Abstract
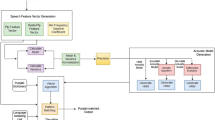
Feature subsets and hidden Markov model (HMM) parameters are the two major factors that affect the classification accuracy (CA) of the HMM-based classifier. This paper proposes a genetic algorithm based approach for simultaneously optimizing both feature subsets and HMM parameters with the aim to obtain the best HMM-based classifier. Experimental data extracted from three spontaneous speech corpora were used to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach and the three other approaches (i.e. the approaches to single optimization of feature subsets, single optimization of HMM parameters, and no optimization of both feature subsets and HMM parameters) that were adopted in the previous work for discrimination between speech and non-speech events (e.g. filled pause, laughter, applause). The experimental results show that the proposed approach obtains CA of 91.05%, while the three other approaches obtain CA of 86.11%, 87.05%, and 83.16%, respectively. The results suggest that the proposed approach is superior to the previous approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum, L. E., Petrie, T., Soules, G., & Weiss, N. (1970). A maximization technique occurring in the statistical analysis of probabilistic functions of Markov chains. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 41(1), 164–171.
Cai, R., Lu, L., Zhang, H. J., & Cai, L. H. (2003). Highlight sound effects detection in audio stream. In IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (pp. 37–40), Baltimore, MD, USA.
Cai, R., Lu, L., Hanjalic, A., Zhang, H. J., & Cai, L. H. (2006). A flexible framework for key audio effects detection and auditory context inference. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 14(3), 1026–1039.
Chan, T. M., Man, K. F., Tang, K. S., & Kwong, S. (2007). A jumping-genes paradigm for optimizing factory WLAN network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 3(1), 33–43.
Chau, C. W., Kwong, S., Diu, C. K., & Fahrner, W. R. (1997). Optimization of HMM by a genetic algorithm. In IEEE ICASSP, Munich, Germany (pp. 1727–1730), Munich, Germany.
Dorsy, R. E., & Mayer, W. J. (1995). Genetic algorithms for estimation problems with multiple optima, non-differentiability, and other irregular features. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 13(1), 53–56.
Jarina, R., & Olajec, J. (2007). Discriminative feature selection for applause sounds detection. In The eighth international workshop on image analysis for multimedia interactive services (WIAMIS) (pp. 13–16), Santorini, Greece.
Juang, B. H., & Rabiner, L. (1990). The segmental K-means algorithm for estimating parameters of hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 38(9), 1639–1641.
Kwong, S., Chau, C. W., & Halang, W. A. (1996). Genetic algorithm for optimizing the nonlinear time alignment of automatic speech recognition systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 43(5), 559–566.
Kwong, S., Chau, C. W., Man, K. F., & Tang, K. S. (2001). Optimization of HMM topology and its model parameters by genetic algorithms. Pattern Recognition, 34(2), 509–522.
Kwong, S., He, Q. H., Ku, K. W., Chan, T. M., Man, K. F., & Tang, K. S. (2002). A genetic classification error method for speech recognition. Signal Processing, 82(5), 737–748.
Li, Y. X., He, Q. H., & Li, T. (2008a). A detection method of lip-smack in spontaneous speech. In International conference on audio, language and image processing (pp. 292–297), Shanghai, China.
Li, Y. X., He, Q. H., & Li, T. (2008b). A novel detection method of filled pause in mandarin spontaneous speech. In The 7th IEEE international conference on computer and information science (pp. 217–222), Marriot Portland City Center, Portland, Oregon, USA.
Man, K. F., Tang, K. S., & Kwong, S. (1996). Genetic algorithm: concepts and applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 45(5), 519–534.
Ogata, J., & Asano, F. (2006). Stream-based classification and segmentation of speech events in meeting recordings. In International workshop on multimedia content representation, classification and security (pp. 793–800), Istanbul, Turkey.
Olajec, J., Jarina, R., & Kuba, M. (2006). GA-based feature extraction for clapping sound detection. In The 8th seminar on neural network applications in electrical engineering (pp. 21–25), University of Belgrade, Serbia.
Petridis, V., Paterakis, E., & Kehagias, A. (1998). A hybrid neural-genetic multi-model parameter estimation algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 9(5), 862–876.
Rabiner, L. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77, 257–286.
Rabiner, L., & Juang, B.-H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Reyes-Gomez, M. J., & Ellis, D. P. W. (2003). Selection, parameter estimation, and discriminative training of hidden Markov models for general audio modeling. In IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (pp. 73–76), Baltimore, MD, USA.
Schuller, B., Eyben, F., & Rigoll, G. (2008). Static and dynamic modeling for the recognition of non-verbal vocalisations in conversational speech. In Perception in multimodal dialogue systems (Vol. 5078, pp. 99–110). Heidelberg: Springer.
Stouten, F., & Martens, J. P. (2003). A feature-based filled pause detection system for Dutch. In IEEE automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop (pp. 309–314), Virgen Islands, USA.
Tang, K. S., Man, K. F., Kwong, S., & He, Q. H. (1996). Genetic algorithms and their applications. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 13(6), 22–37.
Temko, A., Macho, D., & Nadeu, C. (2008). Fuzzy integral based information fusion for classification of highly confusable non-speech sounds. Pattern Recognition, 41(5), 1814–1823.
Yang, J., & Honavar, V. (1998). Feature subset selection using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Intelligent Systems Magazine, 13(2), 44–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YX., Kwong, S., He, QH. et al. Genetic algorithm based simultaneous optimization of feature subsets and hidden Markov model parameters for discrimination between speech and non-speech events. Int J Speech Technol 13, 61–73 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-010-9070-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-010-9070-4