Abstract
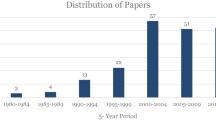
Group formation is an essential process for group development lifecycle. It has been a growing concern to many researchers to be applied automatically in collaborative learning contexts. Forming a group is an atomic process that is affected by various factors. These factors differ depending on the group members characteristics, the context of the grouping process and the techniques used to form the group(s). This paper surveys the recently published work in group formation process providing a systematic literature review in which 30 relevant studies were analyzed. The findings of this review propose two taxonomies. The first one is for the attributes of group formation while the second is for the grouping techniques. Furthermore, we present the main findings and highlight the limitations of existing approaches in computer supported collaborative learning environment. We suggest some potential directions for future research with group formation process in both theoretical and practical aspects. In addition, We emphasize other improvements that may be inter-related with other computing areas such as cloud computing and mobility.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abnar, S., Orooji, F., & Taghiyareh, F. (2012). An evolutionary algorithm for forming mixed groups of learners in web based collaborative learning environments. In 2012 IEEE international conference on technology enhanced education (ICTEE) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Amara, S., Macedo, J., Bendella, F., & Santos, A. (2016). Group formation in mobile computer supported collaborative learning contexts: A systematic literature review. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 19(2), 258–273.
Bonebright, D. A. (2010). 40 years of storming: A historical review of tuckman’s model of small group development. Human Resource Development International, 13(1), 111–120.
Brauer, S., & Schmidt, T. C. (2012). Group formation in elearning-enabled online social networks. In 2012 15th international conference on interactive collaborative learning (ICL) (pp, 1–8). IEEE.
Christodoulopoulos, C. E., & Papanikolaou, K. A. (2007). A group formation tool in an e-learning context. In 19th IEEE international conference on tools with artificial intelligence (ICTAI 2007), vol. 2, (pp. 117–123). IEEE.
Coffield, F., Moseley, D., Hall, E., & Ecclestone, K. (2004). Learning styles and pedagogy in post 16 learning: A systematic and critical review. The Learning and Skills Research Centre.
Dillenbourg, P. (1999). What do you mean by collaborative learning. Collaborative Learning: Cognitive and Computational Approaches, 1, 1–15.
Graf, S., & Bekele, R. (2006). Forming heterogeneous groups for intelligent collaborative learning systems with ant colony optimization. In International conference on intelligent tutoring systems (pp. 217–226). Springer.
Ho, T. F., Shyu, S. J., Wang, F. H., & Li, C. T. J. (2009). Composing high-heterogeneous and high-interaction groups in collaborative learning with particle swarm optimization. In 2009 WRI World congress on computer science and information engineering vol. 4, (pp. 607–611). IEEE.
Huang, Y., Zhu, M., Wang, J., Pathak, N., Shen, C., Keegan, B., Williams, D., & Contractor, N. (2009). The formation of task-oriented groups: Exploring combat activities in online games. In 2009 CSE’09. International conference on computational science and engineering vol. 4, (pp. 122–127). IEEE.
Hubscher, R. (2010). Assigning students to groups using general and context-specific criteria. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 3(3), 178–189.
Jozan, M. M. B., & Taghiyareh, F. (2013). An evolutionary algorithm for homogeneous grouping to enhance web-based collaborative learning. International Journal of Computer Science Research and Application, 3(1), 74–85.
Khandaker, N., Soh, L. K., & Jiang, H. (2006). Student learning and team formation in a structured CSCL environment. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, 151, 185.
Kreijns, K., Kirschner, P. A., & Jochems, W. (2002). The sociability of computer-supported collaborative learning environments. Educational Technology & Society, 5(1), 8–22.
Martin, E., & Paredes, P. (2004). Using learning styles for dynamic group formation in adaptive collaborative hypermedia systems. In Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Adaptive Hypermedia and Collaborative Web-based Systems (AHCW 2004) (pp. 188–198). http://www.ii.uam.es/rcarro/AHCW04/MartinParedes.pdf.
Matazi, I., Messoussi, R., & Bennane, A. (2014). The design of an intelligent multi-agent system for supporting collaborative learning. In 2014 9th International conference on intelligent systems: Theories and applications (SITA-14) (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Moreno, J., Ovalle, D. A., & Vicari, R. M. (2012). A genetic algorithm approach for group formation in collaborative learning considering multiple student characteristics. Computers & Education, 58(1), 560–569.
Mujkanovic, A., Lowe, D., Willey, K., & Guetl, C. (2012). Unsupervised learning algorithm for adaptive group formation: Collaborative learning support in remotely accessible laboratories. In 2012 International conference on information society (i-Society) (pp. 50–57). IEEE.
Okoli, C., & Schabram, K. (2010). A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. Sprouts: Working Papers on Information Systems, 10, 26.
Ounnas, A. (2008). Semantic web-based group formation for e-learning. In: ESWC 2008 Ph. D. Symposium (p. 51).
Ounnas, A., Davis, H. C., Millard, D. E. (2007a). Semantic modeling for group formation. In 11th International Conference on User Modeling, Corfu, Greece (p. 71).
Ounnas, A., Davis, H. C., & Millard, D. E. (2007b). Towards semantic group formation. In Seventh IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, 2007. ICALT 2007. IEEE (pp. 825–827).
Ounnas, A., Davis, H., & Millard, D. (2008a). A framework for semantic group formation. In 2008 Eighth IEEE international conference on advanced learning technologies (pp. 34–38). IEEE.
Ounnas, A., Davis, H., & Millard, D. (2008b). Semantic web-based group formation for e-learning.
Resta, P., & Laferrière, T. (2007). Technology in support of collaborative learning. Educational Psychology Review, 19(1), 65–83.
Rowe, J. P., Shores, L. R., Mott, B. W., & Lester, J. C. (2010). Integrating learning and engagement in narrative-centered learning environments. In International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems (pp. 166–177). Springer.
Rubens, N., Vilenius, M., & Okamoto, T. (2009). Automatic group formation for informal collaborative learning. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/WIC/ACM international joint conference on web intelligence and intelligent agent technology-volume 03 (pp. 231–234). IEEE Computer Society.
Soh, L. K. (2004). On cooperative learning teams for multiagent team formation. In of the AAAIs 2004 Workshop on forming and maintaining coalitions and teams in adaptive multiagent systems.
Soh, L. K., Khandaker, N. (2007). Forming and scaffolding human coalitions with a multi-agent framework. In Proceedings of the 6th international joint conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems (p. 62). ACM.
Soh, L. K., Khandaker, N., & Jiang, H. (2008). I-minds: A multiagent system for intelligent computer-supported collaborative learning and classroom management. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 18(2), 119–151.
Soller, A. (2001). Supporting social interaction in an intelligent collaborative learning system. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education (IJAIED), 12, 40–62.
Srba, I., & Bielikova, M. (2015). Dynamic group formation as an approach to collaborative learning support. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 8(2), 173–186.
Stahl, G., Koschmann, T., & Suthers, D. (2006). Computer-supported collaborative learning: An historical perspective. Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences, 2006, 409–426.
Sukstrienwong, A. (2012). Genetic algorithm for forming student groups based on heterogeneous grouping. In Recent advances in information science: Proceedings of the 3rd European conference of computer science (pp. 92–97).
Sun, G., & Shen, J. (2013). Teamwork as a service: a cloud-based system for enhancing teamwork performance in mobile learning. In 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT) (pp. 376–378), IEEE.
Tien, H. W., Lin, Y. S., Chang, Y. C., & Chu, C. P. (2013). A genetic algorithm-based multiple characteristics grouping strategy for collaborative learning. In International conference on web-based learning (pp. 11–22). Springer.
Tuckman, B. W., & Jensen, M. A. C. (1977). Stages of small-group development revisited. Group & Organization Management, 2(4), 419–427.
Yannibelli, V., & Amandi, A. (2011). Forming well-balanced collaborative learning teams according to the roles of their members: An evolutionary approach. In 2011 IEEE 12th international symposium on computational intelligence and informatics (CINTI) (pp. 265–270). IEEE.
Zheng, Z., & Pinkwart, N. (2014). A discrete particle swarm optimization approach to compose heterogeneous learning groups. In 2014 IEEE 14th international conference on advanced learning technologies (pp. 49–51). IEEE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maqtary, N., Mohsen, A. & Bechkoum, K. Group Formation Techniques in Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. Tech Know Learn 24, 169–190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-017-9332-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-017-9332-1