2021.102682
Fan, J., Zheng, J., Wu, L., Zhang, F.: Estimation of daily maize transpiration using support vector machines, extreme gradient boosting, artificial and deep neural networks models. Agric. Water Manag. 245, 106547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGWAT.2020.106547
Seyedmohammadi, J., Zeinadini, A., Navidi, M.N., McDowell, R.W.: A new robust hybrid model based on support vector machine and firefly meta-heuristic algorithm to predict pistachio yields and select effective soil variables. Ecol. Inform. 74, 102002 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOINF.2023.102002
Nguyen, H.D., Truong, G.T., Shin, M.: Development of extreme gradient boosting model for prediction of punching shear resistance of r/c interior slabs. Eng. Struct. 235, 112067 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENGSTRUCT.2021.112067
Li, S., Xu, K., Xue, G., Liu, J., Xu, Z.: Prediction of coal spontaneous combustion temperature based on improved grey wolf optimizer algorithm and support vector regression. Fuel 324, 124670 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2022.124670
Chia, M.Y., Huang, Y.F., Koo, C.H.: Swarm-based optimization as stochastic training strategy for estimation of reference evapotranspiration using extreme learning machine. Agric. Water Manag. 243, 106447 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGWAT.2020.106447
Bazrafshan, O., Ehteram, M., Dashti Latif, S., Feng Huang, Y., Yenn Teo, F., Najah Ahmed, A., El-Shafie, A.: Predicting crop yields using a new robust Bayesian averaging model based on multiple hybrid ANFIS and MLP models. Ain Shams Eng. J. 13, 101724 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASEJ.2022.101724
Liu, R., Li, G., Wei, L., Xu, Y., Gou, X., Luo, S., Yang, X.: Spatial prediction of groundwater potentiality using machine learning methods with Grey Wolf and Sparrow Search Algorithms. J. Hydrol. 610, 127977 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2022.127977
Bouzateur, I., Bennacer, H., Ouali, M.A., Ziane, M.I., Hadjab, M., Ladjal, M.: A new ANN-PSO framework to chalcopyrite’s energy band gaps prediction. Mater. Today Commun. 34, 105311 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTCOMM.2023.105311
Li, S., Kong, X., Yue, L., Liu, C., Ahmad, M.: Short-term electrical load forecasting using hybrid model of manta ray foraging optimization and support vector regression. J. Clean. Prod. 388, 135856 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135856
Kabir, M.F., Chen, T., Ludwig, S.A.: A performance analysis of dimensionality reduction algorithms in machine learning models for cancer prediction. Healthc. Anal. 3, 100125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HEALTH.2022.100125
Zhou, J., Dai, Y., Tao, M., Khandelwal, M., Zhao, M., Li, Q.: Estimating the mean cutting force of conical picks using random forest with salp swarm algorithm. Results Eng. 17, 100892 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RINENG.2023.100892
Hashem Samadi, S., Ghobadian, B., Nosrati, M., Rezaei, M.: Investigation of factors affecting performance of a downdraft fixed bed gasifier using optimized MLP neural networks approach. Fuel 333, 126 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2022.126249
NSRDB: National Solar Radiation Database (NSRDB:NREL). https://nsrdb.nrel.gov/data-viewer/query/query-tools. Accessed 10 Sept 2022
Sun, L., Wang, T., Ding, W., Xu, J., Lin, Y.: Feature selection using Fisher score and multilabel neighborhood rough sets for multilabel classification. Inf. Sci. (Ny) 578, 887–912 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INS.2021.08.032
Salem, O.A.M., Liu, F., Chen, Y.P.P., Hamed, A., Chen, X.: Fuzzy joint mutual information feature selection based on ideal vector. Expert Syst. Appl. 193, 116453 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2021.116453
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V., Saitta, L.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20, 273–297 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994018
Deo, R.C., Wen, X., Qi, F.: A wavelet-coupled support vector machine model for forecasting global incident solar radiation using limited meteorological dataset. Appl. Energy. 168, 568–593 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2016.01.130
Lima, M.A.F.B., Carvalho, P.C.M., Fernández-Ramírez, L.M., Braga, A.P.S.: Improving solar forecasting using Deep Learning and Portfolio Theory integration. Energy 195, 117016 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2020.117016
Mellit, A., Pavan, A.M.: A 24-h forecast of solar irradiance using artificial neural network: Application for performance prediction of a grid-connected PV plant at Trieste. Italy. Sol. Energy. 84, 807–821 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2010.02.006
Breiman, L.: Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Mirjalili, S.: Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowledge-Based Syst. 89, 228–249 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.KNOSYS.2015.07.006
Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S.M., Lewis, A.: Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 69, 46–61 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVENGSOFT.2013.12.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mantosh Kumar has collected and analysed the data along with computation and mathematical modelling for the methodology adopted. Kumari Namrata supervised the project and formatted the manuscript. Nishant Kumar and Gaurav Saini have worked in optimization technique formulation and also assisted in editing and formulating the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
Authors have no competing interests associated with this research work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Namrata, K., Kumar, N. et al. Solar Irradiance Prediction Using an Optimized Data Driven Machine Learning Models. J Grid Computing 21, 28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-023-09668-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-023-09668-9