Abstract
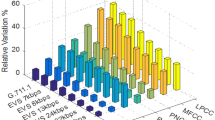
In this paper, a replacement algorithm for Linear Prediction Coefficients (LPC) along with Hamming Correction Code based Compressor (HCDC) algorithms are investigated for speech compression. We started with an CELP system with order 12 and with Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) based residual excitation. Forty coefficients with transmission rate of 5.14 kbps were first used. For each frame of the testing signals we applied a multistage HCDC, we tested the compression performance for parities from 2 to 7, we were able to achieve compression only at parity 4. This rate reduction was made with no compromise in the original CELP signal quality since compression is lossless. The compression approach is based on constructing dynamic reflection coefficients codebook, this codebook is constructed and used simultaneously using a certain store/retrieve threshold. The initial linear prediction codec we used is excited by a discrete cosine transform (DCT) residual, the results were tested using the MOS and SSNR, we had acceptable ranges for the MOS (average 3.6), and small variations of the SSNR (±5 db).
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Al-Bahadili, H. (2008). A novel lossless data compression scheme based on the error correcting hamming codes. Direct Science, Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 56, 143–150.
Chou, W. (2002). Pattern recognition in speech and language processing. Boca Raton: CRC.
Chu, W. (2003). Speech coding algorithms. New York: Wiley.
International Telecommunication Union (1996). Methods for subjective determination of transmission quality (ITU Recommendation P.800).
International Telecommunication Union (2003). One-way transmission time (ITU-T Recommendation G.114). May 2003.
Kain, A., & Macon, M. W. (2000). Design and evaluation of a voice conversion algorithm based on spectral envelope mapping and residual prediction. Center for Spoken Language Understanding (CSLU), Oregon Graduate Institute, OR 97006, USA.
Lam, E. (2004). Analysis of the DCT coefficient distribution. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 11(2).
Rao, A. V., et al. (2003). Pitch adaptive window for improved excitation coding in low rate CELP coder. IEEE Transaction on Speech and Audio Processing, 4(6).
Rix, A. W., Beerends, J. G., Hollier, M. P., & Hekstra, A. P. (2001). Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)—A new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of 2001 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASS).
Robert Gary Stanford website, http://www-ee.stanford.edu/~gray.
Storn, R. (1996). Efficient input reordering for the DCT based on a real valued dimension in time FFT. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 3(8).
Tang, I., He, J., & Huang, L. (2007). A new optimization engine for the LSF vector quantization. In Eighth ACIS international conference on software engineering, artificial intelligence, networking, and parallel/distributed computing (pp. 466–471).
Wah, W. (2005). “LSP-based multiple-description coding for real-time low bit-rate voice over IP”. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 7(1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amro, I., Abu Zitar, R. & Bahadili, H. Speech compression exploiting linear prediction coefficients codebook and hamming correction code algorithm. Int J Speech Technol 14, 65–76 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9091-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9091-7