Abstract
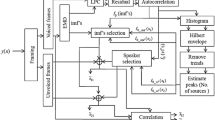
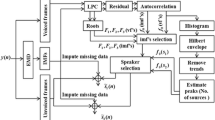
This paper presents a method for separating speech of individual speakers from the combined speech of two speakers. The main objective of this work is to demonstrate the significance of the combined excitation source based temporal processing and short-time spectrum based spectral processing method for the separation of speech produced by individual speakers. Speech in a two speaker environment is simultaneously collected over two spatially separated microphones. The speech signals are first subjected to excitation source information (linear prediction residual) based temporal processing. In temporal processing, speech of each speaker is enhanced with respect to the other by relatively emphasizing the speech around the instants of significant excitation of desired speaker by deriving speaker-specific weight function. To further improve the separation, the temporally processed speech is subjected to spectral processing. This involves enhancing the regions around the pitch and harmonic peaks of short time spectra computed from the temporally processed speech. To do so the pitch estimate is obtained from the temporally processed speech. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated using (i) objective quality measures: percentage of energy loss, percentage of noise residue, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) gain and perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ), and (ii) subjective quality measure: mean opinion score (MOS). Experimental results are reported for both real and synthetic speech mixtures. The SNR gain and MOS values show that the proposed combined temporal and spectral processing method provides an average improvement in the performance of 5.83% and 8.06% respectively, compared to the best performing individual temporal or spectral processing methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ananthapadmanabha, T. V., & Yegnanarayana, B. (1979). Epoch extraction from linear prediction residual for identification of closed glottis interval. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 27, 309–319.
Araki, S., Mukai, R., Makino, S., Nishikawa, T., & Saruwatari, H. (2003). The fundamental limitation of frequency domain blind source separation for convolutive mixtures of speech. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 11(2), 109–116.
Asano, F., Ikeda, S., Ogawa, M., Asoh, H., & Kitawaki, N. (2003). Combined approach of array processing and independent component analysis for blind separation of acoustic signals. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 11(3), 204–215.
Berouti, M., Schwartz, R., & Makhoul, J. (1979). Enhancement of speech corrupted by acoustic noise. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process (pp. 208–211).
Brown, G. J., & Cooke, M. (1994). Computational auditory scene analysis. Computer Speech and Language, 8(4), 297–336.
Brown, G. J., & Wang, D. (2005). Separation of speech by computational auditory scene analysis. In Benesty, J., Makino, S., & Chen, J. (Eds.) Speech enhancement (pp. 371–402). Berlin: Springer.
Buchner, H., Aichner, R., & Kellermann, W. (2005). A generalization of blind source separation algorithms for convolutive mixtures based on second-order statistics. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13(1), 120–134.
Chen, J., Benesty, J., & Huang, Y. A. (2006). Time delay estimation in room acoustic environments: an overview. EURASIP Journal of Applied Signal Processing. doi:10.1155/ASP/2006/26503
Das, N., Routray, A., & Dash, P. K. (2007). ICA methods for blind source separation of instantaneous mixtures: a case study. Neural Information Process. Letters and Reviews, 11(11), 225–246.
Deller, J. R., Hansen, J. H., & Proakis, J. G. (1993). Discrete time processing of speech signals (1st ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Hanson, B., & Wong, D. (1984). The harmonic magnitude suppression (HMS) technique for intelligibility enhancement in the presence of interfering speech. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process (Vol. 9, pp. 65–68).
Jang, G.-J., & Lee, T.-W. (2003). A maximum likelihood approach to single-channel source separation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 4, 1365–1392. Special issue on independent components analysis.
Jang, G.-J., Lee, T.-W., & Oh, Y.-H. (2003). Single-channel signal separation using time-domain basis functions. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 10(6), 168–171.
Koldovsky, Z., & Tichavsky, P. (2007). Time-domain blind audio source separation using advanced ICA methods. In Proc. interspeech, Antwerp, Belgium (pp. 27–31).
Krishnamoorthy, P., & Prasanna, S. R. M. (2007). Processing noisy speech by noise components subtraction and speech components enhancement. In Proc. int. conf. systemics, cybernetics and informatics, Hyberabad, India.
Kumara Swamy, R., Sri Rama Murty, K., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2007). Determining number of speakers from multispeaker speech signals using excitation source information. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 14(7), 481–484.
Lee, C. K., & Childers, D. G. (1988). Cochannel speech separation. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 83, 274–280.
Lim, J. S., & Oppenheim, A. V. (1979). Enhancement and bandwidth compression of noisy speech. Proceedings of the IEEE, 67(12), 1586–1604.
Mahgoub, Y. A., & Dansereau, R. M. (2008). Time domain method for precise estimation of sinusoidal model parameters of co-channel speech. Research Letters in Signal Processing. doi:10.1155/2008/364674.
Makhoul, J. (1975). Linear prediction: A tutorial review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 63, 561–580.
Markel, J. (1972). The SIFT algorithm for fundamental frequency estimation. IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics, 20, 367–377.
Morgan, D. P., George, E. B., Lee, L. T., & Kay, S. M. (1997). Cochannel speaker separation by harmonic enhancement and suppression. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 5, 407–424.
Parsons, T. W. (1976). Separation of speech from interfering speech by means of harmonic selection. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 60, 911–918.
Pedersen, M. S., Wang, D., Larsen, J., & Kjems, U. (2008). Two-microphone separation of speech mixtures. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 19(3), 475–492.
Prasanna, S. R. M., & Subramanian, A. (2005). Finding pitch markers using first order Gaussian differentiator. In IEEE proc. third int. conf. intelligent sensing information process, Bangalore, India (pp. 140–145).
Prasanna, S. R. M., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Extraction of pitch in adverse conditions. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process, Montreal, Quebec, Canada (Vol. 1, pp. I-109–I-112).
Proakis, J. G., & Manolakis, D. G. (1996). Digital signal processing-principles, algorithms, and applications (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Quatieri, T. F., & Danisewicz, R. G. (1990). An approach to co-channel talker interference suppression using a sinusoidal model for speech. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 38, 56–69.
Radfar, M. H., Dansereau, R. M., & Sayadiyan, A. (2007). Monaural speech segregation based on fusion of source-driven with model-driven techniques. Speech Communication, 49(6), 464–476.
Rix, A. W., Hollier, M. P., Hekstra, A. P., & Beerends, J. G. (2002). Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ) the new ITU standard for end-to-end speech quality assessment, part I—time-delay compensation. Journal of Audio Engineering Society, 50(10), 755–764.
Rouat, J., Pichevar, R., Rouat, P. J., & Sherbrooke, U. D. (2005). Source separation with one ear: proposition for an anthropomorphic approach. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing, 9, 1365–1373.
Saruwatari, H., Kurita, S., Takeda, K., Itakura, F., Nishikawa, T., & Shikano, K. (2003). Blind source separation combining independent component analysis and beamforming. EURASIP Journal of Applied Signal Processing, 2003(11), 1135–1146.
Slaney, M. (2005). The history and future of CASA. In Divenyi, P. (Ed.) Speech separation by humans and machines (pp. 199–211). Norwell: Kluwer Academic.
Smith, D., Lukasiak, J., & Burnett, I. (2005). Blind speech separation using a joint model of speech production. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 12(11), 784–787.
Smits, R., & Yegnanarayana, B. (1995). Determination of instants of significant excitation in speech using group delay function. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 3, 325–333.
Strube, H. W. (1981). Separation of several speakers recorded by two microphones (cocktail-party processing). Signal Processing, 3, 355–364.
Wang, D., & Brown, G. J. (2006). Computational auditory scene analysis: principles, algorithms, and applications. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press.
Wang, D. L., & Brown, G. (1999). Separation of speech from interfering sounds based on oscillatory correlation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 10(3), 684–697.
Yegnanarayana, B., Prasanna, S. R. M., & Mathew, M. (2003). Enhancement of speech in multispeaker environment. In Proc. european conf. speech process., technology, Geneva, Switzerland (pp. 581–584).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamoorthy, P., Mahadeva Prasanna, S.R. Two speaker speech separation by LP residual weighting and harmonics enhancement. Int J Speech Technol 13, 117–139 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-010-9074-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-010-9074-0